March 2018 virus activity review from Doctor Web
April 3, 2018
In March, Doctor Web specialists detected and examined numerous new malicious programs. Mass phishing mailing was detected at the beginning of the month. It was performed on behalf of Mail.Ru. Researchers also examined several new Trojans of a large family of malicious programs Trojan.LoadMoney. In mid-March, a dangerous Trojan called Trojan.PWS.Stealer.23012 was detected. It stole files and other confidential information from infected devices. Security researchers also detected a whole range of malicious programs for Google Android in March.
Principal Trends in March
- Mass mailing of phishing email messages
- Distribution of new representatives of the family Trojan.LoadMoney
- Emergence of a dangerous Trojan capable of stealing confidential information
Threat of the month
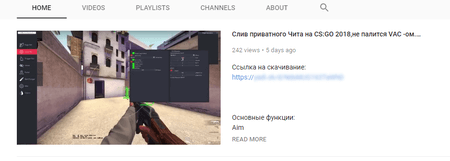
Distribution of Trojan.PWS.Stealer.23012 started on March 11, 2018. Cybercriminals posted links to the Trojan in the comments section of YouTube. Many such videos show use of fraudulent game tutorial methods (so-called “cheats”) that involve special applications. Cybercriminals try to pass the Trojan off as such applications and other useful tools.
The Trojan collects Cookie files on an infected computer in addition to login credentials from several popular browsers, makes a screenshot and copies files from the Windows Desktop. The stolen information is then sent to the cybercriminals’ server along with data on the location of the infected device. For more information on the operation of Trojan.PWS.Stealer.23012, refer to this article published on our website.
According to Dr.Web Anti-virus statistics
- Trojan.Starter.7394
- A Trojan whose main purpose is to launch in an infected system with an executable file possessing a specific set of malicious functions.
- Trojan.Inject
- A family of malicious programs that inject malicious code into the processes of other programs.
- Trojan.Zadved
- This Trojan displays fake search results in the browser window and imitates pop-up messages from social networking sites. In addition to this, the malware can replace advertisements displayed on different Internet resources.
- Trojan.Moneyinst.520
- A malicious program that installs various software, including other Trojans, on a victim's computer.
- Trojan.Encoder.11432
- A network worm that launches a dangerous ransomware Trojan on a victim’s computer. It is also known as WannaCry.
- BackDoor.Meterpreter.56
- A representative of the malware family that allows cybercriminals to remotely control an infected computer and send it various commands.
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts. They inject malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- BackDoor.IRC.Bot.4771
- A representative of the malware family that allows cybercriminals to remotely control an infected computer and send it various commands. The Trojan is controlled via the IRC (Internet Relay Chat) text-messaging protocol.
- Trojan.Encoder.11432
- A network worm that launches a dangerous ransomware Trojan on a victim’s computer. It is also known as WannaCry.
- JS.DownLoader
- A family of malicious JavaScripts. They download and install malicious software on a computer.
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts. They inject malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- Trojan.Encoder.24788
- A malicious program belonging to the family of encryption ransomware Trojans that encrypt files and demand a ransom to decrypt compromised data.
- Java.Jrat.58
- Malware that controls computers remotely (Remote Access Tools, RAT). This malicious program is written in Java.
- Trojan.PWS.Stealer
- A family of Trojans designed to steal passwords and other confidential information stored on an infected computer.
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 15.38% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.11464 — 7.26% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.11539 — 6.62% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.24249 — 5.77% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 3.63% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.2667 — 2.35% requests.
- the detection of the Trojan in dozens of Android smartphone models;
- the emergence of new banking Trojans;
- the detection of malicious programs on Google Play.
According to Doctor Web’s statistics servers
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in email traffic
Encryption ransomware
In March, Doctor Web’s technical support was most often contacted by victims of the following modifications to encryption ransomware:
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
In early March, Doctor Web reported a mass emailing of phishing messages on behalf of Mail.Ru. In these emails, cybercriminals warned users that their accounts would be blocked on the Mail.Ru server and suggested a repeat authorization. A link in the email message led to a fake Mail.Ru website, and the information users provided was immediately sent to the cybercriminals.
The web address of the fraudulent website was added to the databases of the Dr.Web Office and Parental Control.
During March 2018, Doctor Web added 624,474 URLs into the Dr.Web database of non-recommended sites.
| February 2018 | March 2018 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 1,174,380 | + 624,474 | - 46.8% |
Other events in information security
Trojans of the Trojan.LoadMoney family that download other malicious programs to an infected computer have been known since 2013. In March, Doctor Web virus analysts examined several new representatives of this family. Virus writers have not implemented any visual effects in the malicious code, so these Trojans do not manifest themselves in the infected system. Therefore, detecting their malicious activity is not easy. More information on the examined malicious programs of the Trojan.LoadMoney family is available in our overview.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In March, Doctor Web specialists published examination results for Android.Triada.231, which cybercriminals injected into the firmware of over 40 models of Android smartphones. Android.Triada.231 infects the processes of all applications and can covertly perform various malicious actions. During the past month, numerous new Trojans were detected on Google Play. Among them were representatives of the Android.Click family. They can load and display any webpage. Android.BankBot.344.origin was also detected. Additionally, Doctor Web specialists found new banking Trojans created on the basis of the source code of Android.BankBot.149.origin. One of them was dubbed Android.BankBot.325.origin. This banker displayed phishing windows, performed cyber espionage, and provided cybercriminals with remote access to infected devices.
Among the most noticeable March events related to mobile malware:
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.