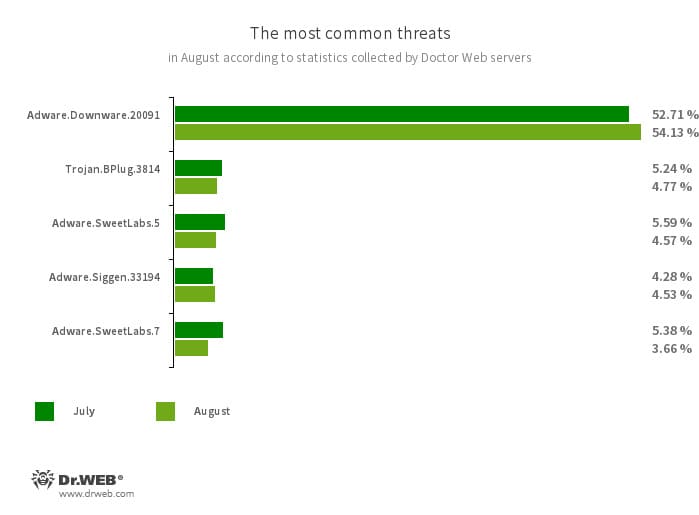
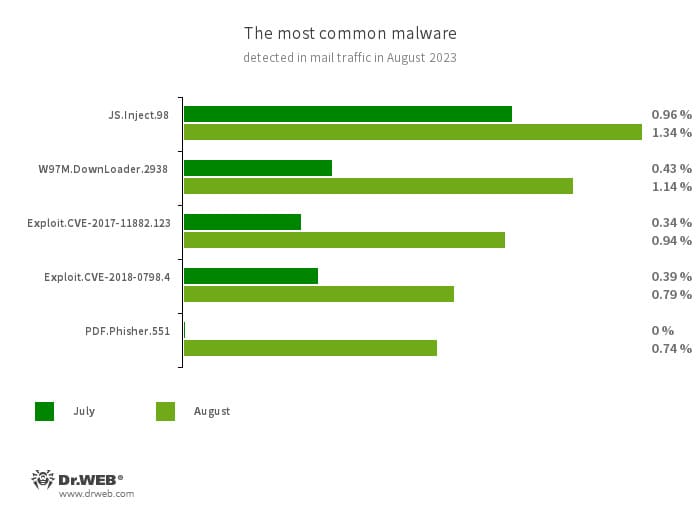
An analysis of Dr.Web August detection statistics revealed a 4.05% increase in the total number of threats detected, compared to July. The number of unique threats increased by 3.35%. Most often, users encountered adware software. In email traffic, malicious scripts, phishing documents, and programs that exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents were most prevalent.
The number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans increased by 23.99%, compared to July. The most common encoder was Trojan.Encoder.3953, with a share of 20.80% of all incidents recorded. July’s leader, Trojan.Encoder.26996, dropped to second place; it attacked users in 17.26% of the cases. Third place was taken by Trojan.Encoder.35534, with a share of 8.85%.
In August, the Android.HiddenAds.3766 trojan app was detected on Google Play. This malware displayed unwanted ads.
Principal trends in August
- An increase in the total number of detected threats
- An increase in the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans
- The emergence of a new malicious app on Google Play
Encryption ransomware
In August, the number of requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans increased by 23.99%, compared to July.
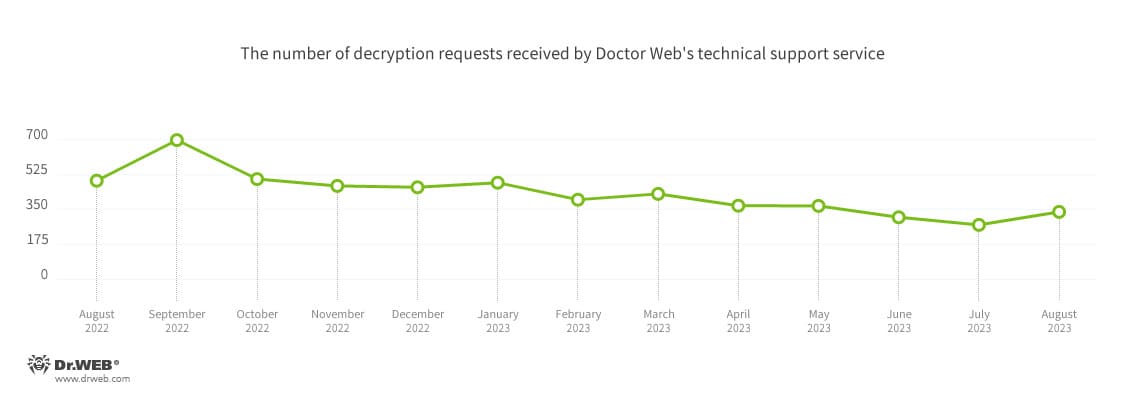
The most common encoders of August:
Dangerous websites
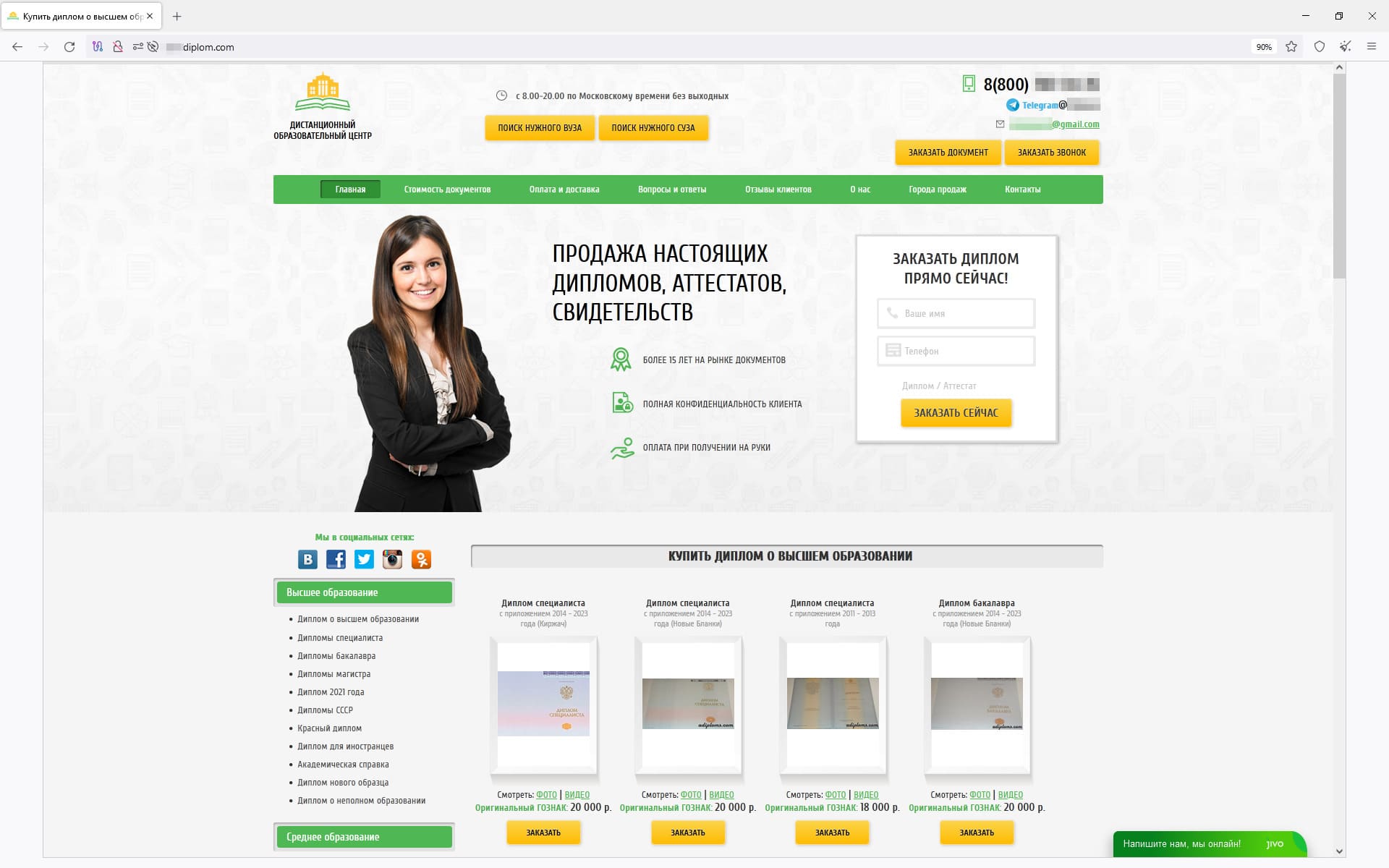
In August, Doctor Web’s Internet analysts discovered more fraudulent websites on which users could allegedly restore or buy new diplomas, passports, and other official documents. When attempting to use such “services”, users risk leaking personal data, losing money, and getting into trouble with law enforcement agencies. An example of one such site is shown in the screenshot below:
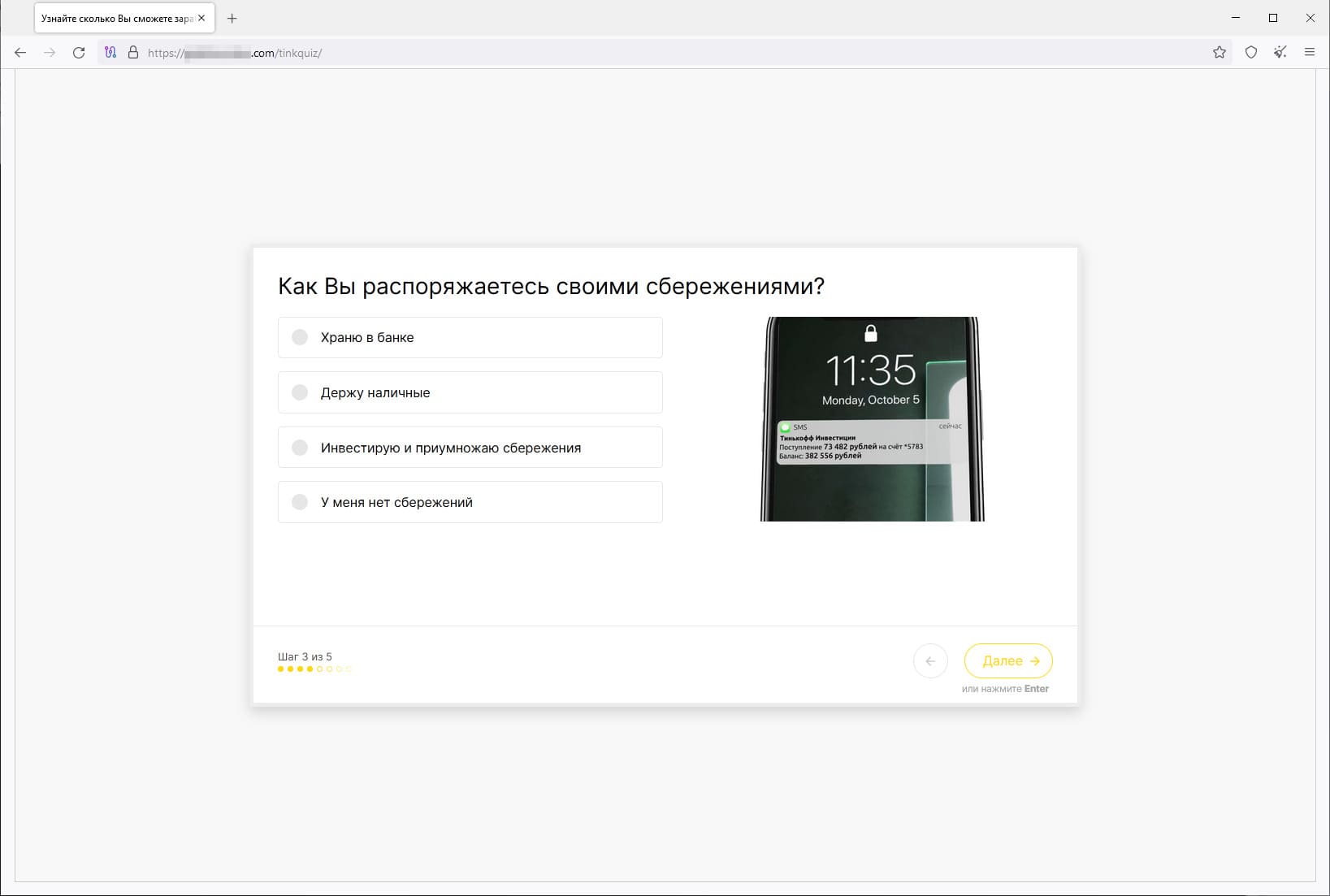
In addition, malicious actors continued to lure users to phishing websites appearing to provide various investment services. On such online resources, visitors are offered the opportunity to gain access to “investment products”. For this, they are asked to take a short test and provide personal information to register an account. If they agree, users are de facto giving away their personal data to an unknown party and can fall victim to scammers. The latter can, for example, pretend to be employees of financial organizations and offer to invest their victim’s money “profitably”. The next screenshots display an example of one such site:
A preliminary test/survey:
A special form for entering personal data such as the first and last names, email address, and phone number:
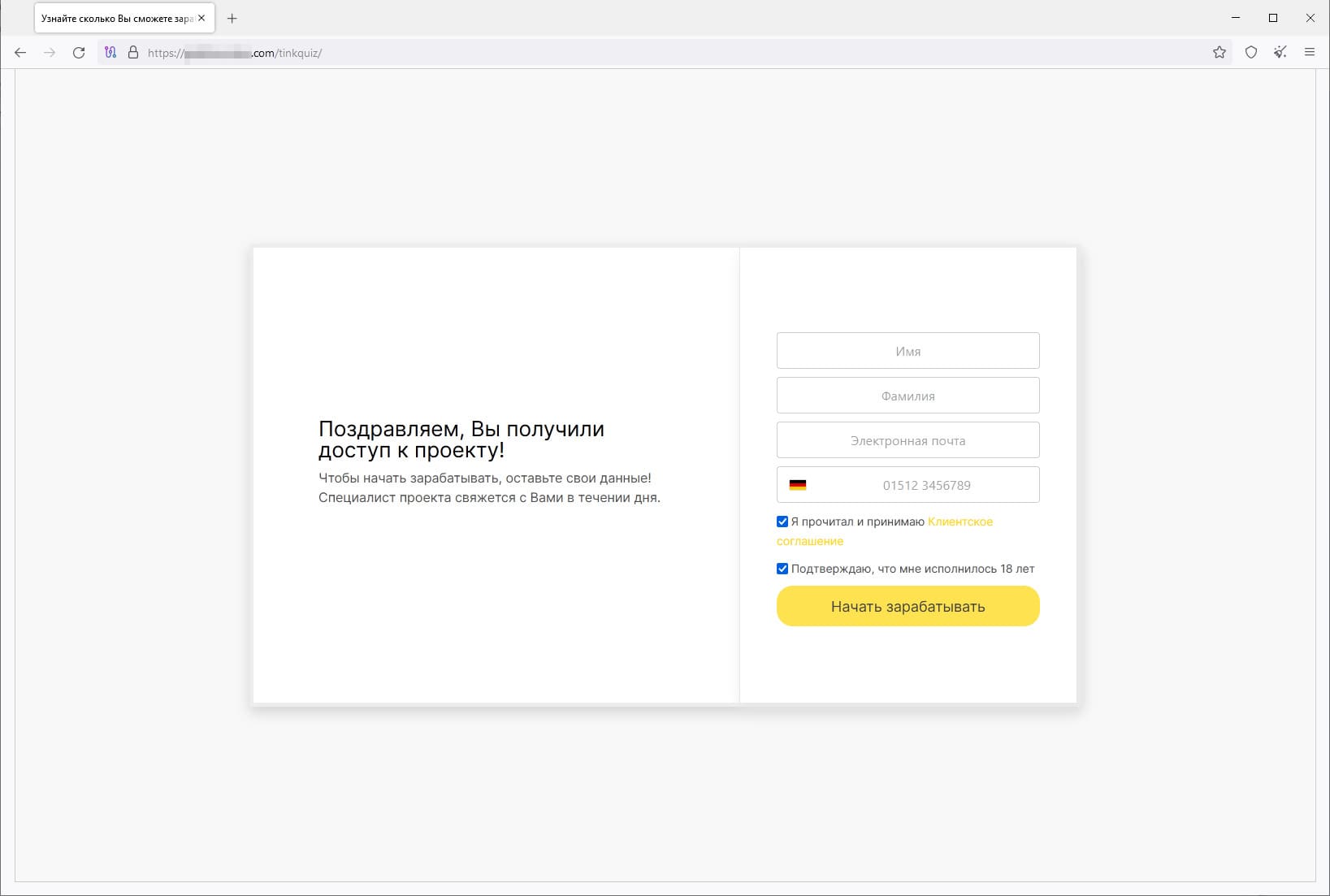
When a user confirms the input of their personal information and presses the “Start making money” button, the website informs them that they have registered successfully: