Doctor Web’s April 2021 virus activity review
May 13, 2021
In April, an analysis of Dr. Web’s statistics revealed a 1.73% increase in the total number of threats compared to the previous month. The number of unique threats dropped by 35.6%. Adware still made up the majority of detected threats. Various malware that includes obfuscated, malicious scripts and programs exploiting vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office utilities were the most frequently detected threats in email traffic.
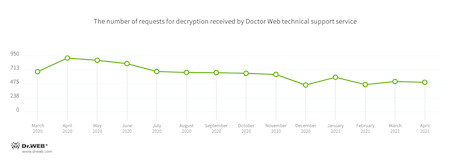
In April, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders decreased by 2.73% compared with March. Trojan.Encoder.567 was the most active, accounting for 15.71% of all incidents.
Principal trends in April
- Growth in malware spreading activity
- Adware remains among the top threats
- The detection of new malicious programs in email traffic
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
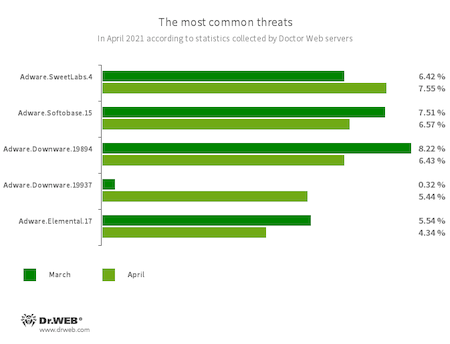
The most common threats in April:
- Adware.SweetLabs.4
- An alternative app store and add-on for Windows GUI from the creators of Adware.Opencandy.
- Adware.Softobase.15
- Installation adware that spreads outdated software and changes browser settings.
- Adware.Downware.19894
- Adware.Downware.19937
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirate software.
- Adware.Elemental.17
- Adware that spreads through file sharing services as a result of link spoofing. Instead of normal files, victims receive applications that display advertisements and install unwanted software.
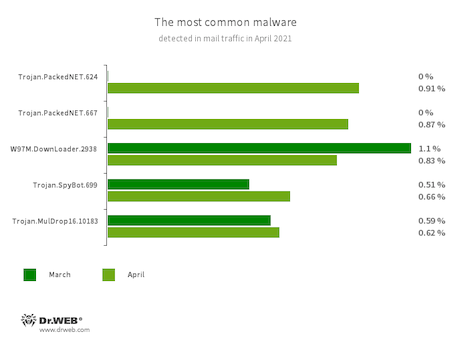
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- Trojan.PackedNET.624
- Trojan.PackedNET.667
- Packed malware written in VB.NET.
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploits vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents and are designed to download other malicious programs onto compromised computers.
- Trojan.SpyBot.699
- A multi-module banking trojan. It allows cybercriminals to download and launch various applications on infected devices and run arbitrary code.
- Trojan.MulDrop16.10183
- A malicious program that downloads unwanted applications to a victim's computer.
Encryption ransomware
In April, Doctor Web's virus laboratory received 2.73% fewer requests to decrypt files from users affected by ransomware compared to the previous month.
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 15.71%
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 14.94%
- Trojan.Encoder.11539 — 1.53%
- Trojan.Encoder.741 — 1.15%
- Trojan.Encoder.11464 — 1.15%
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
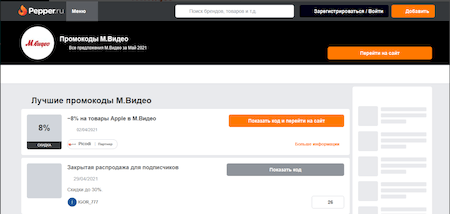
In April 2021, Doctor Web's Internet analysts discovered many phishing sites. Among other things, attackers faked web pages of household appliance stores. For example, the fraudulent sites were disguised as official resources of M.Video. After clicking the “Go to site” button, users found themselves in a fake online store.
This is a snapshot of the fraudulent website with a fake promocodes.
Attackers lured victims to phishing sites using social engineering. They expected that in the hope of getting cheaper goods, buyers would activate special promotional codes. If the user fell for the trick, the fraudster received personal data, which was used, for example, to debit money from the victim's bank account.
In addition, in April, there were cases of redirection to fake payment system sites. There, users entered their bank card details, confirmed the payment, but did not receive the products.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
Last month, Doctor Web virus analysts found out that one of the versions of the client application of the popular third-party catalog of Android programs, APKPure, contains malicious functionality. The trojan detected in it, Android.Triada.4912, used an auxiliary component to download other programs and display various websites.
In addition, our experts identified the first malicious applications in the AppGallery software catalog. They are trojans from the Android.Joker family, capable of executing arbitrary code and subscribing users to paid mobile services.
In addition, another trojans from the Android.FakeApp family, used for fraudulent purposes, were found on Google Play.
The following April events related to mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- The emergence of trojan functionality in the client application of the third-party APKPure catalog
- The detection of the first malicious programs on AppGallery
- Distribution of new trojans through the official Google Play catalog
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.