Doctor Web’s overview of malware detected on mobile devices in October 2018
October 31, 2018
In October, information security specialists discovered an Android Trojan capable of executing C# scripts sent from a remote server, as well as downloading and launching malicious modules. More malicious applications were also detected on Google Play this month.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN OCTOBER
- The detection of malicious programs on Google Play
- Detection of an Android Trojan that could receive and compile a C# code from attackers to execute it on mobile devices
Mobile threat of the month
Doctor Web specialists have detected applications with the built-in downloader Trojan Android.DownLoader.818.origin distributed as a VPN client on Google Play. The malware downloaded and tried to install an adware Trojan to mobile devices. Later, malware analysts uncovered other modifications of this downloader, dubbed Android.DownLoader.819.origin and Android.DownLoader.828.origin. The fraudsters disguised them as games.
The Trojans' unique features are as follows:
- they request administrative privileges to hinder their removal from the system;
- they hide the app icon from the list of programs on the main screen of the operating system;
- they download other Trojans disguised as system software and prompt the user to install them.
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android
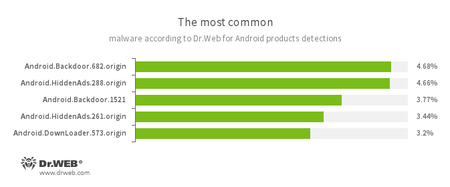
- Android.Backdoor.682.origin
- Android.Backdoor.1521
- The Trojans that execute cybercriminals’ commands and help them to control infected mobile devices.
- Android.HiddenAds.261.origin
- Android.HiddenAds.288.origin
- The Trojans are designed to display intrusive advertisements. They are distributed under the guise of popular applications by other malicious programs, which in some cases quietly install themselves in the system catalog.
- Android.DownLoader.573.origin
- A Trojan that downloads other malware applications.
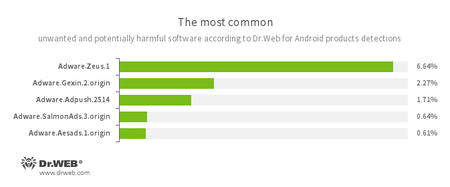
- Adware.Zeus.1
- Adware.Gexin.2.origin
- Adware.Adpush.2514
- Adware.SalmonAds.3.origin
- Adware.Aesads.1.origin
- Unwanted program modules incorporated into Android applications and designed to display obnoxious ads on mobile devices.
Trojans on Google Play
At the beginning of the month, Doctor Web experts detected the Trojan Android.FakeApp.125 on Google Play. It was distributed as a program allegedly paying money for answering simple questions. In reality, Android.FakeApp.125 was loading and displaying fraudulent websites upon the signal of the managing server.
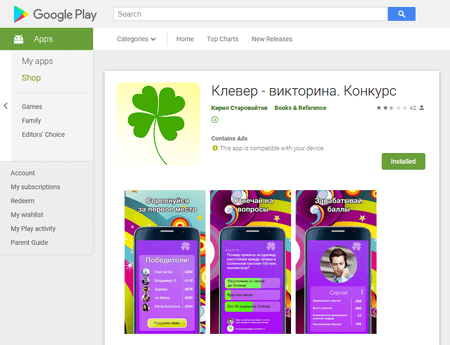
Later, security researchers detected the Trojan Android.Click.245.origin, disguised by cybercriminals as the Clover game, popular in VKontakte. Like Android.FakeApp.125, Android.Click.245.origin loaded fraudulent websites and displayed them to users.
In late October, Doctor Web analysts investigated the malware Android.RemoteCode.192.origin and Android.RemoteCode.193.origin. They were hiding in 18 seemingly harmless programs—barcode scanners, navigation software, file download managers, and various games, installed on at least 1,600,000 Android mobile devices. The Trojans could display advertisements, download and launch malicious modules, as well as open YouTube videos, increasing their popularity.
Aside from that, the Dr.Web virus database was updated with entries to detect new malware Android.DownLoader.3897, Android.DownLoader.826.origin and Android.BankBot.484.origin. They downloaded and tried to install banking Trojans on mobile devices.
Other threats
Among the mobile malware detected in October was the Android banker Android.BankBot.1781 with a modular architecture. At the command of the managing server, it could download various Trojan plug-ins, as well as download and execute C# scripts. Android.BankBot.1781 could steal bank card data, SMS messages, and other confidential information.
Cybercriminals distribute malicious programs to Android mobile devices via Google Play and fraudulent or hacked websites. To protect smartphones and tablets, it is recommended that users install Dr.Web anti-virus products for Android.
Your Android needs protection
Use Dr.Web
- The first Russian Anti-virus for Android
- More than 135 million downloads on Google Play alone
- Free for users of Dr.Web home products