Doctor Web’s October 2022 virus activity review
December 2, 2022
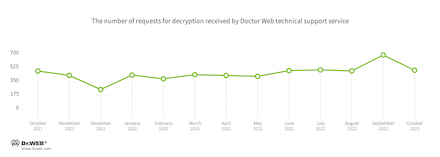
The number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders decreased by 28.06% in October. After a brief activity decrease in September, Trojan.Encoder.26996 once again became the most common encoder, with a share of 27.05 of all incidents recorded. At the same time, the leader of the previous month, Trojan.Encoder.3953, dropped down to second place with a share of 25.46%.
During October, Doctor Web’s malware analysts discovered many new threats on Google Play. Among them were trojan apps, adware, and unwanted software.
Principal trends in October
- An increase in the total number of detected threats
- A decrease in the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans
- The emergence of new threats on Google Play
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
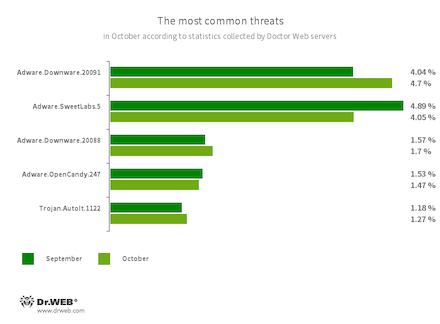
The most common threats of the month:
- Adware.Downware.20091
- Adware.Downware.20088
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirated software.
- Adware.SweetLabs.5
- An alternative app store and an add-on for Windows GUI (graphical user interface) from the creators of “OpenCandy” adware.
- Adware.OpenCandy.247
- A family of applications that install other software on a system, including other adware.
- Trojan.AutoIt.1122
- The detection name for a packed version of the Trojan.AutoIt.289 malicious app written in the AutoIt scripting language. This trojan is distributed as part of a group of several malicious applications, including a miner, a backdoor, and a self-propagating module. Trojan.AutoIt.289 performs various malicious actions that make it difficult for the main payload to be detected.
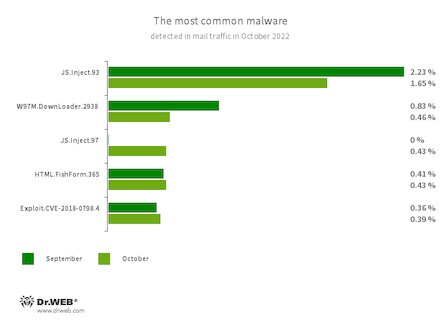
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts that inject a malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents. They can also download other malicious programs to a compromised computer.
- HTML.FishForm.365
- A webpage spread via phishing emails. It is a bogus authorization page that mimics well-known websites. The credentials a user enters on the page are sent to the attacker.
- Exploit.CVE-2018-0798.4
- An exploit designed to take advantage of a Microsoft Office software vulnerability and allow an attacker to run arbitrary code.
Encryption ransomware
In October, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders decreased by 28.06% compared to September.
- Trojan.Encoder.26996—27.05%
- Trojan.Encoder.3953—25.99%
- Trojan.Encoder.567—2.65%
- Trojan.Encoder.30356—1.33%
- Trojan.Encoder.34790—1.33%
Dangerous websites
In October, we observed an increase in the number of fake job-search websites. On such sites, fraudsters, disguised as representatives of large Russian companies, offered users employment with attractive conditions. This included simple duties, flexible working hours, and high wages. For example, fraudsters created fake job vacancies for the position of a “remote order-processing employee”. Candidates were required to register an account, after which they allegedly could immediately begin working. However, to withdraw their “earned” money, they were requested to “activate” their account by paying a fee.
To lure as many users as possible into a trap, scammers sent out phishing emails with links to such websites.
The screenshot above shows an example of a fraudulent site with a fake job offer. Scammers use the name and logo of the real company on whose behalf they are proposing the position. In addition, this webpage contains fake comments which are meant to assure potential victims that this job offering is secure and legitimate.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In October, we observed a slight decrease in the activity of advertising trojans compared to the previous month. Nonetheless, they remain one of the most common threats that Android users encounter. Moreover, there was noticeable activity of banking trojans and applications that can be used for cyber espionage.
Over the past month, Doctor Web’s malware analysts found many new threats on Google Play. These include fake programs from the Android.FakeApp family that are used in various fraudulent schemes. Adware and unwanted software were also among them.
The following October events involving mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- The activity of ads-displaying trojans;
- The emergence of new threats on Google Play.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.
[% END %]