March 2018 mobile malware review from Doctor Web
April 3, 2018
In March, Doctor Web published examination results for Android.Triada.231, which cybercriminals injected into the firmware of dozens of Android smartphone models. Virus analysts also detected numerous malicious programs on Google Play. Among them was Android.BankBot.344.origin, the Android banker designed to steal money from Russian users. Trojans from the Android.Click were also detected. They can load and display any webpage. Also in March, Doctor Web specialists found new banking Trojans created on the basis of the source code of Android.BankBot.149.origin.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN MARCH
- Detection of a dangerous Trojan in the firmware of dozens of models of Android mobile devices
- Detection of malicious programs on Google Play
- The emergence of new banking Trojans
Mobile threat of the month
Over the past month, Doctor Web reported the detection of Android.Triada.231 in the firmware of more than 40 models of Android devices. This malicious program, known since 2017, infects the processes of all running applications and can covertly perform various actions upon a cybercriminal’s command. For instance, it can install and remove software. After Doctor Web specialists informed developers of the mobile devices infected by the Trojan, some of the companies quickly released firmware updates that removed Android.Triada.231.
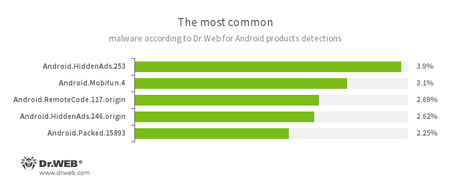
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android
- Android.HiddenAds.253
- Android.HiddenAds.246.origin
- Trojans designed to display unwanted ads on mobile devices. They are distributed under the guise of popular apps by other malicious programs, which sometimes covertly install them in the system directory.
- Android.Mobifun.4
- A Trojan designed to download other Android applications.
- Android.RemoteCode.117.origin
- A Trojan that downloads and launches various program modules, including malicious ones.
- Android.Packed.15893
- Detection for Android Trojans protected by a program packer.
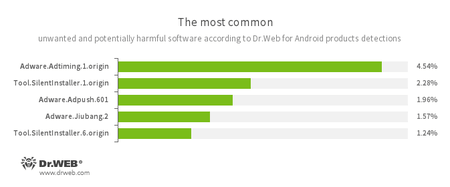
- Adware.Adtiming.1.origin
- Adware.Adpush.601
- Adware.Jiubang.2
- Unwanted program modules incorporated into Android applications and designed to display obnoxious ads on mobile devices.
- Tool.SilentInstaller.1.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.6.origin
- Riskware designed to silently launch applications without the user’s action.
Banking Trojans
At the beginning of March, Doctor Web virus analysts detected Android.BankBot.344.origin on Google Play. It was distributed as a universal application for operation with online banking systems of several Russian financial organizations. The malicious program suggested to a potential victim logging into their account by filling in login credentials or by registering with their bank card information. All input information was then sent to cybercriminals. Afterwards they could steal money from the users’ accounts. More information about this malware can be found in the corresponding review published by Doctor Web.
In mid-March, Doctor Web specialists reported on new Android bankers created with the use of the source code of Android.BankBot.149.origin. One of them was dubbed Android.BankBot.325.origin. This Trojan tracks the launch of banking programs and software for operation with social networks and cryptocurrencies, and displays fraudulent authorization forms on top of their windows. After users input logins, passwords and other confidential information, Android.BankBot.325.origin sends it to cybercriminals. In addition, virus writers used the Trojan for cyber espionage and remote access to infected devices.
Trojans on Google Play
In March, Doctor Web specialists detected more than 70 programs with Trojans of the Android.Click family on Google Play. Malicious applications, which were named Android.Click.415, Android.Click.416 and Android.Click.417, were spread under disguise of popular software, inside fake games, in various recipe collections and knitting guidebooks. Upon the command of the command and control server, these Trojans could load and display any webpages, including fraudulent ones.
Malicious programs for mobile Android devices are a serious threat because cybercriminals use them to steal confidential information, control infected smartphones and tablets, and steal money from bank accounts. Virus writers still spread Trojans via Google Play and inject them into firmware. Doctor Web recommends mobile device owners install Dr.Web for Android to protect their mobile devices from malicious and unwanted applications.
Your Android needs protection!
Use Dr.Web
- First Russian anti-virus for Android
- Over 135 million downloads—just from Google Play!
- Available free of charge for users who purchase Dr.Web home products