Doctor Web’s December 2022 virus activity review
January 27, 2023
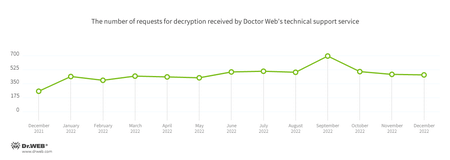
The number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders decreased by 1.5%, compared to November. Most often, victims were targeted by Trojan.Encoder.3953, Trojan.Encoder.26996, and Trojan.Encoder.34027.
During December, Doctor Web’s malware analysts again discovered many new threats on Google Play. Among them were both trojan and unwanted applications.
Principal trends in December
- An increase in the total number of detected threats
- A decrease in the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans
- Numerous threats discovered on Google Play
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
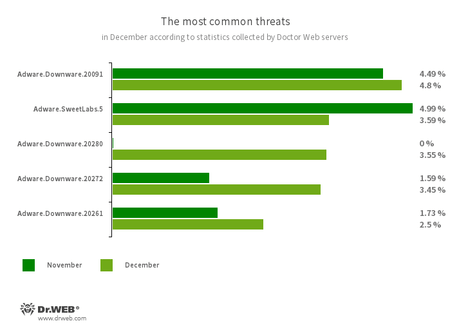
The most common threats of the month:
- Adware.Downware.20091
- Adware.Downware.20261
- Adware.Downware.20272
- Adware.Downware.20280
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirated software.
- Adware.SweetLabs.5
- An alternative app store and an add-on for Windows GUI (graphical user interface) from the creators of “OpenCandy” adware.
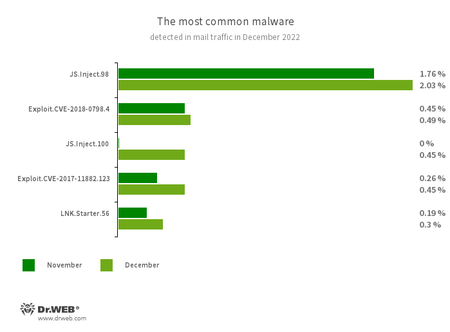
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts that inject a malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- Exploit.CVE-2018-0798.4
- Exploit.CVE-2017-11882.123
- Exploits designed to take advantage of Microsoft Office software vulnerabilities and allow an attacker to run arbitrary code.
- LNK.Starter.56
- The detection name for a shortcut that is crafted in a specific way. This shortcut is distributed through removable media, like USB flash drives. To mislead users and cover up its operation, it has a default icon of a disk. When launched, it executes malicious VBS scripts from a hidden directory located on the same drive as the shortcut itself.
Encryption ransomware
In December 2022, the number of requests to decrypt files damaged by encoder trojans decreased by 1.5%, compared to November.
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 22.98%
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 18.12%
- Trojan.Encoder.34027 — 6.80%
- Trojan.Encoder.30356 — 1.94%
- Trojan.Encoder.35209 — 1.94%
Dangerous websites
In December 2022 Doctor Web’s Internet analysts again observed an increased number of websites disguised as the online resources of large Russian oil and natural gas companies. On those sites, potential victims were offered the chance to make a profitable investment in certain projects.
The screenshot above depicts an example of one such site. Fraudsters offer users the opportunity to trade in natural gas, while the webpage contains fake counters for the total number of visitors and the number of membership positions left to register. The second counter shows that almost no positions are left. This method is used to push victims into making an impulse purchase—they agree to the offer without planning in advance and under the influence of their emotions. To “begin” trading, site visitors are required to provide personal information.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
According to detection statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android, the last month of 2022 saw an increase in adware trojan and spyware activity. With that, during December, many new threats were once again discovered on Google Play. Among them were dangerous trojans from the Android.Joker family that subscribed victims to paid services, fake apps from Android.FakeApp family that are used in various fraudulent schemes, and unwanted software.
The following December events involving mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- An increase in the activity of adware trojans and spyware apps;
- The emergence of other threats on Google Play.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.
[% END %]