Doctor Web’s July 2021 virus activity review
August 11, 2021
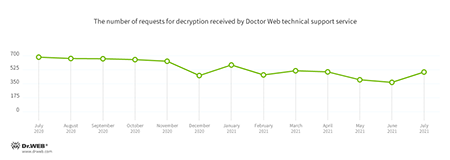
In July, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders increased by 35.2% compared with June. Trojan.Encoder.26996 was the most active, accounting for almost half of all incidents.
Principal trends in July
- A decrease in the number of unique threats
- Adware remains among the top threats
- Spreading of backdoors in email traffic
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
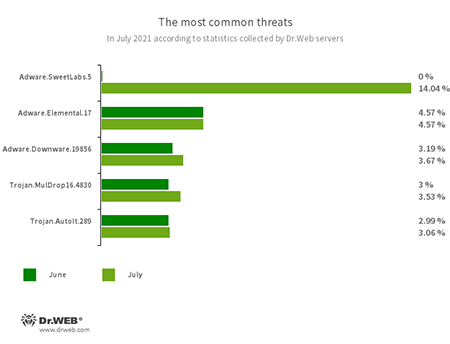
The most common threats in July:
- Adware.SweetLabs.5
- An alternative app store and add-on for Windows GUI from the creators of Adware.Opencandy.
- Adware.Elemental.17
- Adware that spreads through file sharing services as a result of link spoofing. Instead of normal files, victims receive applications that display advertisements and install unwanted software.
- Adware.Downware.19856
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirate software.
- Trojan.MulDrop16.4830
- A malicious program that downloads unwanted applications to a victim's computer.
- Trojan.AutoIt.289
- A malicious utility program written in the AutoIt language and is distributed as part of a miner or RAT trojan. It performs various malicious actions that make it difficult to detect the main payload.
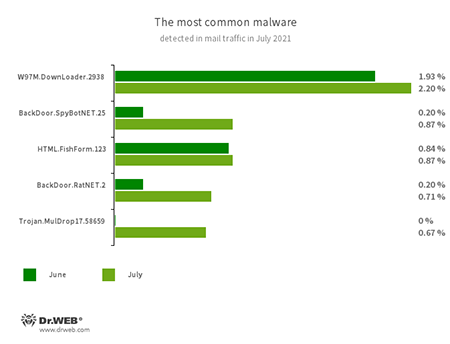
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploits vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents and are designed to download other malicious programs onto compromised computers. It is designed to download other malware onto a compromised computer.
- BackDoor.SpyBotNET.25
- A backdoor written in .NET and designed to operate with a file system (to copy, create, delete, etc. catalogs), terminate processes, and take screenshots.
- HTML.FishForm.123
- The web page spread via phishing emails. It is a bogus authorization page that mimics well-known websites. The credentials a user enters on the page are sent to the attacker.
- BackDoor.RatNet.2
- A backdoor that reads passwords stored in the browser.
- Trojan.MulDrop17.58659
- A malicious program that downloads unwanted applications to a victim's computer.
Encryption ransomware
User requests to decrypt files affected by encoders increased by almost 35.2% compared to June.
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 47.8%
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 10.44%
- Trojan.Encoder.11539 — 1.10%
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 0.82%
- Trojan.Encoder.11464 — 0.82%
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
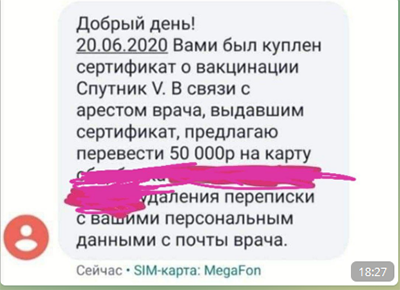
In July 2021, Doctor Web analysts’ attention was drawn to increased incidents of distribution threatening SMS. In our latest virus review, we wrote about user offers to buy fake certificates or QR codes, but the criminals have taken things further - for 50,000 rubles, they now offer users the opportunity to cover up any traces of their having bought the fake products.
The screenshot shows an example of a threatening SMS that contains a proposition to send money to the cybercriminals card. However, there is no information about the possible consequences should the recipient of the chain letter not follow the attacker’s instruction.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In July, Doctor Web analysts discovered a new family of banking trojans for the Android OS, named Coper. These malicious applications have a modular architecture and a number of defense mechanisms. The trojans are able to intercept and send SMS, control notifications, display phishing windows over launched programs, track information entered on the keyboard, and perform other malicious actions.
There was also the emergence of new malware in the Google Play catalog. Among the malware were trojans from the Android.Joker,family, which subscribe victims to paid services, and a malicious program from the Android.FakeApp family. You remember this program as the application that downloaded fraudulent sites where potential victims were asked to receive "payments" from the state.
Among the recorded threats, the most active were again adware trojans and trojans that execute arbitrary code and download other software.
The following July events related to mobile malware were the most noteworthy:
- detection of a new family of banking trojans for Android OS
- the detection of threats on Google Play
- adware activity and trojans capable of downloading and executing arbitrary code
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.