Doctor Web presents the virus activity review for February 2015
March 4, 2015
The shortest month of a year did not go without new malware. At the beginning of February, Doctor Web security researchers finished their examination of a complex multi-purpose Trojan for Linux, while at the end of the month they published results of their analysis of a new version of backdoor for Mac OS X. Also, during February 2015 malicious programs for Android were still active.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN FEBRUARY
- New Linux Trojans
- Virus writers still show their interest in Mac OS X.
- New malicious programs for Android continue to spread.
Threat of the month
At the end of February, Doctor Web analysts have completed a study of the Trojan-backdoor Mac.BackDoor.OpinionSpy.3, allowing attackers to spy on Mac OS X users. It spread via sites that are offering free software, together with harmless applications whose distributions incorporated an additional executable file. Being launched with administrator privileges during the installation, this program would download and install the backdoor on the Mac.
This malicious program is detected and successfully removed by Dr.Web Anti-virus for Mac OS X. More information about this backdoor can be found in the corresponding news article.
Encryption ransomware
The number of requests for decryption received by the Doctor Web technical support service
| January 2015 | February 2015 | Movement |
|---|---|---|
| 1305 | 1840 | +40,9% |
Encryption ransomware, that encrypts files on personal computers and demands a ransom for their decryption, still poses a serious threat.
The most common ransomware programs in February 2015:
- Trojan.Encoder.567;
- Trojan.Encoder.398;
- Trojan.Encoder.741.
Use Data Loss Prevention to save your files from encryption ransomware
| Only available in Dr.Web Security Space 9 and 10. |
| More about encryption ransomware |
 |
What do I do, if… |  |
Configuration tutorial |  |
Free decryption |
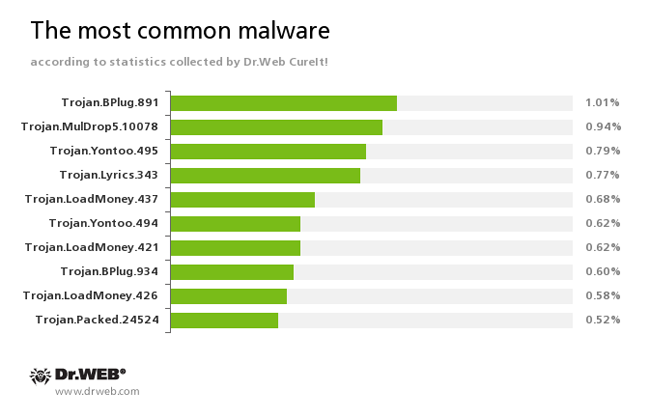
According to the statistics gathered by Dr.Web CureIt!
Trojan.BPlug
These plugins for popular browsers display annoying ads to users as they browse web pages.Trojan.MulDrop5.10078
Installs various unwanted applications and adware on an infected computer.Trojan.Yontoo
Plugins for popular browsers that demonstrate ads to users as they browse web pages.Trojan.Lyrics
A family of Trojans that display annoying ads and open objectionable web pages without user consent.Trojan.LoadMoney
Downloader programs generated by servers belonging to the LoadMoney referral programme. These programs download and install various unwanted software programs on a victim's computer.Trojan.Packed.24524
The Trojan installs adware and other unwanted programs.
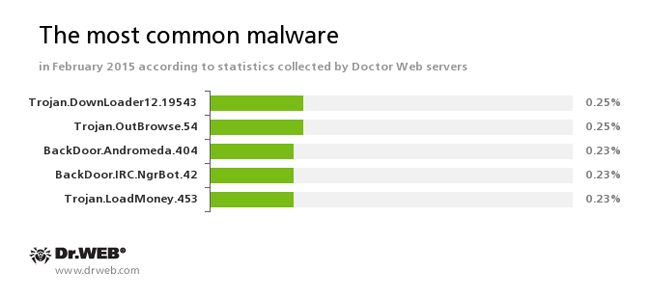
According to Doctor Web's statistics servers
Trojan.DownLoader12.19543
This Trojan displays fake search results in the browser window and imitates pop-up messages from social networking sites.Trojan.OutBrowse.54
One of the representatives of a family of adware Trojans, which are spread via referral programmes and focus on generating income from file downloads.BackDoor.Andromeda.404
This downloader Trojan is intended to download other malware from remote servers of the cybercriminals and run this malware on infected machines.BackDoor.IRC.NgrBot.42
A fairly common Trojan which is known to the information security researchers since 2011. Malicious programs of this family are able to execute intruder-issued commands on infected machines, and cybercriminals use the IRC (Internet Relay Chat) text-messaging protocol to control those PCs.Trojan.LoadMoney
Downloader programs generated by servers belonging to the LoadMoney referral programme. These programs download and install various unwanted software programs on a victim's computer.
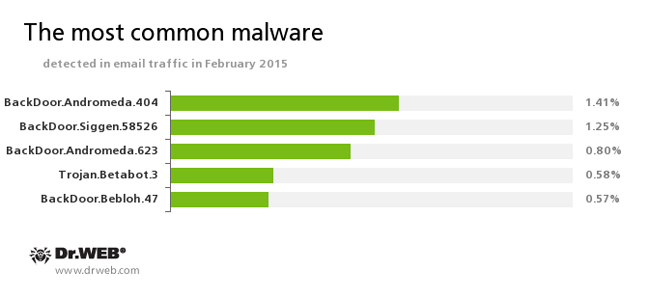
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in the email traffic
BackDoor.Andromeda
The downloader Trojans are designed to download other malware from remote servers of the cybercriminals and run this malware on infected machines.BackDoor.Siggen.58526
The Trojan covertly downloads and launches other malicious programs in the infected system and executes the commands of the cybercriminals.Trojan.Betabot.3
The Trojan can steal data entered in web forms (including the information involved in online banking), execute commands from a remote server, change the DNS settings on the infected computer, and carry out DDoS attacks.BackDoor.Bebloh.47
A malicious program belonging to the banking Trojans family. This application poses a threat to the users of e-banking services (RBS), because it allows attackers to steal confidential information by intercepting data submitted through forms in the browser window and by embedding its code into bank web pages.
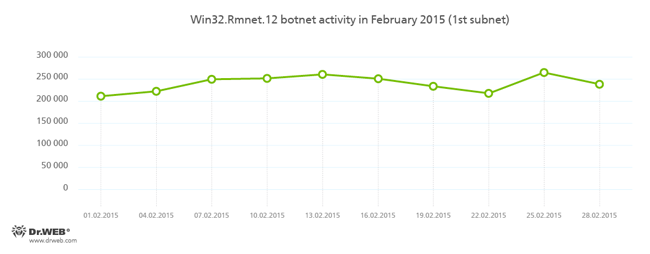
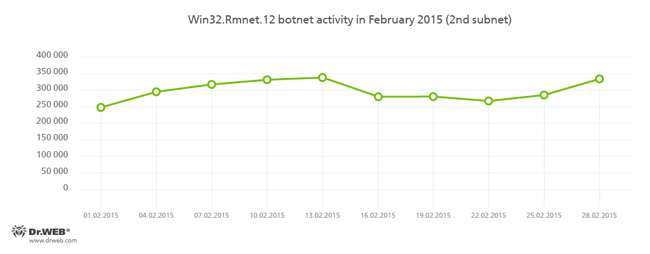
Botnets
Despite the numerous reports of news agencies, that on February 24, 2015, the command and control servers of Rmnet were shut down by the combined efforts of several organizations, Doctor Web security researchers have registered no significant decline in the botnet's activity. Doctor Web’s anti-virus laboratory monitors the subnets' activity of the botnet which was created by cybercriminals using the Win32.Rmnet.12 file infector. This activity is shown in the charts below:
More information about the activity of the botnet can be found on our website in a corresponding news article.
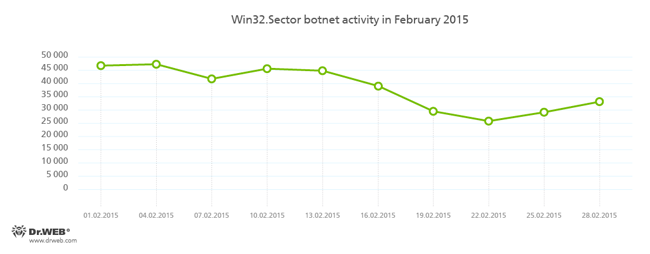
The botnet, which was created using the Win32.Sector file injector, is still active:
The Win32.Sector file infector's key functions are to:
- download various executables via P2P networks and run them on infected machines;
- inject its code into running processes;
- terminate certain anti-viruses and block access to the sites of their respective developers;
- Infect the file objects on local disks and removable media (where it creates an autorun.inf file during the infection process) as well as the files stored in public network folders.
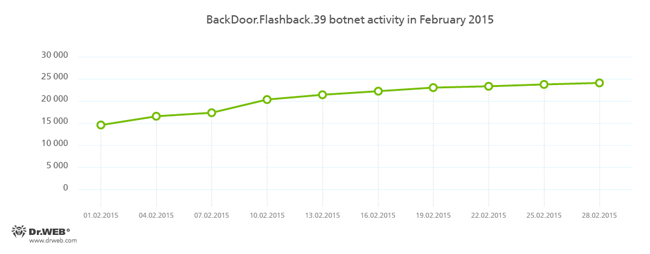
BackDoor.Flashback.39
The Trojan for Mac OS X which was distributed on a wide scale in April 2012. The infection was carried out via Java vulnerabilities. The purpose of this Trojan is to download and run a payload on the infected machine; the payload can be any executable file specified in the directive the Trojan receives from the hacker who controls it.
Linux threats
Attackers' interest in Linux doesn't appear to decrease either. In particular, in early February, Doctor Web security experts researched a complex multi-purpose backdoor for Linux named Linux.BackDoor.Xnote.1. This malware is able to perform the following operations with the file system upon a corresponding command from hackers:
- List files and directories inside the specified directory.
- Send the file size data to the server.
- Create a file to store the received data there.
- Receive a file.
- Send a file to a command and control server.
- Delete a file.
- Delete a directory.
- Signal a command and control server that it is ready to receive a file.
- Create a directory.
- Rename a file.
- Run a file.
In addition, the backdoor can run a shell with the specified environment variables and grant the command and control server access to this shell, start SOCKS proxy on the infected machine, start its own portmap implementation and carry out DDoS-attacks.
More information about how to distribute and how to work Linux.BackDoor.Xnote.1 can be found in a published by Doctor Webnews article.
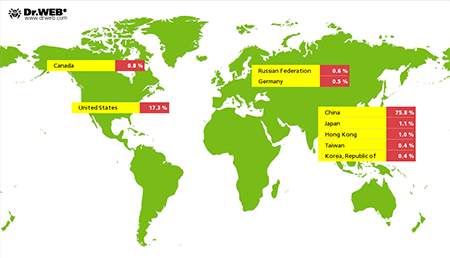
Linux-Trojan Linux.BackDoor.Gates.5 is still active and continue to carry out DDoS attacks on various sites in the Internet. In February, Doctor Web registered 1,129 IP addresses that were attacked (that is 3,880 less than in November). As before, most of them were located in China:
Fraudulent and non-recommended sites
During February 2015, Doctor Web added 22,033 URLs into the Dr.Web database of non-recommended sites.
| January 2015 | February 2015 | Movement |
|---|---|---|
| 10 431 | 22 033 | +111,2% |
Parental Control, which is available in Dr.Web Security Space 10.0, can provide protection from various Internet scams. The Parental Control component lets you limit access to websites related to a certain topic and filter suspicious content. Besides, using its database of non-recommended URLs, the component can shield users from fraudulent sites, potentially dangerous and shocking content, and from sites which are known to distribute malware.
Learn more about Dr. Web non-recommended sites
Malicious and unwanted software for Android
In February a large variety of malicious programs and riskware for Android was discovered. It included:
- Aggressive advertising modules
- Ransomware
- SMS Trojans
- Banking Trojans
Advertising modules
In the past month, aggressive advertisement modules employed by developers of Android applications became urgent again. Programs containing modules of this kind were downloaded from Google Play by tens of millions of users.Ransomware
Malicious applications, discovered in February, contained many new ransomware Trojans. Some of them were extremely dangerous programs that would encrypt files on compromised devices.SMS Trojans
In February, the Dr.Web virus database was updated with lots of new entries for SMS Trojan horses that would send messages at premium numbers without user knowledge or consent.Banking Trojans
Banking malware remains a central issue for Android users. In particular, South Korean owners of Android devices came under attack once more: to infect their smartphones and tablets, cybercriminals organized over 80 spam campaigns involving short messages with malware download links.
Find out more with Dr.Web
Virus statistics Virus encyclopedia All virus reviews Laboratory-live
[% END %]