Nice chatting with you: what connects cheap Android smartphones, WhatsApp and cryptocurrency theft?
Real-time threat news | Hot news | Threats to mobile devices | All the news
April 14, 2025
Starting from June 2024, the Doctor Web virus laboratory has received a number of reports from our customers who installed Dr.Web Security Space antivirus on their newly purchased Android phones. A scan of the system partition revealed a suspicious application disguised as WhatsApp messenger. During their investigation, our analysts were able to establish that those cases were not a mere blip on the radar. It turned out that they were all part of a campaign to steal cryptocurrency through clipping.
Clipping means stealing information by intercepting and/or spoofing data that a user copies to the clipboard. Most commonly, clippers are designed to search the clipboard for strings corresponding to cryptocurrency wallet addresses. On average, such strings contain between 25 and 42 characters. And to avoid any hassle, users typically use standard "copy" and "paste" operations to work with such data. A clipper can take advantage of this by intercepting the contents of the clipboard and discreetly replacing all cryptocurrency wallet addresses with those of the cybercriminals.
Using messengers trojanized by clippers to steal financial information is not a new tactic for hackers: one such campaign began in 2023. At that time, a group of attackers used a number of legitimate platforms, such as YouTube, to distribute links to malicious Telegram and WhatsApp apps. These links were placed in the video descriptions. The main target audience was Chinese users, who do not have access to foreign messengers. And since they have to use a number of tricks to get around the geoblocking, usually by downloading programs from third-party sites, this campaign was quite successful.
Now the attackers moved to the next level, gaining access to the supply chain of a number of Chinese manufacturers of Android-based smartphones. These are the smartphones that have been reported to Doctor Web's virus lab. Fraudulent applications were detected directly in the software pre-installed on the phone. In this case, the malicious code was added to the WhatsApp messenger.
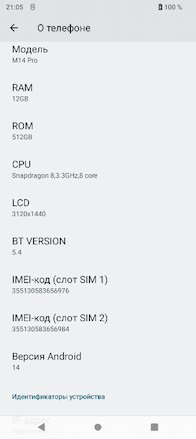
It should be noted that in most cases the compromised devices were low-end and had names similar to the models of well-known brands: S23 Ultra, Note 13 Pro, P70 Ultra, and so on. At the same time, their actual technical specifications were far from what their product page claimed. The threat actors used an application that allowed them to easily spoof all of the technical information displayed not only on the About Device page but also in the reports of such popular applications as AIDA64 and CPU-Z. In addition, although the About Device page claimed that the phones have the latest version of Android 14 installed on them, all of the devices were actually running the same build of Android 12. A third of the models listed below are manufactured under the SHOWJI brand. Unfortunately, we were unable to identify the manufacturer of the remaining models.
| SHOWJI S19 Pro | Note 30i | Camon 20 |
| SHOWJI Note 13 Pro | S23 Ultra | P70 Ultra |
| SHOWJI X100S Pro | S18 Pro | M14 Ultra |
| SHOWJI Reno12 Pro | 6 Pro | S24 Ultra |
Smartphone models purchased by our users that came with preinstalled malicious software
Product descriptions in bad Russian boasting “Fast Tastydragon CPU” [sic!] and “50 million cameras” [even sic’er!]
Screenshot of the application used to spoof technical specifications of the device and the result of its operation
To verify device specifications with greater certainty, you can use an app called DevCheck. In most cases, this application accurately determines the product specifications, even if the manufacturer is trying to mislead the consumer.
To create their trojanized WhatsApp application, the threat actors used the LSPatch tool. This framework allows the behavior of the main application to be modified, without altering its code, and additional software modules to be loaded. In this case, the criminals placed the malicious module com.whatsHook.apk in the assets folder, which performs the following functions:
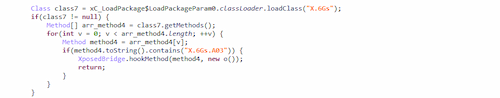
- application update hijacking. Now, instead of checking for updates at hxxps://www.whatsapp[.]com/android/current/WhatsApp[.]apk, the application accesses one of the attackers' servers, e.g., hххps://apk-download[.]pro/download/whatsapp[.]apk. This keeps the application trojanized and allows it to make the changes the threat actors need;
Method that hijacks requests to the legitimate update server
Class that swaps the legitimate update address with the fake one
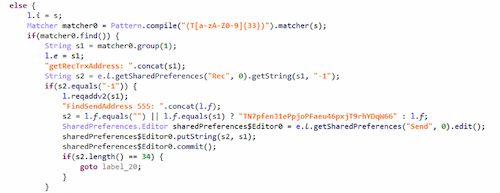
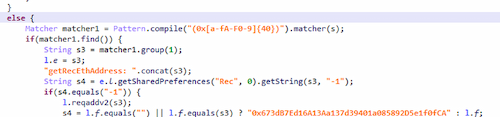
- searches for strings in received and sent messages that match the wallet address patterns for the Tron (34-character string starting with T) and Ethereum (42-character string starting with 0x) cryptocurrencies and replaces them with the attackers' addresses. The cybercriminals expanded the basic clipper functionality, and now the victim does not even suspect that something is wrong. In the case of an outgoing message, the compromised device displays the correct address of the victim's own wallet, while the recipient of the message is shown the address of the fraudsters' wallet. And when an incoming message is received, the sender sees the address of their own wallet; meanwhile, on the victim's device, the incoming address is replaced with the address of the hackers' wallet. The scammers change wallet addresses with each iteration of the campaign, but the trojan also contains backup addresses ("TN7pfenJ1ePpjoPFaeu46pxjT9rhYDqW66", "0x673dB7Ed16A13Aa137d39401a085892D5e1f0fCA") that can be used if for some reason communication cannot be established with the C2 server. In addition, the trojan sends all messages from all WhatsApp chats to the attacker's server;
Parser that searches for strings matching Tron wallet addresses
Parser that searches for strings matching Ethereum wallet addresses
- searches for all .jpg, .png, and .jpeg images in the following folders and sends them to the attackers’ server
| DCIM | DOWNLOADS |
| PICTURES | DOCUMENTS |
| ALARMS | SCREENSHOTS |
This is done to find the so-called mnemonic (recovery) phrase for crypto wallets, which is a set of 12-24 words in a specific order. Such a phrase is displayed once when a wallet is created, and many users simply take a screenshot of it instead of writing it down or saving it to a separate medium. For legitimate purposes, such phrases allow the wallet to be accessed if the user forgets the password. For attackers, obtaining such data means the ability to instantly withdraw all the money from the cryptocurrency wallet.
An example of a mnemonic phrase for recovering access to a cryptocurrency wallet. The user must enter these words in numerical order.
- sends information about the device: the device manufacturer, model, language settings, and the name of the trojanized application. In total, the scammers modified about 40 different applications. These include the aforementioned WhatsApp and Telegram, as well as other messengers, QR code scanners, etc. But, most important, it was popular cryptocurrency wallet applications (MathWallet, Trust Wallet, and others) that were affected.
This trojan has been given the unique name Shibai in the Doctor Web virus database due to the string Log.e("", "-------------------SHIBAI-释放------------") contained in its code. We assume that this is a reference to the name of another crypto coin.
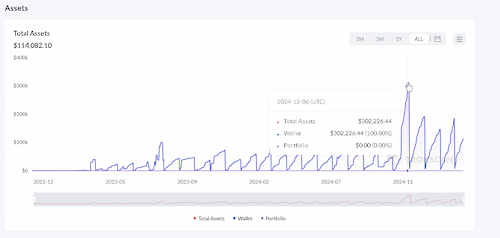
Unfortunately, this campaign has gained a great deal of momentum. The hackers employ more than 60 C2 servers to manage it and approximately 30 domains to distribute malicious applications. We were also able to obtain information about the financial gains made by the trojan’s creators. One of the wallets has received more than a million dollars over the last two years. Overall assets in another wallet amounted to half a million dollars. The rest of the wallets (about 20 of them) held amounts up to $100,000. It is impossible to get a complete picture of the profitability of this campaign, as the wallet addresses are obtained from the server of the attackers, and they may be different from time to time.
One of the crypto wallets with the most assets
To protect yourself from such attacks, our virus analysts recommend installing Dr.Web Security Space antivirus for mobile devices, shunning smartphones with features that clearly do not match their price, downloading applications only from trusted sources, such as Google Play, RuStore and AppGallery, and not storing on their devices screenshots with mnemonic phrases, passwords, and keys in unencrypted form.
Read more about Tool.LSPatch.1
Read more about Android.Clipper.31