Mobile threats in May 2014
Virus reviews | Threats to mobile devices | All the news
June 4, 2014
From May 1-31, Dr.Web for Android detected 7,005,453 incidents, and, as before, of those threats discovered, various profit-generating advertising modules, embedded by software developers into their products, were found in the greatest abundance. Adware.Leadbolt advertising modules accounted for 9.81% of the incidents; Adware.Airpush ranked second with 9.06%; and Adware.Revmob modules ranked third.
Discovered on 3.36% of the devices involved in the incidents, Android.SmsBot.120.originwas May 2014’s most common malicious program for Android. Android.Backdoor.69.origin ranked second with 2.71%, and Android.SmsBot.105.origin (1.89%) ranked third. The ten most common Android Trojans detected by Dr.Web anti-virus software in May are listed in the following table:
| ? | Threat name | % |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Android.SmsBot.120.origin | 3,36 |
| 2 | Android.Backdoor.69.origin | 2,71 |
| 3 | Android.SmsBot.105.origin | 1,89 |
| 4 | Android.SmsSend.685.origin | 1,37 |
| 5 | Android.SmsBot.122.origin | 1,21 |
| 6 | Android.SmsSend.1215.origin | 0,96 |
| 7 | Android.SmsSend.315.origin | 0,91 |
| 8 | Android.Spy.83.origin | 0,91 |
| 9 | Android.SmsSend.859.origin | 0,88 |
| 10 | Android.SmsSend.991.origin | 0,86 |
The greatest number of threats—292,336—were discovered by the anti-virus on May 17, and the smallest number—189,878—were identified on May 8, 2014.
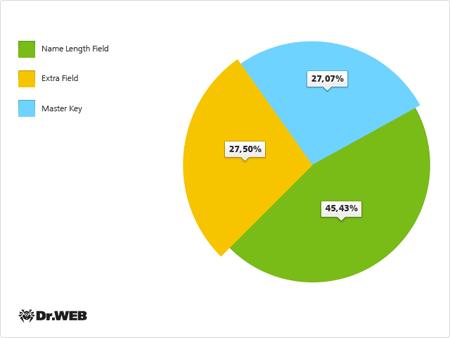
The Security Auditor (a special component that exposes operating system vulnerabilities) revealed 995,966 vulnerabilities on protected devices. You may recall that Dr.Web for Android detects several types of vulnerabilities:
- Master Key is a flaw in Android security routines that enables the installation of unsigned applications from packages containing files with identical names.
- Extra Field and the Name Length Field are vulnerabilities that allow intruders to embed into modified apk packages malicious code that will bypass automatic security verification during installation.
The frequency with which these vulnerabilities were being detected on mobile devices from May 1-31, 2014, is illustrated in the diagram below.
According to statistics collected by Doctor Web, 81.03% of users adjusted their Android OS settings to allow applications from unknown sources to be installed on their devices; this could become yet another pathway through which potentially dangerous programs could penetrate them. Meanwhile, 18.97% of users enabled the debugging mode in their Android settings which also increases the risk of data leaks. Furthermore, 3.84% of Android handheld owners have rooted devices. This can also cause their smart phones or tablets to become infected and can also significantly complicate malware removal.
Doctor Web's security researchers will continue to monitor the security situation and keep users informed about all the developments.
Learn more with Dr.Web
Virus statistics Virus descriptions Virus monthly reviews Laboratory-live