May 2015 virus activity review from Doctor Web
May 29, 2015
In terms of information security, May 2015 appeared to be rather uneventful. During the last spring month, no major instances of malicious mass mailings were detected. Botnets also kept a low profile.
Principal Trends In May
- Growing number of detected adware and unwanted installer applications that target OS X
- Noticeable increase in activity on the part of cybercriminals who continue tricking Internet users into giving away their money
- New malicious programs for Android
Threat of the month
Existence of numerous installers of useless and unwanted applications is not news to Windows users. However, not so many programs of this kind target OS X. Due to this fact, security researchers took a great interest in an installer application that has been added to Dr.Web virus databases under the name of Adware.Mac.InstallCore.1.
Consisting of several components, Adware.Mac.InstallCore.1 can not only install unwanted programs on the user’s computer but also change the browser home page and the search engine used by default. Moreover, this program encompasses debugging functions; that is, once it is launched, it scans the system for the presence of virtual machines, anti-viruses, or some other applications. If the scan returns positive results, the malware will not prompt the user to install additional programs. The following list presents some programs and utilities, which Adware.Mac.InstallCore.1 can install on the system:
- Yahoo Search
- MacKeeper (Program.Unwanted.MacKeeper)
- ZipCloud
- WalletBee (Adware.Mac.DealPly.1)
- MacBooster 2 (Program.Unwanted.MacBooster)
- PremierOpinion (Mac.BackDoor.OpinionSpy)
- RealCloud
- MaxSecure
- iBoostUp
- ElmediaPlayer
Find out more about the installer in this news article.
OS X
Adware.Mac.InstallCore.1 is not the only adware for OS X examined in May 2015. For example, an application called WalletBee has been added to Dr.Web virus databases under the name of Adware.Mac.DealPly. This application serves the purpose of installing different extensions for Chrome and Safari.
Another adware for Apple computers, which was added to Dr.Web virus databases as Adware.Mac.WebHelper, unites WebTools and ShopMall applications. The malicious package contains several scripts for command interpreter SH, a set of Python scripts, and a few binary files.
Automatic launch of Adware.Mac.WebHelper is executed with the help of PLIST files. This application can modify the home page in Chrome, Firefox, and Safari. It can also change the default search engine to my-search-start.com. Adware.Mac.WebHelper contains a binary file that executes two AppleScripts (for Chrome and Safari) in infinite loop. These scripts inject a JavaScript code into web pages browsed by the user. Running of this code, in turn, results in downloading 4 other JavaScripts that display advertisements in the browser window.
One other program that encompasses the same functionality and targets OS X is called Mac.Trojan.Crossrider. Trojans belonging to the Crossrider family are well known to Windows users. However, this modification targets Apple computers.
Mac.Trojan.Crossrider is distributed in the guise of an installation package (Safari Helper). Running of Mac.Trojan.Crossrider triggers a stealthy installation of the FlashMall extension for Safari, Chrome, and Firefox. Moreover, the malware adds two following applications to the system startup list: “WebSocketServerApp” and “Safari Security”. The first application is responsible for the communication with the command and control server and the second one installs browser extensions. Also, the malware modifies the startup scripts for the browser extensions to be updated in the future.
All adware programs and malicious applications for OS X detected by Doctor Web security researchers have been added to Dr.Web virus databases for OS X.
Find out more about malicious programs for OS X!
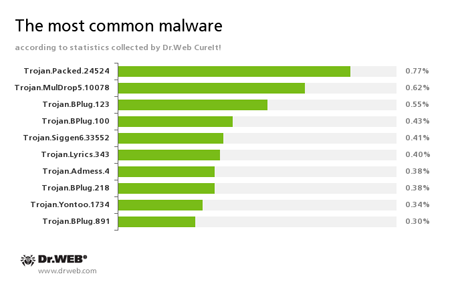
According to the statistics gathered by Dr.Web CureIt!
In May, 84,063,249 malicious programs and riskware were detected.
| April 2015 | May 2015 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| 73,149,430 | 84,063,249 | + 14.9% |
Trojan.Packed.24524
This Trojan installs adware and other unwanted programs.
Trojan.MulDrop5.10078
This malicious program installs various unwanted applications and adware on the infected computer.
Trojan.BPlug
These plug-ins for popular browsers display annoying advertisements to users as they browse web pages.
Trojan.Siggen6.33552
This malicious program is designed for installation of other malware.
Trojan.Lyrics
A family of Trojans that display annoying advertisements and open dubious web pages without user consent.
Trojan.Admess
A family of Trojans designed to replace existing advertisements with new ones and to display unsolicited advertisements to users as they browse various web pages.
Trojan.Yontoo
These plug-ins for popular browsers display advertisements to users as they browse web pages.
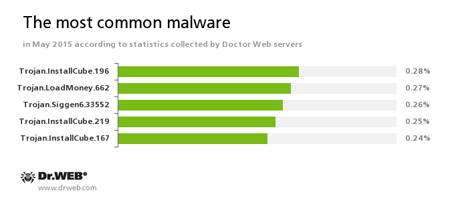
According to Doctor Web’s statistics servers
Trojan.InstallCube
A family of downloader programs designed to install unwanted and useless applications on the user’s computer.
Trojan.Siggen6.33552
This malicious program is designed for installation of other malware.
Trojan.LoadMoney
A family of downloader programs generated by servers belonging to the LoadMoney affiliate program. These applications download and install unwanted software on the victim's computer.
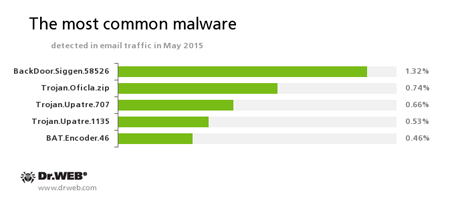
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in email traffic
BackDoor.Siggen.58526
This Trojan covertly downloads and launches other malicious programs in the infected system and executes commands issued by cybercriminals.
Trojan.Oficla
A family of Trojans mainly distributed via email messages. Once one of these Trojans infects a system, it hides its further activity. Trojan.Oficla connects the computer to a botnet, which allows cybercriminals to upload other malicious software to the compromised machine. After the system gets infected, cybercriminals that control the botnet get control over the victim’s computer. In particular, they become able to upload, install, and use any malicious software they choose.
Trojan.Upatre
A family of Trojans that covertly download and install other malicious applications on the infected computer.
BAT.Encoder.46
A representative of encryption ransomware that encrypts files using the legitimate GPG utility with BAT scripts.
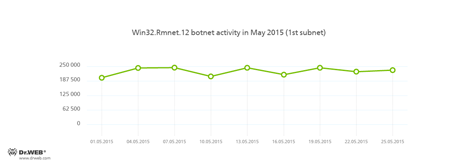
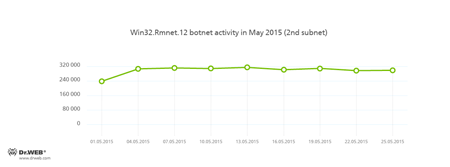
Botnets
Doctor Web security researchers continue to monitor a number of active botnets. Among them is a botnet created by cybercriminals using the file infector Win32.Rmnet.12. The average daily activity of the botnet's two subnets is shown in the following graphs:
Rmnet is a family of viruses spread without any user intervention. They can embed content into loaded web pages (this theoretically allows cybercriminals to get access to the victim's bank account information), steal cookies and passwords stored by popular FTP clients, and execute other commands issued by cybercriminals.
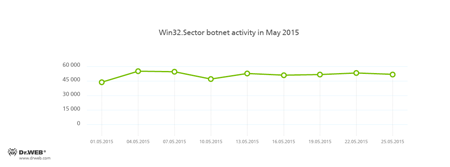
The botnet consisting of computers infected with the Win32.Sector file virus is still active. This malicious program can:
- Download various executable files via P2P networks and run them on infected machines.
- Inject its code into running processes.
- Shut down certain anti-viruses and block access to the sites of their respective developers.
- Infect files stored on local disks, removable data devices (where it creates the autorun.inf file), and in public network folders.
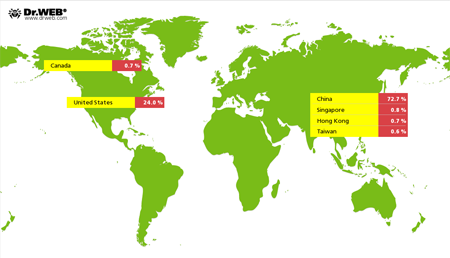
In comparison with April 2015, cybercriminals intensified their attacks on Internet resources with the use of Linux.BackDoor.Gates.5. In May, the number of attacked IP addresses increased by more than 65.5 per cent and was estimated 5,498. Cybercriminals also changed the focus of their attacks. Thus, China became again the country leading in the number of compromised resources, while the United States were ranked second.
Encryption ransomware
The number of requests for decryption received by the Doctor Web technical support service
| April 2015 | May 2015 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| 1,359 | 1,200 | - 11.6% |
The most common ransomware programs in May 2015
- BAT.Encoder
- Trojan.Encoder.858
- Trojan.Encoder.567
- Trojan.Encoder.263
- Trojan.Encoder.741
Dr.Web Security Space 10.0 for Windows
protects against encryption ransomware
This feature is not available in Dr.Web Anti-virus for Windows
| Preventive Protection | Data Loss Prevention |
|---|---|
 |  |
Threats to Linux
In May 2015, Doctor Web security researchers examined a number of malicious programs that can infect computers with the Linux operating system. One of them was created by the Chinese hacker group called ChinaZ. The malware was named Linux.Kluh.1. Its main purpose is to infect routers running Linux. Similar to other programs written by ChinaZ, Linux.Kluh.1 serves the purpose of launching the following DDoS attacks: HTTP Flood (Linux.Kluh.1 can disguise itself as a Baidu crawler if a corresponding command is received from the command and control server), Spoofed SYN Flood, SYN Flood, and other DDoS attacks executed by sending mass requests to DNS servers. Among particular features of this Trojan one can mention the address of the Internet resource with the malware’s command and control server.
Another dangerous program targeting Linux acquired the name of Linux.Iframe.4. This is a malicious plug-in for the Apache web server that injects Iframe into web pages browsed by users redirecting the victim to the web page run by cybercriminals. To avoid false triggering, cybercriminals implemented into the Trojan’s architecture a function to check for the UserAgent parameter. This feature identifies the browser version and the victim’s IP.
Signatures of all malicious programs targeting Linux and detected in May have been added to Dr.Web virus databases for Linux.
Dangerous websites
In May, noticeable increase in activity on the part of cybercriminals who continue tricking Internet users into giving away their money was registered. To attract the potential victim’s attention, cybercriminals send bulk SMS messages with the text informing the recipient that they have won a car. All SMS messages contain a link to a web page that looks like an official Internet resource of some car dealer and provides detailed information regarding this “promotional campaign”.
To collect the main prize, visitors of the fake site are asked to pay 1% of the car’s value in tax via a payment terminal or to purchase the MTPL insurance.
During May 2015, 221,346 URLs of non-recommended sites were added to Dr.Web database.
| April 2015 | May 2015 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 129,199 | + 221,346 | + 71.32% |
Malicious and unwanted programs for Android
During May, a number of new malicious programs for Android were detected. Among the most noticeable events related to malware for Android we can mention
- Attacks using various banking Trojans
- Detection of new SMS Trojans
- Emergence of new Android ransomware
Learn more with Dr.Web
Virus statistics Virus descriptions Virus monthly reviews Laboratory-live
[% END %]