July 2019 virus activity review from Doctor Web
August 5, 2019
In July Dr.Web’s statistics showed a 54.21% decrease in the number of detected threats compared to June. While the unique threats almost doubled. E-mail traffic was dominated by malware that uses Microsoft Office programs’ vulnerabilities. Adware and unwanted programs still occupy the top of all detected threats. The lead ransomware in July, Trojan.Encoder.858, accounted for 21.15% of all requests for data decryption received in support of Doctor Web.
Doctor Web’s researchers have prepared a study that describes trends in the most common threats for smart devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) as a whole. This review is based on statistical data that has been gathered from our honeypots since 2016 and intends to draw attention to the security problem in the field of IoT.
Principal trends in July
- An increase in spreading activity of unique malware
- A decline in ransomware activity
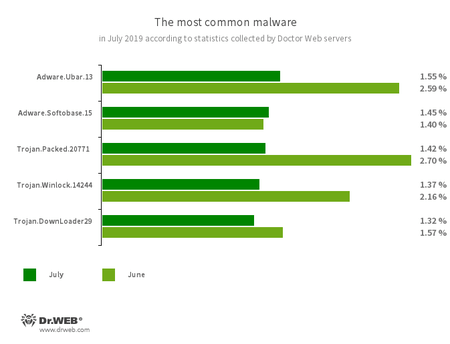
According to Doctor Web’s statistics servers
Threats of the month:
- Adware.Ubar.13
- A torrent client designed to install unwanted programs on a user’s device.
- Adware.Softobase.15
- Installation adware that spreads outdated software and changes the browser’s settings.
- Trojan.Packed.20771
- This program installs malicious browser extensions that redirect search results to different websites.
- Trojan.Winlock.14244
- A ransomware trojan that blocks or limits a user’s access to the Windows operating system and its functionalities. In order to unlock the system, a user must transfer money to the cybercriminals.
- Trojan.DownLoader29.14148
- Downloads and runs malicious software without the user’s permission.
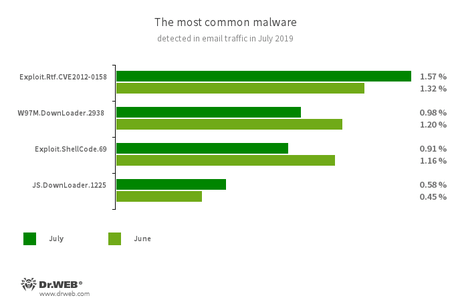
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- Exploit.Rtf.CVE2012-0158
- A modified Microsoft Office document. It exploits the CVE2012-0158 vulnerability in order to run malicious code.
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office applications. Designed to download other malware onto a compromised computer.
- Exploit.ShellCode.69
- Another malicious Microsoft Office Word document that uses the CVE-2017-11882 vulnerability.
- JS.DownLoader.1225
- A family of malicious JavaScripts. They download and install malicious software on a computer.
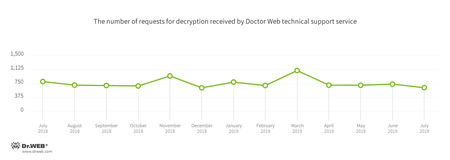
Encryption ransomware
In July, the most common cases involving the following ransomware were registered by Doctor Web’s technical support service:
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 21.15%
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 9.45%
- Trojan.Encoder.11464 — 8.01%
- Trojan.Encoder.25574 — 4.93%
- Trojan.Encoder.18000 — 3.90%
- Trojan.Encoder.11539 — 3.08%
- Trojan.Encoder.28004 — 1.85%
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
During July 2019, Doctor Web added 123,251 URLs to the Dr.Web database of non-recommended sites.
| June 2019 | July 2019 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 151 162 | + 123 251 | -18.46% |
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In mid-July, Doctor Web researchers detected a new dangerous trojan Android.Backdoor.736.origin on Google Play, through which attackers remotely controlled infected Android devices. This backdoor was able to install apps, steal sensitive data and perform other malicious actions at the developer’s command.
Among other detected threats were new trojans of the Android.HiddenAds family, which hid their icons from the main screen and displayed ads. Additionally, Doctor Web analysts discovered several programs with embedded the advertising module Adware.HiddenAds.9.origin. They displayed banners even while being closed.
New entries for detecting trojans of the Android.Spy family, which were used for cyber espionage, were added to the Dr.Web’s virus database.
Among the most notable July events related to mobile malware:
- detection of a dangerous backdoor that executes malicious commands;
- detection of new malicious programs on Google Play;
- the spread of trojans designed for cyber espionage.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our monthly review.