Doctor Web’s February 2023 virus activity review
April 6, 2023
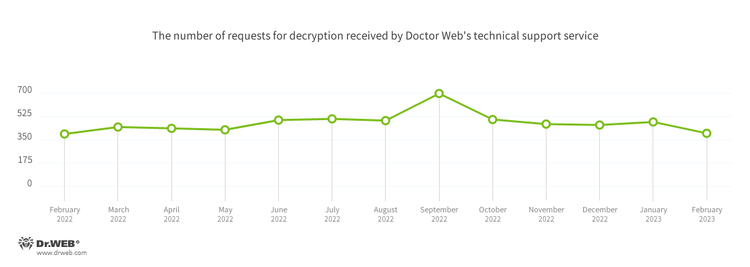
The number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans decreased by 17.63%, compared to the previous month. Most often victims of these encoder trojans were targeted by Trojan.Encoder.3953, Trojan.Encoder.26996, and Trojan.Encoder.35534.
During February, Doctor Web’s specialists discovered dozens of new malicious apps on Google Play. Among them were many fake apps capable of loading fraudulent and unwanted sites, as well as trojans that subscribed Android device users to paid services.
Principal trends in February
- An increase in the total number of detected threats
- A decrease in the number of user requests to decrypt files damaged by encoder trojans
- The discovery of many new malicious apps on Google Play
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
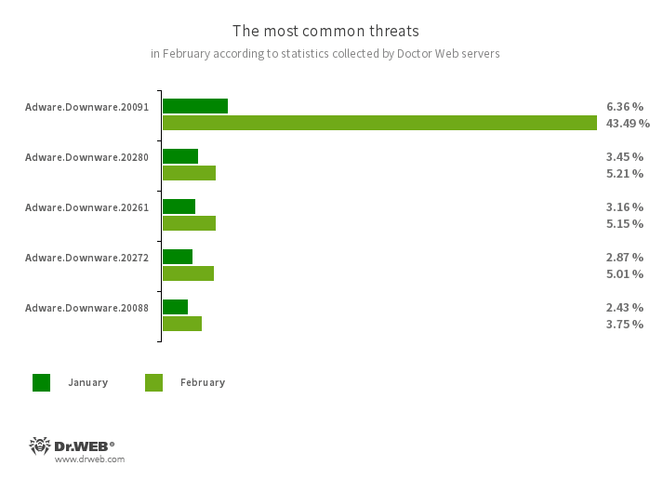
The most common threats of the month:
- Adware.Downware.20091
- Adware.Downware.20280
- Adware.Downware.20261
- Adware.Downware.20272
- Adware.Downware.20088
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirated software.
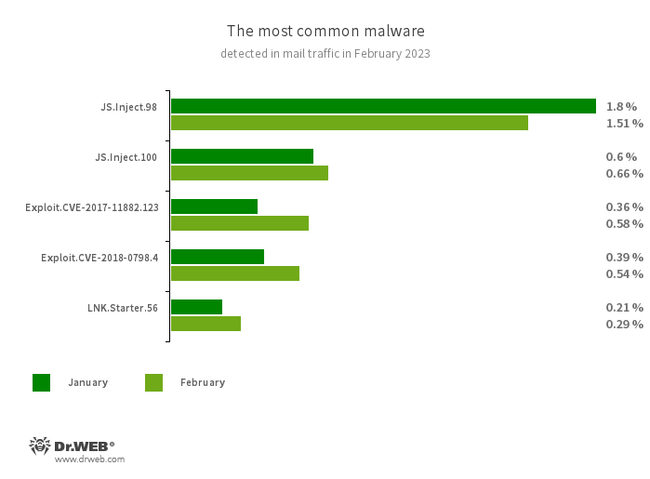
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts that inject a malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- Exploit.CVE-2017-11882.123
- Exploit.CVE-2018-0798.4
- Exploits designed to take advantage of Microsoft Office software vulnerabilities and allow an attacker to run arbitrary code.
- LNK.Starter.56
- The detection name for a shortcut that is crafted in a specific way. This shortcut is distributed through removable media, like USB flash drives. To mislead users and cover up its operation, it has a default icon of a disk. When launched, it executes malicious VBS scripts from a hidden directory located on the same drive as the shortcut itself.
Encryption ransomware
In February, the number of requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans decreased by 17.63%, compared to January.
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 23.62%
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 21.26%
- Trojan.Encoder.35534 — 5.51%
- Trojan.Encoder.34027 — 2.36%
- Trojan.Encoder.30356 — 1.97%
Dangerous websites
In February, Doctor Web’s Internet analysts continued detecting the emergence of fraudulent websites. Among them were other online resources that allegedly allowed visitors to make money through investments. On such sites, users were asked to take a poll, and then to provide their personal data for account registration. This information, if entered, ended up in the scammers' hands and later could be used in various attacks. In addition, malicious actors continued trying to lure potential victims onto websites that offered allegedly free lottery tickets. Every visitor of such a web resource was a “winner”. To receive their non-existent prize, users had to pay a “commission” or pay for the “delivery” of their money.
The screenshots above demonstrate examples of pages of one of these fraudulent websites. A visitor has allegedly won 224.138 rubles in an online lottery draw. In order to “receive” their prize, the victim is asked to provide their bankcard information and pay a “commission” of 1,176 rubles.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
According to detection statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android, in February, users once again most often encountered trojans from the Android.HiddenAds family. At the same time, banking trojans, ransomware, and spyware malware posed less of a threat. With that, during the month, Doctor Web’s specialists discovered dozens of new malicious apps on Google Play. Among them were programs from the Android.FakeApp family, which were capable of loading fraudulent and other unwanted websites, and also trojan applications from the Android.Joker and Android.Subscription families, which subscribe users to paid services.
The following February events involving mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- An increase in the activity of ad-displaying trojans.
- A decrease in the activity of banking trojans and ransomware.
- The discovery of numerous threats on Google Play.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.
[% END %]