Doctor Web’s September 2022 virus activity review
October 31, 2022
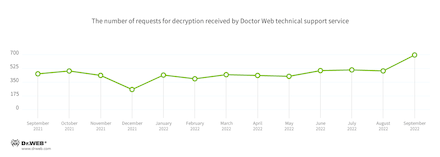
The number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders increased by 41.26% last month. The most common encoder in September was Trojan.Encoder.3953 with a share of 25.83% of all incidents recorded. At the same time, Trojan.Encoder.26996, which was the leading encoder for many months, dropped down to second place.
Doctor Web’s malware analysts uncovered new threats on the Google Play catalog. Among them were various fake apps from the Android.FakeApp family, which are being used by cybercriminals in various scam schemes, and adware.
Principal trends in September
- A decrease in the total number of detected threats
- A significant increase in the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans
- The active distribution of malicious PDF documents via emails
- The emergence of new threats on Google Play
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
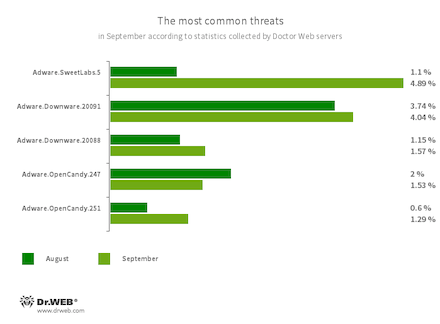
The most common threats of the month:
- Adware.SweetLabs.5
- An alternative app store and an add-on for Windows GUI (graphical user interface) from the creators of “OpenCandy” adware.
- Adware.Downware.20091
- Adware.Downware.20088
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirated software.
- Adware.OpenCandy.247
- Adware.OpenCandy.251
- A family of applications that install other software on a system, including other adware.
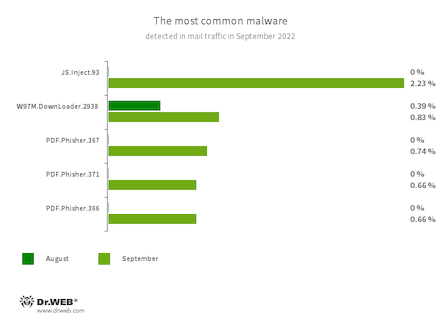
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts that inject a malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents. They can also download other malicious programs to a compromised computer.
- PDF.Fisher.367
- PDF.Fisher.371
- PDF.Fisher.366
- PDF documents used in phishing newsletters.
Encryption ransomware
In September, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders increased by 41.26% compared to August.
- Trojan.Encoder.3953—25.83%
- Trojan.Encoder.26996—23.94%
- Trojan.Encoder.11539—2.61%
- Trojan.Encoder.567—2.37%
- Trojan.Encoder.35209—1.90%
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
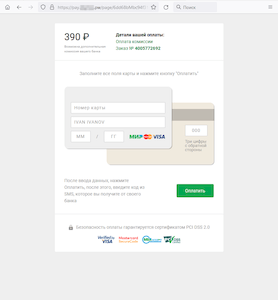
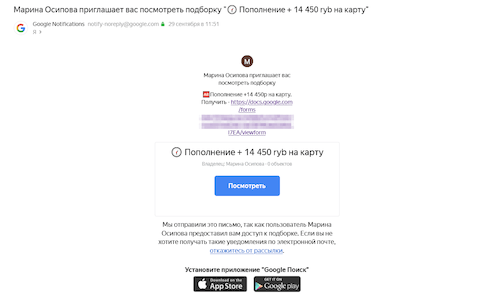
In September 2022, Doctor Web’s Internet analysts continued registering active spam campaigns with emails containing links to fraudulent websites. Among them were sites on which Russian users could allegedly obtain free lottery tickets. In reality, there were no tickets, and cybercriminals misled potential victims by simulating prize draws. With that, every visitor was informed that they were the winner. To “receive” the prize, users were asked to provide their bank card details and pay a “commission” for the money transfer.
Below are examples of two such websites. On one of them, a lottery game is simulated, and the user receives a message about the win. On the other, a commission is allegedly paid for “transferring” the prize to the victim’s bank card.
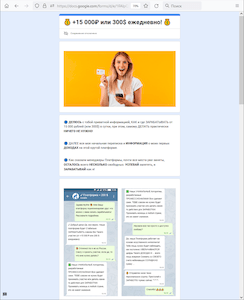
On other websites, users were invited to join various investing platforms that were allegedly affiliated with famous financial and gas and oil companies. To do this, they had to take a survey and then register an account, providing their first and last name, email address, and mobile phone number. Upon completing the “registration”, victims of such a scam scheme are then typically redirected to various sites, including unwanted ones. Moreover, cybercriminals can later use the provided data to organize phishing attacks or make fraudulent phone calls.
An example of a phishing email declaring an opportunity to get free money on a bank card. For this, the potential victim is asked to follow the link provided in the email. When the user clicks on this link, a fraudulent site is loaded. This site contains information on “easy income” and an advertisement for another scam website that is allegedly related to a large Russian bank.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
Last month, we observed the increased activity of banking trojans that target Android device users. With that, there was a slight decrease in the activity of malicious apps designed to display unwanted ads. At the same time, we noted that the activity of the Android.Spy.4498 trojan, which is designed to steal information from other apps’ notifications, continued to decrease.
Over the course of September, Doctor Web’s virus laboratory specialists discovered new threats on Google Play. Among them were other trojans from the Android.FakeApp family, which are being used by cybercriminals in various fraudulent schemes, and applications containing unwanted adware components.
The following September events involving mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- An increase in the activity of banking trojans;
- A minor decrease in the activity of adware trojans;
- The continued decline in the activity of the Android.Spy.4498 spying trojan;
- The emergence of new threats on Google Play.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.