Doctor Web’s July 2022 virus activity review
Last month, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders increased by 1.81%. Trojan.Encoder.26996 was again the top encoder trojan, responsible for 28.65% of all incidents recorded.
The most widespread Android threats were adware trojans from the Android.HiddenAds family and the Android.Spy.4498 trojan, which steals information from other apps’ notifications. In addition, Doctor Web’s malware analysts discovered malicious programs in the firmware of several smartphone models. These threats were involved in the attack on WhatsApp and WhatsApp Business messengers.
Principal trends in July
- A decrease in the total number of detected threats
- Adware continues to be among the most active threats
- An increased number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
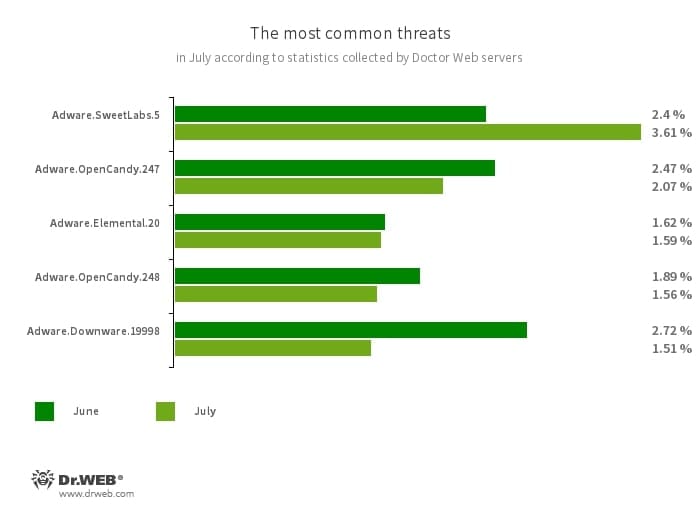
The most common threats of the month:
- Adware.SweetLabs.5
An alternative app store and Add-On for Windows GUI (graphical user interface) by the creators of “OpenCandy” Adware.
- Adware.OpenCandy.247
- Adware.OpenCandy.248
A family of applications that install other software on a system, including other adware.
- Adware.Elemental.20
Adware that spreads through file sharing services as a result of link spoofing. Instead of normal files, victims receive applications that display advertisements and install unwanted software.
- Adware.Downware.19998
Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirated software.
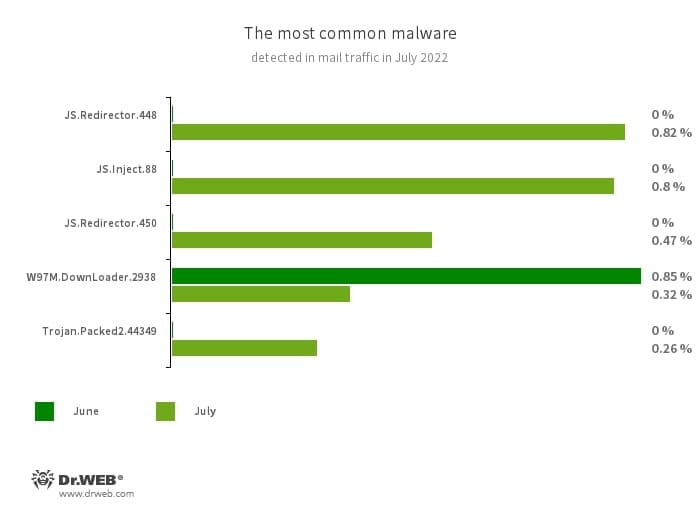
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- JS.Redirector.448
- JS.Redirector.450
Malicious scripts that redirect users to webpages controlled by fraudsters.
- JS.Inject
A family of malicious JavaScripts that inject a malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- Trojan.Packed2.44349
The detection name of malicious apps protected by a special software packer.
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
A family of downloader trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents. They can also download other malicious programs to a compromised computer.
Encryption ransomware
In July, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders increased by 1.81% compared to June.
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 28.65%
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 12.20%
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 5.67%
- Trojan.Encoder.30356 — 3.35%
- Trojan.Encoder.11539 — 3.05%
Dangerous websites
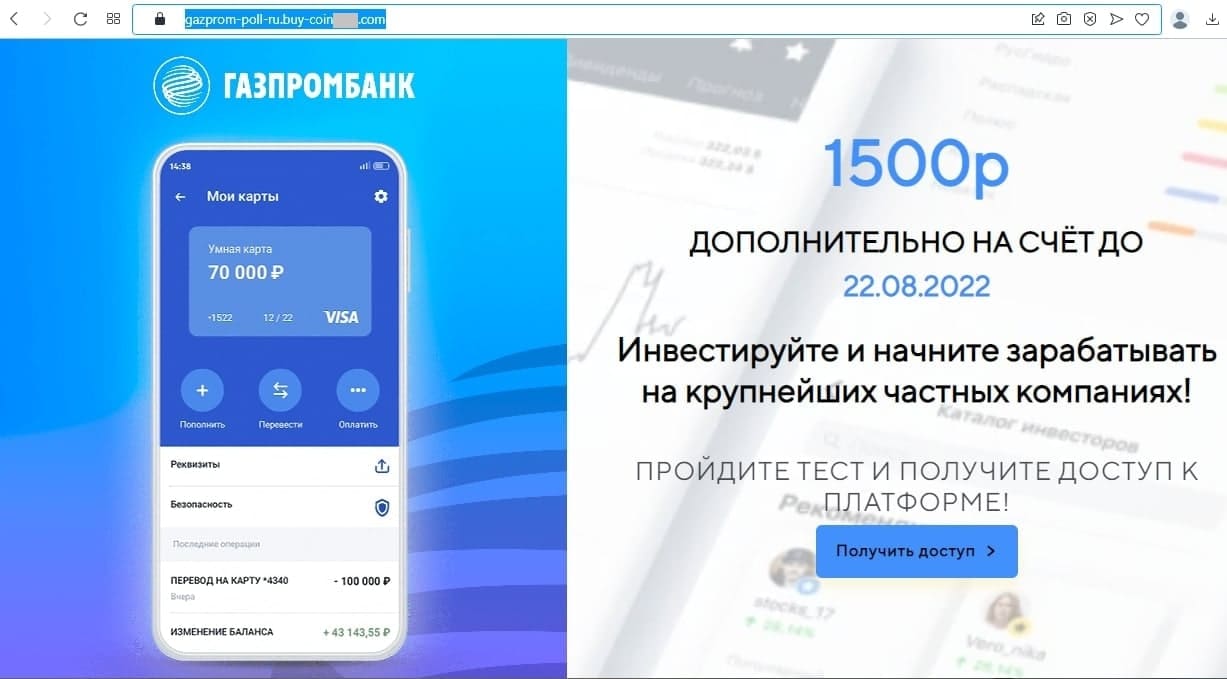
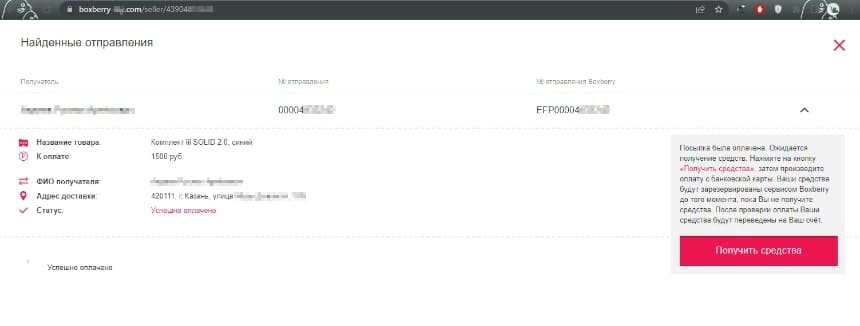
Last month, Doctor Web’s Internet analysts once again observed high activity on the part of cybercriminals who were massively spreading phishing emails containing links to fraudulent websites. Fake websites of famous banks, online stores, oil and natural gas companies, logistics and others companies are among the attackers’ most popular choices when it came to luring potential victims. On such fake websites, users, for example, are traditionally invited to become investors or receive a payment for goods delivered to the buyers. Fraudsters are aiming for the same goals as usual: they want users’ confidential information, including bank card data, and their victims’ money.
An example of a fraudulent website that allegedly belongs to a large Russian bank. The information on it states that after completing a “test”, users will gain access to a special trading platform..
An example of a fake site of one of the transport companies. Here, for every visitor, a unique page containing their personal information and a link is generated. Upon clicking on this link, potential victims will allegedly be able to receive a payment for the delivered goods.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In July, the Android.Spy.4498 trojan, which hijacks information from other apps’ notifications, was once again the most widespread Android threat. Nonetheless, its activity continues to gradually decrease. At the same time, last month we saw increased activity on the part of one of its modifications, Android.Spy.4837. Adware trojans also remain among the most widespread Android threats.
Last month, our specialists uncovered an attack on WhatsApp and WhatsApp Business messenger users. It involved malicious apps that infect the firmware of a number of Android device models.
The following July events related to mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- A decrease in Android.Spy.4498 trojan activity;
- Adware trojans remain one of the most widespread Android threats;
- An attack on WhatsApp and WhatsApp Business messenger users was detected.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.