June 2019 virus activity review from Doctor Web
July 3, 2019
In June, Dr.Web server statistics registered a significant increase in the number of common and unique threats compared with May. Adware and installers are still leading in the total number of detected threats; the highest malware activity has been detected in email traffic. The dangerous stealer, Trojan.PWS.Maria.3 (Ave Maria), previously used to target an oil and gas company, is active again. The Trojan.Nanocore.23 trojan with remote access that helps control an infected computer is distributed via email. A malware campaign using the Trojan.Encoder.858 encoder also took place in June.
Principal trends in June
- Increased malware distribution
- Emailing stealers and RAT Trojans
- Increased encoder activity
Threat of the month
In June, a sample of the rare Trojan.MonsterInstall Node.js trojan was studied in the Doctor Web virus lab. When launched on a victim's device, it downloads and installs the modules it needs for operation, collects information about the system, and sends it to the developer’s server. After receiving a response from the server, it adds itself to autorun and starts mining the TurtleCoin cryptocurrency. Developers of this malware use cheats for popular games from their own webpages to distribute the trojan and infect files on other similar websites.
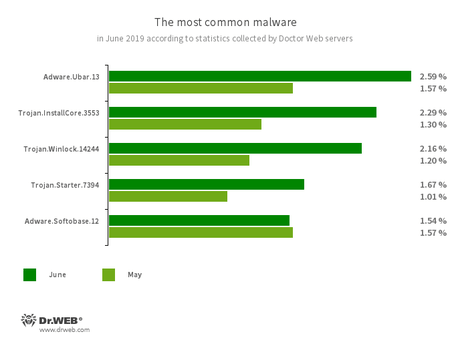
According to Doctor Web’s statistics servers
Threats of this month:
- Adware.Ubar.13
- A torrent client that installs unwanted software on devices.
- Trojan.InstallCore.3553
- Another notorious adware installer. It displays ad banners and installs software without users’ permission.
- Trojan.Winlock.14244
- Blocks or restricts user access to the operating system and its main functions. To access the system, users are required to transfer money to the trojan developer’s account.
- Trojan.Starter.7394
- A trojan that launches other malware on a device.
- Adware.Softobase.12
- An installer that distributes outdated software. It changes browser settings.
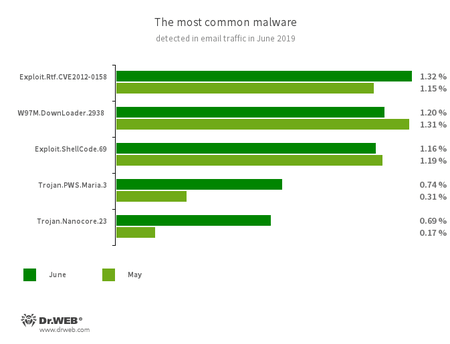
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- Exploit.Rtf.CVE2012-0158
- A modified Microsoft Office Word document that exploits the CVE2012-0158 vulnerability to execute malicious code.
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents and can download other malicious programs to a compromised computer.
- Exploit.ShellCode.69
- A malicious Microsoft Office Word document that exploits the CVE-2017-11882 vulnerability.
Rising threats of the month:
- Trojan.PWS.Maria.3
- A stealer distributed by email in malicious Excel files. It uses the popular CVE-2017-11882 vulnerability to launch an executable file. It was first seen in a phishing campaign targeting the Italian oil and gas industry.
- Trojan.Nanocore.23
- A dangerous trojan with remote access. It allows cybercriminals to control an infected computer, including the camera and microphone on the device if available.
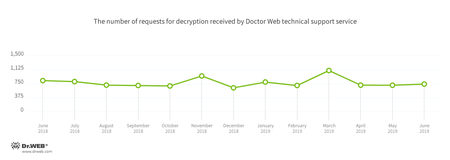
Encoders
In June, Doctor Web’s technical support service registered cases involving the following encoders:
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 30.31%
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 7.02%
- Trojan.Encoder.11464 — 6.47%
- Trojan.Encoder.11539 — 3.33%
- Trojan.Encoder.18000 — 3.14%
- Trojan.Encoder.28004 — 2.59%
- Trojan.Encoder.25574 — 1.66%
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
In June 2019, the Dr.Web database was updated with a total of 151,162 non-recommended website URLs.
| May 2019 | June 2019 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 223,952 | + 151,162 | – 32.5% |
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In June, Doctor Web virus analysts discovered many more malicious and unwanted programs on Google Play, including the Android.HiddenAds advertising trojans, displaying ad banners over other applications and the operating system interface, as well as the Android.FakeApp fraudulent software. The latter loaded websites where potential victims were invited to participate in online polls for a cash reward. To receive the money, users allegedly had to pay a certain commission or a test fee. If they agreed, however, they received no reward. Another member of this malware family, Android.FakeApp.174, loaded websites where users were signed up for obnoxious and fraudulent notifications.
New trojan downloaders were also detected this month, such as the Android.DownLoader.3200 and Android.DownLoader.681.origin. They downloaded other malicious applications on Android devices. Doctor Web experts also analyzed the new Adware.OneOceans.2.origin adware module, embedded into programs and games by developers.
The following mobile malware event of June was the most noteworthy:
- detection of new malware on Google Play.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.