Doctor Web’s March 2021 virus activity review
April 13, 2021
In March, analysis of Dr.Web’s statistics revealed a 16.72% increase in the total number of threats compared to the previous month. The number of unique threats also increased by 19.49%. Adware and unwanted software still occupy the top spot for detected threats. Various malware that includes obfuscated trojans, malicious scripts, and programs exploiting vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office utilities were the most frequently detected threats in email traffic.
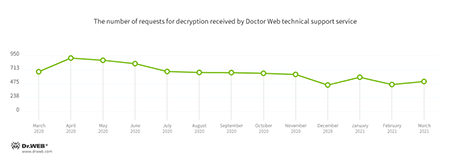
In March, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders increased by 11.33% compared with February. Trojan.Encoder.567 was the most active, accounting for 23.76% of all incidents.
Principal trends in March
- Growth in malware spreading activity
- Adware remain among the most active threats
- An increase in the number of requests to decrypt files affected by encoders
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
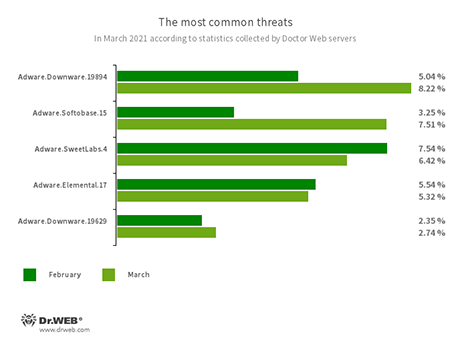
The most common threats in March:
- Adware.Downware.19894
- Adware.Downware.19629
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirate software.
- Adware.Softobase.15
- Installation adware that spreads outdated software and changes browser settings.
- Adware.SweetLabs.4
- An alternative app store and add-on for Windows GUI from the creators of Adware.Opencandy.
- Adware.Elemental.17
- Adware that spreads through file sharing services as a result of link spoofing. Instead of normal files, victims receive applications that display advertisements and install unwanted software.
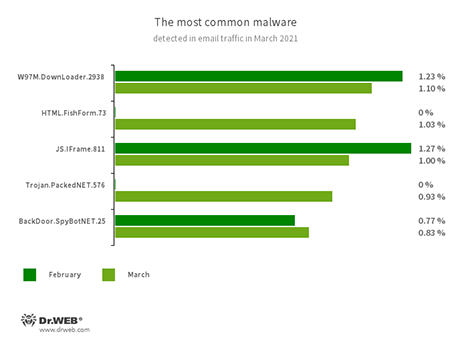
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploits vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents and can download other malicious programs onto a compromised computer.
- HTML.FishForm.73
- The web page spread via phishing emails. It is a bogus authorization page that mimics well-known websites. The credentials a user enters on the page is sent to the attacker.
- JS.IFrame.811
- A malicious script embedded into web pages. The script’s execution allows one to redirect visitors to the unwanted and dangerous websites, display annoying ads in the browser, or track user actions.
- Trojan.PackedNET.576
- Packed malware written in VB.NET.
- BackDoor.SpyBotNET.25
- A backdoor written in VB.NET and designed to operate with a file system (to copy, create, delete catalogs, etc.), terminate processes, and take screenshots.
Encryption ransomware
In March, Doctor Web’s virus laboratory registered 11.33% more requests to decode files encoded by trojan ransomware than in February.
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 23.76%
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 17.16%
- Trojan.Encoder.29750 — 3.63%
- Trojan.Encoder.30356 — 1.65%
- Trojan.Encoder.11464 — 1.32%
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
During March 2021, Doctor Web Internet analysts added numerous fraudulent and malicious resources to the Dr.Web database of non-recommended websites. In March, the fraudsters continued to actively distribute websites with fake lotteries and giveaways. To receive an apparent prize, the victim was most likely prompted to pay a commission under various pretexts.
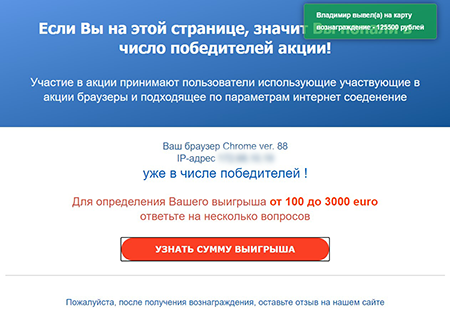
This is a snapshot of the fraudulent website with a fake giveaway. It displays the visitor's IP address along with the browser used and announces the lottery win. It then invites the user to find out the winning amount by answering several questions.
All these websites had similar looks: sections with fake reviews, pop-up windows with the "winners", a bogus chat with technical support, etc. Using common methods of social engineering, fraudsters pushed users into disclosing bank card data and paying a commission.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In March, malware that is able to download and execute arbitrary code, as well as trojans that showed ads were again among the most common mobile threats. In addition, users often faced unwanted advertising software.
Various modifications of Android.Joker were again distributed through the Google Play catalog. Their main function is to subscribe victims to paid mobile services. Doctor Web’s virus analysts also discovered other fraudulent trojans from Android.FakeApp family.
The following March events related to mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- The emergence of new malware in the Google Play catalog
- The increased activity of trojans that subscribe users to paid services
- The active use of malicious applications in various fraud schemes
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.