Doctor Web’s April 2021 review of virus activity on mobile devices
May 13, 2021
In April, Doctor Web reported on the discovery of the Android.Triada.4912 trojan embedded in one of the versions of the client application of the popular third-party Android app catalog APKPure. With that, new trojans from the Android.FakeApp family were found on the official Android app catalog Google Play. They were spread as useful software and loaded various fraudulent websites. Doctor Web’s specialists have also uncovered Android.Joker trojans on Huawei’s AppGallery catalog. These malicious applications subscribed victims to premium mobile services.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN APRIL
- The discovery of the trojan functionality in the client app of the popular third-party Android catalog APKPure
- The spreading of new threats through the Google Play catalog
- The discovery of threats in the AppGallery app store
Mobile threat of the month
At the beginning of April, Doctor Web reported on the discovery of malicious functionality found by our malware analysts in the popular third-party Android software catalog APKPure. Unidentified attackers embedded an Android.Triada.4912 trojan into it, with version 3.17.18 being particularly affected. The Android.Triada.4912 launched an additional module hidden in its resources. This module performed the main malicious tasks, downloading other trojan components and various applications, as well as loading different websites.
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android
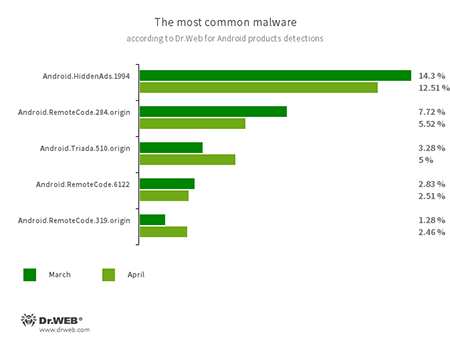
- Android.HiddenAds.1994
- A trojan designed to display obnoxious ads, distributed as popular applications. In some cases, it can be installed in the system directory by other malware.
- Android.RemoteCode.284.origin
- Android.RemoteCode.6122
- Android.RemoteCode.319.origin
- Malicious applications that download and execute arbitrary code. Depending on their modification, they can load various websites, open web links, click on advertising banners, subscribe users to premium services and perform other actions.
- Android.Triada.510.origin
- A multifunctional trojan performing various malicious actions. This malware belongs to the trojan family that infects other app processes. Some modifications of this family were found in the firmware of Android devices, which attackers implanted during manufacturing. Some of them can also exploit various vulnerabilities to gain access to protected system files and folders.
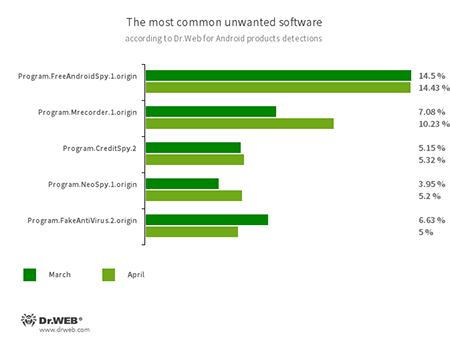
- Program.FreeAndroidSpy.1.origin
- Program.Mrecorder.1.origin
- Program.NeoSpy.1.origin
- Software that monitors Android user activity and may serve as a tool for cyber espionage. These apps can track device locations, collect information from SMS and social media messages, copy documents, photo and video, spy on phone calls, etc.
- Program.CreditSpy.2
- The detection name for programs designed to assign credit ratings to users based on their personal data. These applications upload SMS, contact information from phonebooks, call history and other information to the remote server.
- Program.FakeAntiVirus.2.origin
- The detection name for adware programs that imitate anti-virus software. These apps inform users of non-existing threats, mislead them and demand they purchase the full version of the software.
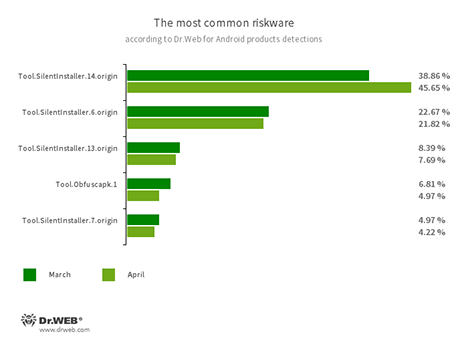
- Tool.SilentInstaller.6.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.7.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.13.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.14.origin
- Riskware platforms that allow applications to launch APK files without installation. They create a virtual runtime environment that does not affect the main operating system.
- Tool.Obfuscapk.1
- The detection name for applications protected by the Obfuscapk obfuscation tool. This tool is used to automatically modify and scramble Android apps’ source code to make reverse engineering more difficult. Cybercriminals use the tool to protect malicious applications from being detected by anti-virus programs.
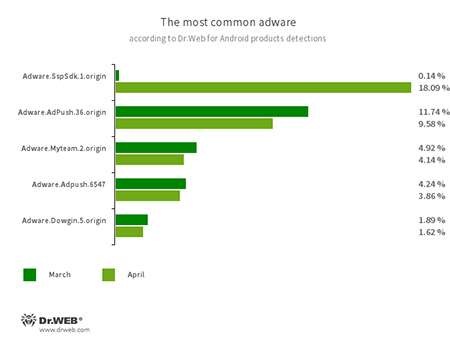
Program modules incorporated into Android applications and designed to display obnoxious ads on Android devices. Depending on their family and modifications, they can display full screen ads and block other apps’ windows, show various notifications, create shortcuts and load websites.
- Adware.SspSdk.1.origin
- Adware.Adpush.36.origin
- Adware.Adpush.6547
- Adware.Myteam.2.origin
- Adware.Dowgin.5.origin
Threats on Google Play
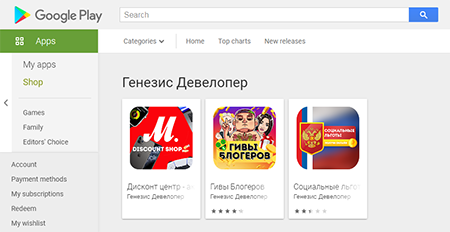
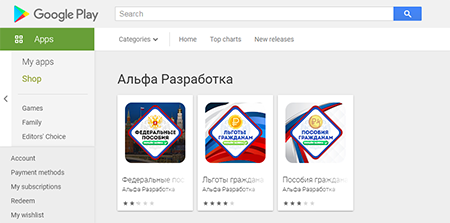
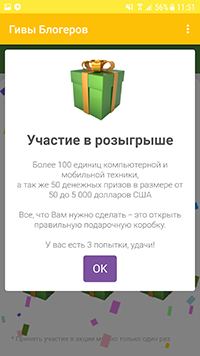
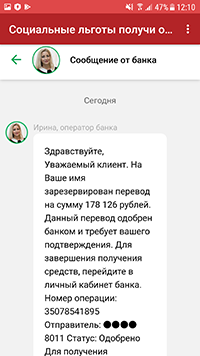
In April, new trojans from the Android.FakeApp malware family were discovered. They were spread under the guise of reference software with information about payments and compensations from the government, as well as apps that allegedly could be used to receive discounts for buying goods in famous retail stores and to win gifts from popular bloggers. In reality, these fake apps were only misleading victims. They didn’t work as described and only displayed fraudulent websites that allowed attackers to steal Android users’ personal information and money. These trojans were added to the Dr.Web virus database as Android.FakeApp.255, Android.FakeApp.254, Android.FakeApp.256, Android.FakeApp.259, Android.FakeApp.260, and Android.FakeApp.261.
Examples of the bogus apps’ appearance is shown below:
Other threats
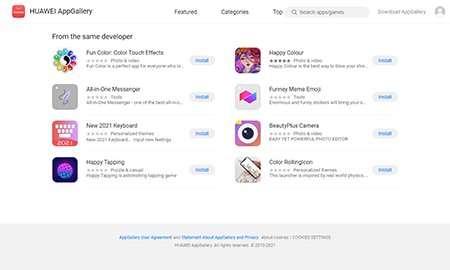
Last month, Doctor Web’s malware analysts discovered the first malicious apps in the Huawei’s AppGallery catalog. They belong to the Android.Joker trojan family and are capable of executing arbitrary code and subscribing users to premium mobile services. These trojans were spread as various seemingly harmless apps, such as virtual keyboards, online messenger, a camera app and some others. In total, over 538.000 users have downloaded them.
To protect your Android device from malware and unwanted programs, we recommend installing Dr.Web for Android.

Your Android needs protection.
Use Dr.Web
- The first Russian anti-virus for Android
- Over 140 million downloads—just from Google Play
- Available free of charge for users of Dr.Web home products