Doctor Web’s May 2023 review of virus activity on mobile devices
June 28, 2023
In May, Doctor Web’s specialists once again discovered malicious apps from the Android.FakeApp family on Google Play. They were being distributed under the guise of games and could load online casino sites. In addition, more trojans that subscribe users to paid services were uncovered.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN MAY
- A decrease in adware trojan activity
- An increase in spyware trojan activity
- A decrease in banking trojan and ransomware activity
- The emergence of other threats on Google Play
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android
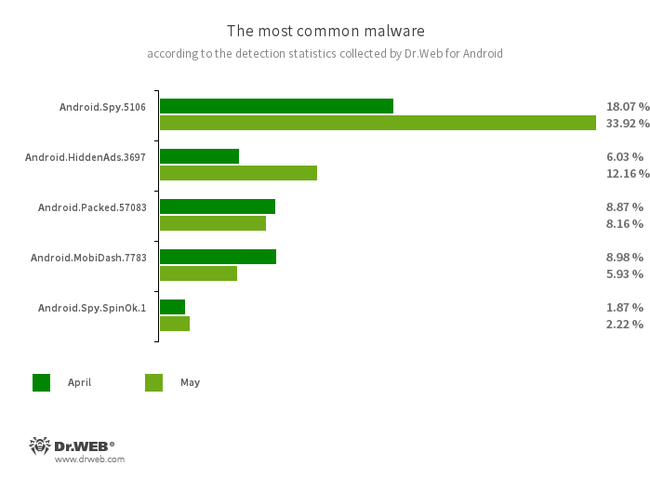
- Android.Spy.5106
- The detection name for a trojan that presents itself as modified versions of unofficial WhatsApp messenger mods. This malicious program can steal the contents of notifications and offer users other apps from unknown sources for installation. And when such a modified messenger is used, it can also display dialog boxes containing remotely configurable content.
- Android.HiddenAds.3697
- A trojan app designed to display intrusive ads. Trojans of this family are often distributed as popular and harmless applications. In some cases, other malware can install them in the system directory. When these infect Android devices, they typically conceal their presence from the user. For example, they “hide” their icons from the home screen menu.
- Android.Packed.57083
- The detection name for malicious applications protected with an ApkProtector software packer. Among them are banking trojans, spyware, and other malicious software.
- Android.MobiDash.7783
- A trojan that displays obnoxious ads. It is a special software module that developers incorporate into applications.
- Android.Spy.SpinOk.1
- The detection name for Android applications with a built-in marketing SDK that is designed to maintain users’ interest in apps with the help of a system of tasks, mini games and alleged prize drawings. This module has hidden spyware functionality. It collects information about files stored on Android devices and is capable of transferring them to malicious actors. It can also substitute and upload clipboard contents to a remote server.
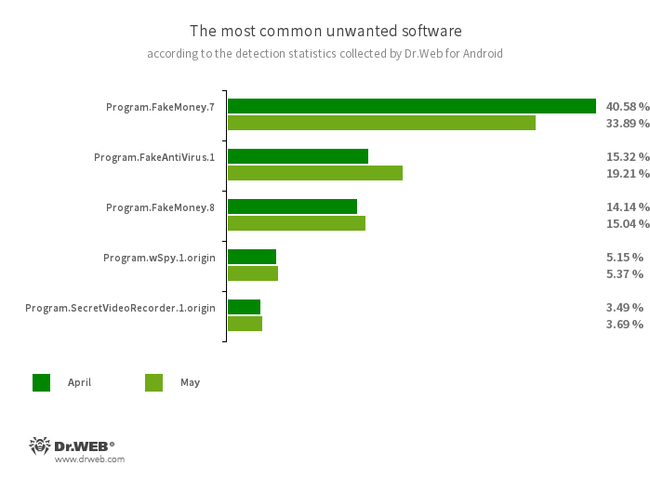
- Program.FakeMoney.7
- Program.FakeMoney.8
- The detection name for Android applications that allegedly allow users to earn money by watching video clips and ads. These apps make it look as if rewards are accruing for completed tasks. To withdraw their “earnings”, users allegedly have to collect a certain sum. But even if they succeed, in reality they cannot get any real payments.
- Program.FakeAntiVirus.1
- The detection name for adware programs that imitate anti-virus software. These apps inform users of nonexistent threats, mislead them, and demand that they purchase the software’s full version.
- Program.wSpy.1.origin
- A commercial spyware app designed to covertly monitor Android device user activity. It allows intruders to read SMS and chats in popular messaging software, listen to the surroundings, track device location and browser history, gain access to the phonebook and contacts, photos and videos, and take screenshots and pictures through a device’s built-in camera. In addition, it has keylogger functionality.
- Program.SecretVideoRecorder.1.origin
- The detection name for various modifications of an application that is designed to record videos and take photos in the background using built-in Android device cameras. It can operate covertly by allowing notifications about ongoing recordings to be disabled. It also allows an app’s icon and name to be replaced with fake ones. This functionality makes this software potentially dangerous.
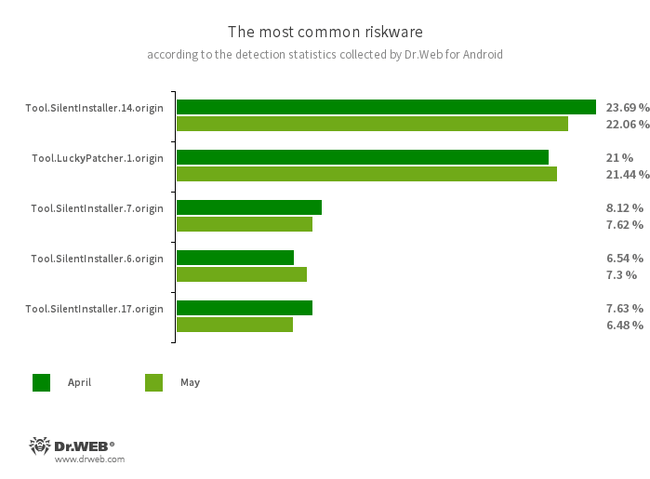
- Tool.SilentInstaller.14.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.7.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.6.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.17.origin
- Riskware platforms that allow applications to launch APK files without installing them. They create a virtual runtime environment that does not affect the main operating system.
- Tool.LuckyPatcher.1.origin
- A tool that allows apps installed on Android devices to be modified (i.e., by creating patches for them) in order to change the logic of their work or to bypass certain restrictions. For instance, users can apply it to disable root access verification in banking software or to obtain unlimited resources in games. To add patches, this utility downloads specially prepared scripts from the Internet, which can be crafted and added to the common database by any third-party. The functionality of such scripts can prove to be malicious; thus, patches made with this tool can pose a potential threat.
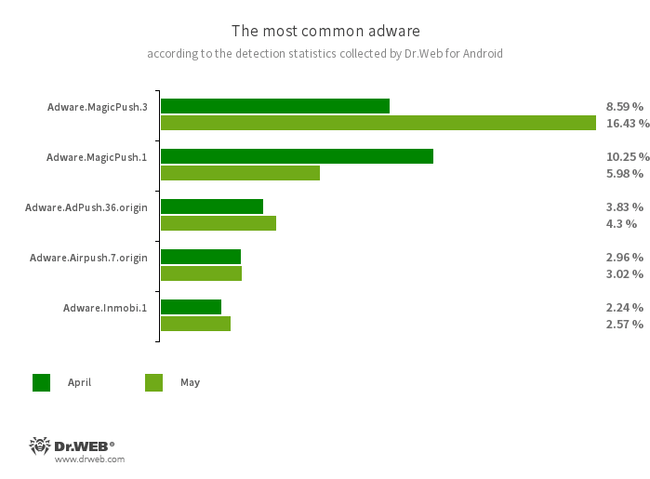
- Adware.MagicPush.3
- Adware.MagicPush.1
- Adware modules embedded into Android applications. They display pop-up banners over the OS user interface when such hosting apps are not in use. These banners contain misleading information. Most often, they inform users about suspicious files that have allegedly been discovered, or they offer to block spam for users or to optimize their device’s power consumption. To do this, they ask users to open the corresponding app containing such an adware module. Upon opening the app, users are shown an ad.
- Adware.AdPush.36.origin
- A member of a family of adware modules that can be built into Android apps. It displays notifications containing ads that mislead users. For example, such notifications can look like messages from the operating system. In addition, this module collects a variety of confidential data and is able to download other apps and initiate their installation.
- Adware.Airpush.7.origin
- A member of a family of adware modules that can be built into Android apps and display various ads. Depending on the modules’ version and modification, these can be notifications containing ads, pop-up windows or banners. Malicious actors often use these modules to distribute malware by offering their potential victims diverse software for installation. Moreover, such modules collect personal information and send it to a remote server.
- Adware.Inmobi.1
- The detection name for some versions of the Inmobi adware SDK, which are capable of making phone calls and adding events entries into an Android device’s calendar.
Threats on Google Play
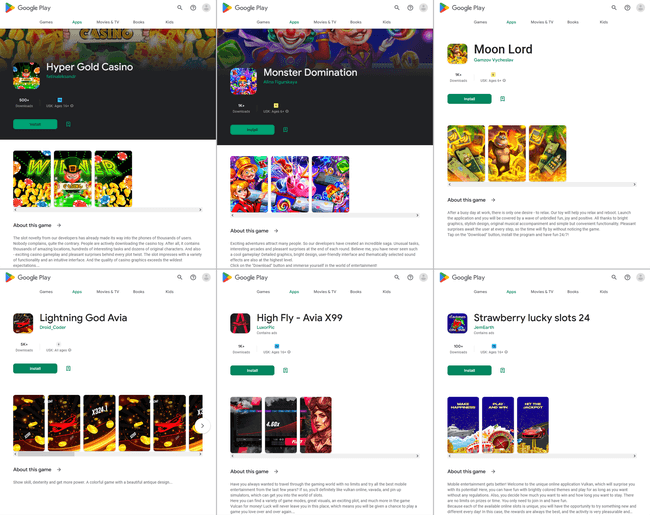
In May, Doctor Web's virus laboratory discovered more malicious apps from the Android.FakeApp family. Among them were Android.FakeApp.1352, Android.FakeApp.1354, Android.FakeApp.1348, Android.FakeApp.1357, Android.FakeApp.1358, Android.FakeApp.1359, and Android.FakeApp.1360. Threat actors distributed them under the guise of various games. However, instead of providing gaming functionality, these fake apps could load online casino websites.
Examples of how one of these trojan applications operates as a game and also loads an online casino site:
Moreover, trojans subscribing victims to paid services were also spotted on Google Play. Android.Harly.66, hidden in the Screen Desktop Pet interactive game with animated characters, was one of them. Others were distributed as a metal detector app called Stud Finder, a picture-searching tool called Picture Search, and a sticker collection app for the WhatsApp messenger going by the name of Relaxing Stickers. In accordance with Dr.Web anti-virus classification, they were dubbed Android.Joker.2117, Android.Joker.2118, and Android.Joker.2119 respectively.
To protect your Android device from malware and unwanted programs, we recommend installing Dr.Web anti-virus products for Android.

Your Android needs protection.
Use Dr.Web
- The first Russian anti-virus for Android
- Over 140 million downloads—just from Google Play
- Available free of charge for users of Dr.Web home products