Doctor Web’s Q2 2025 review of virus activity on mobile devices
July 1, 2025
The activity of Android.Banker banking trojans increased by 73.15%, compared to the previous quarter. At the same time, some other banking trojan families were detected less often, e.g., Android.BankBot (by 37.19%) and Android.SpyMax (by 19.14%).
In April, our virus analysts informed the public about the discovery of a large-scale campaign to steal cryptocurrency from Android smartphone users. During this campaign, malicious actors hid Android.Clipper.31 in a modified version of the WhatsApp messenger and implanted it into the firmware of some budget Android smartphone models. This trojan hijacks messages sent and received in the messenger, searches the Tron and Ethereum crypto wallet addresses in them, and replaces legitimate addresses with ones belonging to the scammers. At the same time, the trojan conceals this substitution, and users of infected devices see the “correct” wallets in their messages. Moreover, Android.Clipper.31 sends all images in the jpg, png, and jpeg formats to a remote server to search mnemonic phrases for their victims’ crypto wallets.
Also in April, we reported on a spyware trojan targeting Russian military personnel. The Android.Spy.1292.origin malicious program was hidden in a modified version of Alpine Quest mapping software. It was distributed via a fake Telegram channel of an app created by the threat actors as well as via one of the Russian Android app catalogs. Android.Spy.1292.origin sent various confidential data to the attackers, including user accounts, their mobile phone number, contacts from the phone book, and information about the infected device’s geolocation and the files stored in its memory. When commanded by malicious actors, the trojan could steal specified files. The malware creators were particularly interested in confidential documents sent via popular messengers as well as in Alpine Quest’s location log file.
At the same time, during this most recent observation period, Doctor Web’s virus laboratory detected more threats on Google Play. Among them were various trojans and unwanted ad-displaying software.
Principal trends of Q2 2025
- Android.HiddenAds adware trojans intensified their activity
- Adware trojans from the Android.MobiDash family also heightened their activity
- Android.Banker banking trojans were less commonly detected on protected devices, compared to the previous quarter
- Decreased numbers of Android.BankBot and Android.SpyMax banking trojan family attacks were noted
- A trojan designed to steal cryptocurrency was found in the firmware of several budget Android smartphone models
- Malicious actors distributed a trojan that spied on Russian military personnel
- More threats emerged on Google Play
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web Security Space for mobile devices
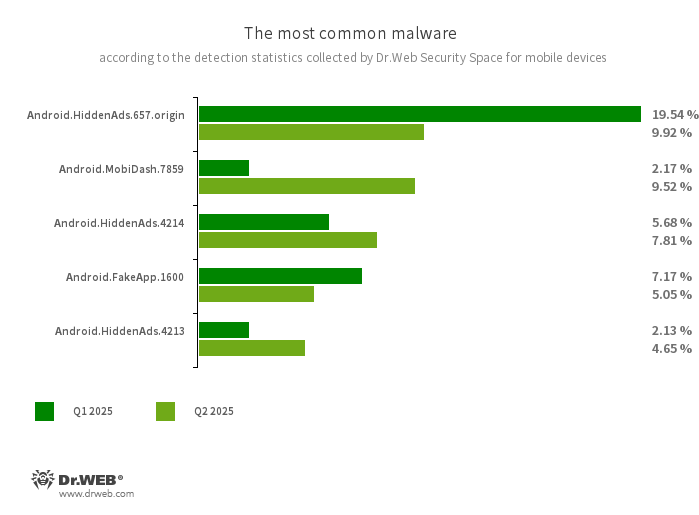
- Android.HiddenAds.657.origin
- Android.HiddenAds.4214
- Android.HiddenAds.4213
- Trojan apps designed to display intrusive ads. Members of the Android.HiddenAds family are often distributed as popular and harmless applications. In some cases, other malware can install them in the system directory. When these infect Android devices, they typically conceal their presence from the user. For example, they “hide” their icons from the home screen menu.
- Android.MobiDash.7859
- A trojan app that displays obnoxious ads. It is a special software module that developers incorporate into applications.
- Android.FakeApp.1600
- A trojan app that loads a website that is hardcoded into its settings. Known modifications of this malicious program load an online casino site.
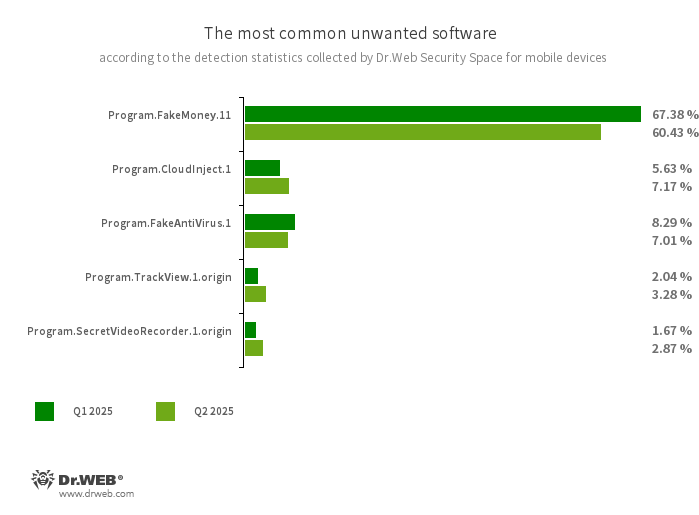
- Program.FakeMoney.11
- The detection name for Android applications that allegedly allow users to earn money by completing different tasks. These apps make it look as if rewards are accruing for each one that is completed. At the same time, users are told that they have to accumulate a certain sum to withdraw their “earnings”. Typically, such apps have a list of popular payment systems and banks that supposedly could be used to withdraw the rewards. But even if users succeed in accumulating the needed amount, in reality they cannot get any real payments. This virus record is also used to detect other unwanted software based on the source code of such apps.
- Program.CloudInject.1
- The detection name for Android programs that have been modified using the CloudInject cloud service and the eponymous Android utility (the latter was added to the Dr.Web virus database as Tool.CloudInject). Such programs are modified on a remote server; meanwhile, the modders (users) who are interested in such modifications cannot control exactly what will be added to the apps. Moreover, these programs receive a number of dangerous system permissions. Once modification is complete, modders can remotely manage these apps—blocking them, displaying custom dialogs, tracking when other software is being installed or removed from a device, etc.
- Program.FakeAntiVirus.1
- The detection name for adware programs that imitate anti-virus software. These apps inform users of nonexistent threats, mislead them, and demand that they purchase the software’s full version.
- Program.TrackView.1.origin
- The detection name for a program that allows users to be monitored via their Android devices. Malicious actors can utilize it to track a target device’s location, take photos and video with the camera, eavesdrop via the microphone, record audio, etc.
- Program.SecretVideoRecorder.1.origin
- The detection name for various modifications of an application that is designed to record videos and take photos in the background, using built-in Android device cameras. It can operate covertly by allowing notifications about ongoing recordings to be disabled. It also allows an app’s icon and name to be replaced with fake ones. This functionality makes this software potentially dangerous.
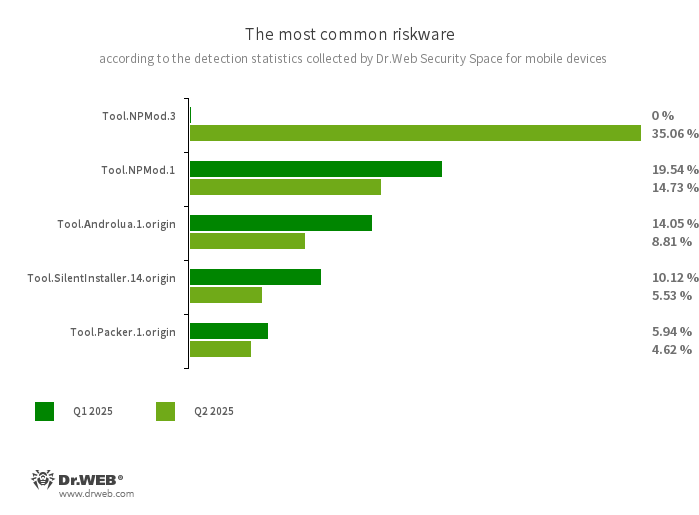
- Tool.NPMod.3
- Tool.NPMod.1
- The detection name for Android programs that have been modified using the NP Manager utility. A special module is embedded in such apps, and it allows them to bypass digital signature verification once they have been modified.
- Tool.Androlua.1.origin
- The detection name for some potentially dangerous versions of a specialized framework for developing Android software based on the Lua scripting language. The main logic of Lua-based apps resides in the corresponding scripts that are encrypted and decrypted by the interpreter upon execution. By default, this framework often requests access to a large number of system permissions in order to operate. As a result, the Lua scripts that it executes can potentially perform various malicious actions in accordance with the acquired permissions.
- Tool.SilentInstaller.14.origin
- A riskware platform that allows applications to launch APK files without installing them. It creates a virtual runtime environment in the context of the apps in which they are integrated. The APK files launched with the help of this platform can operate as if they are part of such programs and can also obtain the same permissions.
- Tool.Packer.1.origin
- A packer tool designed to protect Android applications from unauthorized modifications and reverse engineering. This tool is not malicious in itself, but it can be used to protect both harmless and malicious software.
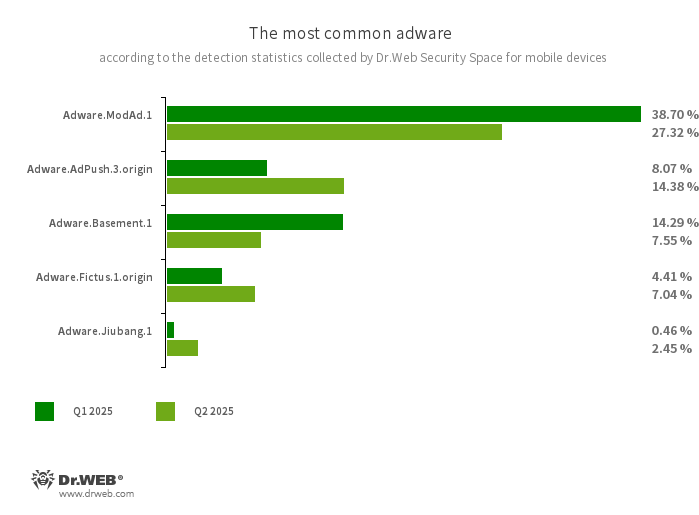
- Adware.ModAd.1
- The detection name for some modified versions (mods) of the WhatsApp messenger, whose functions have been injected with a specific code. This code is responsible for loading target URLs by displaying web content (via the Android WebView component) when the messenger is in operation. Such web addresses perform redirects to advertised sites, including online casino, bookmaker, and adult sites.
- Adware.AdPush.3.origin
- Adware modules that can be built into Android apps. They display notifications containing ads that mislead users. For example, such notifications can look like messages from the operating system. In addition, these modules collect a variety of confidential data and are able to download other apps and initiate their installation.
- Adware.Basement.1
- These are apps that display unwanted ads which often lead to malicious and fraudulent websites. They share a common code base with the Program.FakeMoney.11 unwanted applications.
- Adware.Fictus.1.origin
- An adware module that malicious actors embed into the cloned versions of popular Android games and applications. Its incorporation is facilitated by a specialized net2share packer. Copies of software created this way are then distributed through various software catalogs. When installed on Android devices, such apps and games display obnoxious ads.
- Adware.Jiubang.1
- Unwanted ad-displaying software for Android devices that displays a banner showing recommended programs when applications are being installed.
Threats on Google Play
Over the course of the second quarter of 2025, Doctor Web’s virus analysts discovered several dozen threats on Google Play, including various fake programs from the Android.FakeApp family. These trojans were again actively being distributed under the guise of finance-related programs and, instead of the promised functionality, could load fraudulent websites.
Android.FakeApp.1863 and Android.FakeApp.1859 are examples of the trojans that were discovered. The former was hidden in the “TPAO” app and targeted Turkish users who were told that the app could help them “easily control their deposits and incomes”. The latter was disguised as a “financial assistant” (“Quantum MindPro”) and was geared toward a French-speaking audience.
Games remain another popular disguise for such fake programs. Under certain conditions, they load online casino and bookmaker websites instead of providing gaming functionality.
Android.FakeApp.1840 (“Pino Bounce”) is one of the fake games that could load an online casino site.
In addition, our specialists detected the unwanted ad-displaying software Adware.Adpush.21912. It was hidden in the “Coin News Promax” app, which contains informational materials about cryptocurrencies. Adware.Adpush.21912 displays notifications that, when clicked, load into WebView the link specified by the С2 server.
To protect your Android device from malware and unwanted programs, we recommend installing Dr.Web anti-virus products for Android.
Indicators of compromise