Doctor Web’s Q4 2025 virus activity review
January 12 2026
In email traffic, trojan apps—like downloaders, password stealers, and droppers—were most frequently detected. Moreover, exploits, backdoors, and various malicious scripts were also distributed via email.
Users whose files were affected by encoder trojans had mostly encountered Trojan.Encoder.35534, Trojan.Encoder.41868, and Trojan.Encoder.29750.
In October, we informed users about the Android.Backdoor.Baohuo.1.origin backdoor, which cybercriminals were distributing in modified versions of the Telegram X messenger. This malicious program steals logins and passwords for Telegram accounts as well as other sensitive data. Using this backdoor, threat actors can control the victims’ hacked accounts and also gain full control over the messenger itself, performing various actions on behalf of users.
In November, our anti-virus laboratory released a study of a targeted attack carried out by the Cavalry Werewolf hacker group on a Russian state institution. During the examination, Doctor Web’s experts identified many of the malicious instruments being used by the threat actors, including open-source tools that cybercriminals utilize in their campaigns. Our specialists also studied the features of this hacker group and the actions it typically takes in compromised networks.
Already in December, we published information about the unique trojan dubbed Trojan.ChimeraWire, which artificially increases the popularity of websites. To do so, it pretends to be a human so that its actions are not blocked by the anti-bot protection of the sites. The malicious program automatically searches target websites in search engines, opens them, and performs clicks on their webpages in accordance with the parameters received from the malicious actors. Trojan.ChimeraWire infects computers with the help of several malicious programs that exploit DLL Search Order Hijacking class vulnerabilities and also utilize anti-debugging techniques to avoid detection.
Over the course of Q4, Doctor Web’s Internet analysts identified new fraudulent websites that promised potential victims quick and easy money. More phishing sites and fake marketplace Internet resources were also found.
Our specialists uncovered yet more malicious apps on Google Play. Among them were Android.Joker trojans, which subscribe Android device owners to paid services, as well as Android.FakeApp malicious apps, which are used by cybercriminals to implement various fraudulent schemes. At the same time, Dr.Web Security Space for mobile devices detection statistics revealed that Android banking trojans increased their activity.
Principal trends in Q4 2025
- The number of threats detected on protected devices increased
- The number of unique threats used in attacks decreased
- More users requested help to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans
- Banking trojans targeting Android device owners were more active
- Threat actors distributed the Android.Backdoor.Baohuo.1.origin backdoor, which hacks the Telegram accounts of Android users
- New malicious apps emerged on Google Play
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
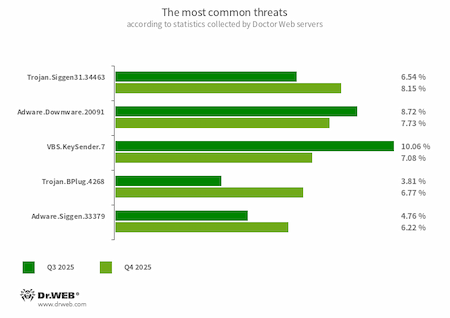
The most common threats in Q4 2025:
- Trojan.Siggen31.34463
- A trojan written in the Go programming language and designed to download various miner trojans and adware into infected systems. This malware is a DLL file located at %appdata%\utorrent\lib.dll. To launch, it exploits a DLL Search Order Hijacking vulnerability in the uTorrent torrent client.
- Adware.Downware.20091
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirated software.
- VBS.KeySender.7
- A malicious script that, in an infinite loop, searches for windows containing the text mode extensions, разработчика, and розробника and sends them an Escape key press event, forcibly closing them.
- Trojan.BPlug.4268
- The detection name for a malicious component of the WinSafe browser extension. This component is a JavaScript file that displays intrusive ads in browsers.
- Adware.Siggen.33379
- A fake Adblock Plus browser ad blocker that is installed on the system by other malware to display advertisements.
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
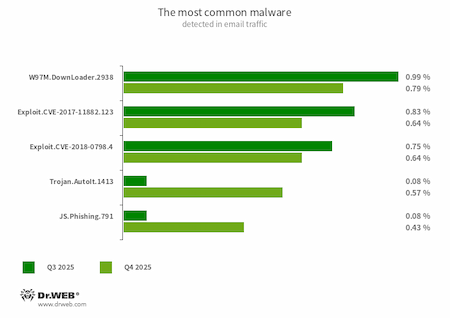
The most common threats in email traffic in Q4 2025:
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents. They can also download other malicious programs to a compromised computer.
- Exploit.CVE-2017-11882.123
- Exploit.CVE-2018-0798.4
- Exploits designed to take advantage of Microsoft Office software vulnerabilities and allow an attacker to run arbitrary code.
- Trojan.AutoIt.1413
- The detection name for a packed version of the Trojan.AutoIt.289 malicious app, written in the AutoIt scripting language. This trojan is distributed as part of a group of several malicious applications, including a miner, a backdoor, and a self-propagating module. Trojan.AutoIt.289 performs various malicious actions that make it difficult for the main payload to be detected.
- JS.Phishing.791
- A malicious JavaScript script that generates a phishing web page.
Encryption ransomware
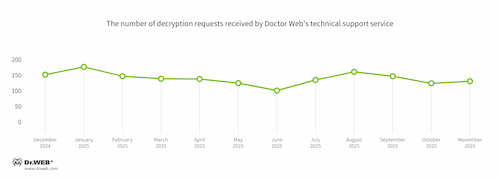
In Q4 2025, the number of requests made to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans increased by 1.15%, compared to Q3 2025.
The dynamics of the decryption requests received by Doctor Web’s technical support service:
The most common encoders of Q4 2025:
- Trojan.Encoder.35534 — 24.90% of user requests
- Trojan.Encoder.41868 — 4.21% of user requests
- Trojan.Encoder.29750 — 3.42% of user requests
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 2.68% of user requests
- Trojan.Encoder.30356 — 0.38% of user requests
Network fraud
Over the course of Q4 2025, Doctor Web’s Internet analysts observed the emergence of new fake marketplace websites. Fraudsters, allegedly on behalf of online trading platforms, offer potential victims the opportunity to play a carousel-type game (similar to roulette) with the chance of winning a prize. After several attempts, the user “gets lucky”, but to receive the prize, they are supposedly required to pay first for the shipping, then insurance, some taxes, etc. In some cases, the victim is told that the item in question is allegedly unavailable and is offered the chance to exchange it for money. If the user agrees, they are again asked to make some more payments in the form of insurance, some account activation, etc.
Example of a fake marketplace website offering a “prize drawing”
More Internet resources on which scammers sell non-existent theater tickets were added to our unwanted and malicious websites database. Such sites offer victims the chance to attend popular theatrical performances, often at attractive prices. However, after victims pay, they do not get the tickets and have essentially given their money away to the fraudsters.
One of the fraudulent sites that sells non-existent theater tickets
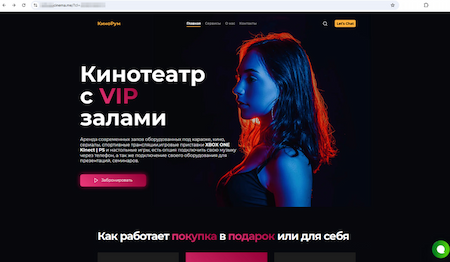
Other sites that imitate the websites of private cinemas and offer users a chance to buy movie tickets have also been detected. Victims do not receive any tickets after paying for them on such sites.
The fake website of a private cinema
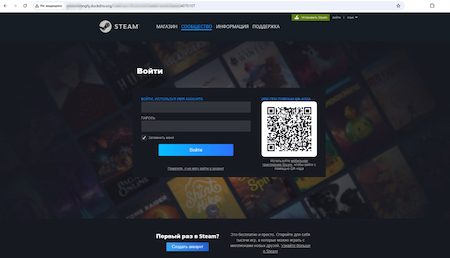
Our specialists detected several phishing web resources with some of them being fake sites of the Steam platform. Malicious actors used them to obtain user account data by asking potential victims to provide a login and password for authentication.
A phishing website that imitates the real Steam Internet portal and asks potential victim to log into their account
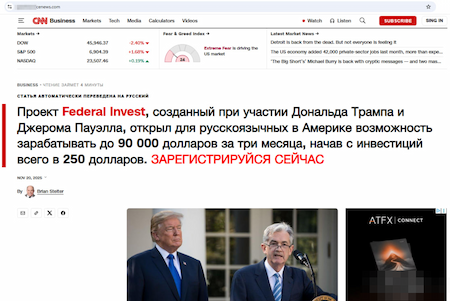
In addition, scammers again lured potential victims into non-existent investment projects. One of the detected sites invited Russian-speaking users living in America to invest $250 in a project called Federal Invest with the chance to “make up to 90,000 dollars in 3 months”. This project was allegedly created with the participation of Donald Trump.
A fraudulent site offering the chance to join a “profitable investment project”
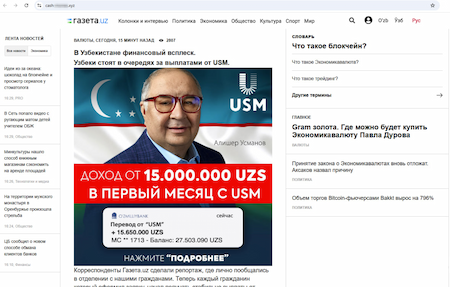
Another website reported that Uzbek users can achieve an income of at least 15,000,000 Uzbek soums already within the first month of joining the advertised project, which is allegedly related to a large holding company.
A fraudulent website promising residents of Uzbekistan some large profits by joining the “investment project”
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
According to detection statistics collected by Dr.Web Security Space for mobile devices, in Q4 2025, the ad-displaying trojans Android.MobiDash and Android.HiddenAds remained the most common Android threats, despite a decline in their activity. Malicious programs that belong to the Android.Siggen family and have various functionality rose to third place. Over the course of last three months, banking trojan activity increased, with the Android.Banker family showing the greatest growth.
Program.CloudInject apps, modified via the CloudInject cloud service, were the most common unwanted software. Among the potentially dangerous programs, or riskware, the most active were Tool.NPMod apps, which had been modified using the NP Manager utility. The most commonly detected adware programs were Adware.Adpush modules that developers embed into Android apps.
In October, Doctor Web released a report on Android.Backdoor.Baohuo.1.origin, a dangerous backdoor that threat actors embedded into Telegram X messenger modifications. This malware steals confidential information and allows the attackers to control both the victim's account and the messenger itself by changing its operating logic.
During the fourth quarter, our virus analysts discovered new threats on Google Play, including Android.Joker trojans, which subscribe users to paid services, and Android.FakeApp malicious apps, which are used for fraudulent purposes.
The following Q4 2025 events involving mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- Adware trojans remained the most common Android threats.
- Android.Banker banking trojan activity increased.
- The dangerous backdoor Android.Backdoor.Baohuo.1.origin was found in a third-party Telegram X messenger mods.
- New malicious programs emerged on Google Play.
To find out more about the security-threat landscape for mobile devices in Q4 2025, read our special overview.