Doctor Web’s January 2023 virus activity review
March 2, 2023
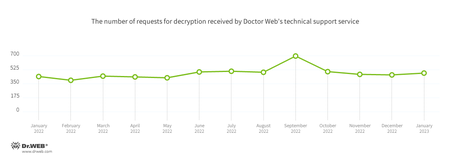
The number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans increased by 5.01%, compared to the previous month. Most often victims were targeted by Trojan.Encoder.26996, Trojan.Encoder.3953, and Trojan.Encoder.35209 ransomware.
During January, Doctor Web’s virus laboratory tracked many new threats on Google Play. Among them were dozens of fraudulent apps and another trojan software that subscribed victims to paid services.
Principal trends in January
- A decrease in the total number of detected threats
- An increase in the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans
- The emergence of dozens of new threats on Google Play
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
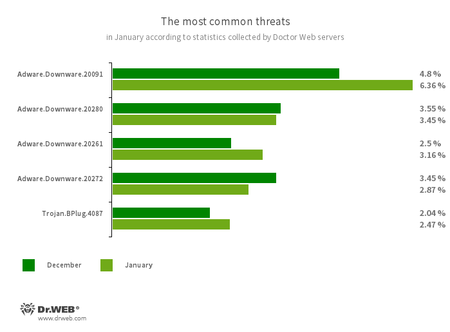
The most common threats of the month:
- Adware.Downware.20091
- Adware.Downware.20280
- Adware.Downware.20261
- Adware.Downware.20272
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirated software.
- Trojan.BPlug.4087
- The detection name for a malicious component of the WinSafe browser extension. This component represents a JavaScript file that displays intrusive ads in browsers.
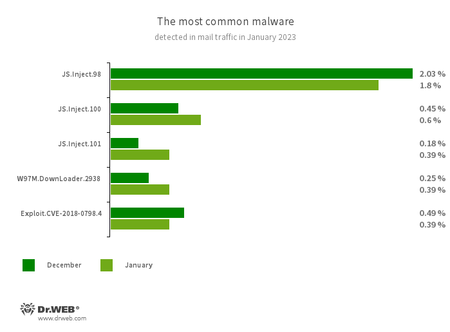
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts that inject a malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents. They can also download other malicious programs to a compromised computer.
- Exploit.CVE-2018-0798.4
- An exploit designed to take advantage of Microsoft Office software vulnerabilities and allow an attacker to run arbitrary code.
Encryption ransomware
In January 2023, the number of requests to decrypt files damaged by encoder trojans increased by 5.01%, compared to December.
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 22.43%
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 19.39%
- Trojan.Encoder.35209 — 5.45%
- Trojan.Encoder.34027 — 4.55%
- Trojan.Encoder.35534 — 3.64%
Dangerous websites
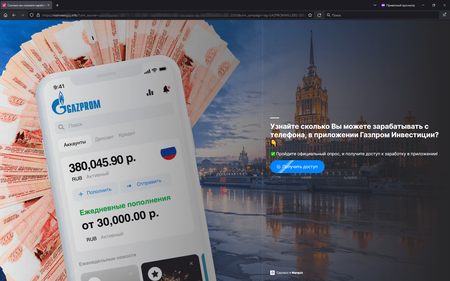
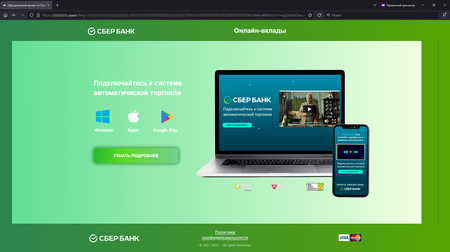
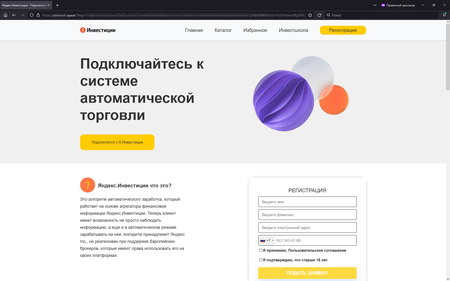
In January 2023, Doctor Web’s Internet analysts again observed an increase in the number of fraudulent websites—investment-related phishing sites in particular. Malicious actors offered potential victims the chance to improve their welfare by investing in various financial instruments. For example, they were invited to register an account for some services that were allegedly affiliated with large Russian companies. In reality, such web resources were fakes, and any user-provided personal information ended up in the scammers’ hands.
The screenshots above depict examples of fraudulent websites that try to look like the official services of large Russian companies. On such sites, potential victims can be asked to take part in a preliminary poll or immediately invited to register an ‘account” by filling out a special form with their personal data.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
According to detection statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android, January 2023 again witnessed increased activity on the part of adware trojans. In addition, banking trojans and ransomware were also detected more often on protected devices. At the same time, Doctor Web’s virus laboratory uncovered dozens of new threats on Google Play. Among them were various fraudulent apps from the Android.FakeApp family and also the Android.Joker and Android.Harly trojans that subscribed victims to paid services.
The following January events involving mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- An increase in the activity of trojan apps that display ads, banking trojans, and ransomware.
- The emergence of other threats on Google Play.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.
[% END %]