Doctor Web’s January 2021 review of virus activity on mobile devices
February 24, 2021
In January, Dr.Web anti-virus products for Android detected 11.32% less threats on protected devices compared to December, 2020. The number of observed malware decreased by 11.5% and adware by 15.93%. At the same time, the number of detected unwanted apps and riskware increased by 11.66% and 7.26% respectively. According to gathered statistics, the most common threats for users were adware trojans and malware designed to download other software and execute arbitrary code.
Throughout January, Doctor Web malware analysts uncovered a large number of threats on Google Play. Numerous modifications of the Adware.NewDich adware modules built into various apps were among them. Moreover, new trojans from the Android.FakeApp family designed to load fraudulent websites, as well as malicious apps from the Android.Joker family subscribing users to premium mobile services and executing arbitrary code were also discovered.
With that, our specialists have observed new attacks involving banking trojans. One of them was found in a fake banking app available on Google Play while others were spread through malicious websites created by cybercriminals.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN JANUARY
- A decreased number of threats detected on Android devices
- The discovery of a large number of malware and unwanted apps on Google Play
Threat of the month
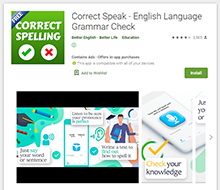
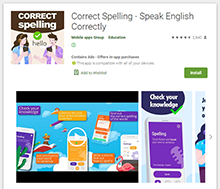
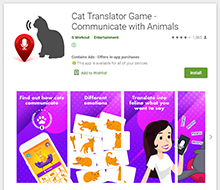
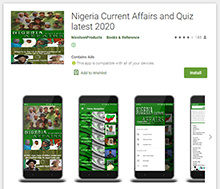
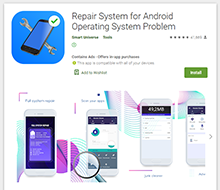
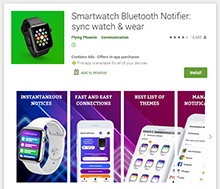
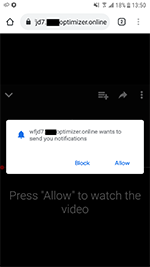
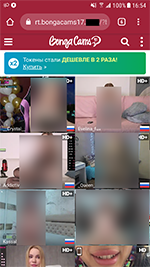
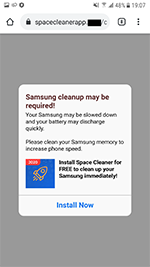
At the beginning of January, Doctor Web malware analysts found a number of apps with built-in Adware.NewDich adware modules that load various websites upon C&C server command. For instance, they can load both harmless sites and sites that contain ads, as well as bogus or fraudulent sites used for phishing. Because they are loaded when users are not interacting with apps containing Adware.NewDich modules, it is troublesome for Android device owners to figure out why their gadgets are behaving strangely.
Examples of software that were found to contain these adware modules are shown below:
Examples of websites they load:
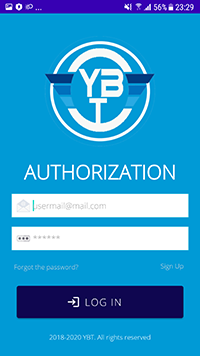
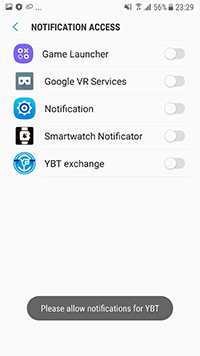
Web pages of various referral programs that redirect users to the apps hosted on Google Play are often loaded by Adware.NewDich modules. The app called “YBT Exchange”, supposedly designed to work with one of the crypto exchanges was one of them. Doctor Web malware analysts, however, found that this software is nothing but a new banking trojan, which was added to the virus base as Android.Banker.3684. Its functionality included the hijacking of logins, passwords and confirmation codes. It was also able to intercept contents of incoming notifications, for which the trojan requested specific system permissions. After our report to Google, this banker was removed from the Android app store.
Doctor Web malware analysts found that at least 21 apps had these adware modules built into them. The conducted research indicated that owners of these apps and the developers of Adware.NewDich are likely directly related. Soon after this adware network attracted significant attention of the IT community and security specialists, its administrators panicked and began rolling out software updates, trying to implement mechanisms to avoid the anti-virus software from detecting this adware or simply removing the modules from the apps. One of the affected programs was later removed from Google Play completely. With that, nothing prevents the actors behind Adware.NewDich from updating the remaining software at any time and reintroducing modules, which our specialists have already observed several times.
The list of the apps containing the Adware.NewDich modules:
| Name of the packet | Presence of the Adware.NewDich module | The app was removed from Google Play |
|---|---|---|
| com.qrcodescanner.barcodescanner | Was present in last relevant 1.75 version | Yes |
| com.speak.better.correctspelling | Present in relevant 679.0 version | No |
| com.correct.spelling.learn.english | Present in relevant 50.0 version | No |
| com.bluetooth.autoconnect.anybtdevices | Present in relevant 2.5 version | No |
| com.bluetooth.share.app | Present in relevant 1.8 version | No |
| org.strong.booster.cleaner.fixer | Absent in relevant 5.9 version | No |
| com.smartwatch.bluetooth.sync.notifications | Absent in relevant 85.0 version | No |
| com.blogspot.bidatop.nigeriacurrentaffairs2018 | Present in relevant 3.2 version | No |
| com.theantivirus.cleanerandbooster | Absent in relevant 9.3 version | Нет |
| com.clean.booster.optimizer | Absent in relevant 9.1 version | No |
| flashlight.free.light.bright.torch | Absent in relevant 66.0 version | No |
| com.meow.animal.translator | Absent in relevant 1.9 version | No |
| com.gogamegone.superfileexplorer | Absent in relevant 2.0 version | No |
| com.super.battery.full.alarm | Absent in relevant 2.2 version | No |
| com.apps.best.notepad.writing | Absent in relevant 7.7 version | No |
| ksmart.watch.connecting | Absent in relevant 32.0 version | No |
| com.average.heart.rate | Absent in relevant 7.0 version | No |
| com.apps.best.alam.clocks | Absent in relevant 4.7 version | No |
| com.booster.game.accelerator.top | Absent in relevant 2.1 version | No |
| org.booster.accelerator.optimizer.colorful | Absent in relevant 61.0 version | No |
| com.color.game.booster | Absent in relevant 2.1 version | No |
Features of Adware.NewDich:
- It is built into full-featured software to hide from users and not arouse any suspicion.
- The activity develops with a delay (up to several days) after the hosting applications are installed and launched.
- Promoted websites loading is performed when the apps containing these modules are closed and users are not interacting with or using them for some time.
- The malicious actors constantly monitor if anti-virus software detects the modules and promptly make changes to them to release new versions to counter the detection.
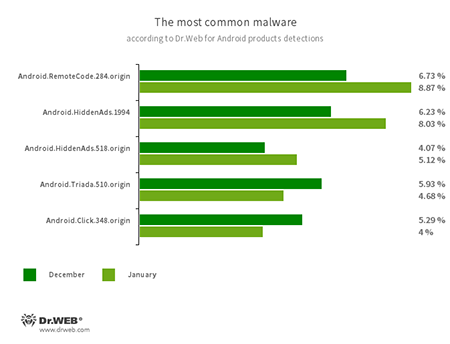
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android
- Android.RemoteCode.284.origin
- A malicious application that downloads and executes arbitrary code. Depending on its modification, it can load various websites, open web links, click on advertising banners, subscribe users to premium services and perform other actions.
- Android.HiddenAds.1994
- Android.HiddenAds.518.origin
- Trojans designed to display obnoxious ads and distributed as popular applications. In some cases, they can be installed in the system directory by other malware.
- Android.Triada.510.origin
- A multifunctional trojan performing various malicious actions. This malware belongs to the trojan family that infects other apps’ processes. Some modifications of this family were found in the firmware of Android devices, which attackers implanted during manufacturing. Some of them can also exploit various vulnerabilities to gain access to the protected system files and folders.
- Android.Click.348.origin
- A malicious application that loads websites, clicks on banner ads, and follows links. It can be distributed as harmless programs without arousing suspicion among users.
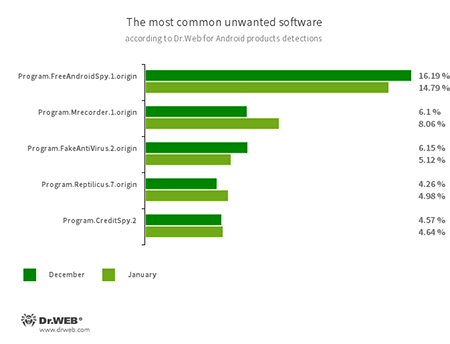
- Program.FreeAndroidSpy.1.origin
- Program.NeoSpy.1.origin
- Program.Mrecorder.1.origin
- Program.Reptilicus.7.origin
- Software that monitors Android user activity and may serve as a tool for cyber espionage. These apps can track device locations, collect information from SMS and social media messages, copy documents, photo and video, spy on phone calls, etc.
- Program.FakeAntiVirus.2.origin
- The detection name for adware programs that imitate anti-virus software. These apps inform users of non-existing threats, mislead them and demand they purchase the full version of the software.
- Program.CreditSpy.2
- The detection name for programs designed to assign credit ratings to users based on their personal data. These applications upload SMS, contact information from phonebooks, call history and other information to the remote server.
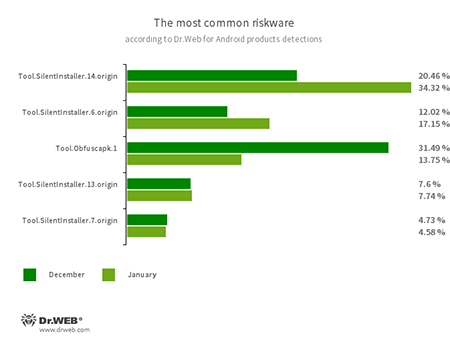
- Tool.SilentInstaller.6.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.7.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.13.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.14.origin
- Riskware platforms that allow applications to launch APK files without installation. They create a virtual runtime environment that does not affect the main operating system.
- Tool.Obfuscapk.1
- The detection name for applications protected by the Obfuscapk obfuscation tool. This tool is used to automatically modify and scramble Android apps’ source code to make reverse engineering more difficult. Cybercriminals use the tool to protect malicious applications from being detected by anti-virus programs.
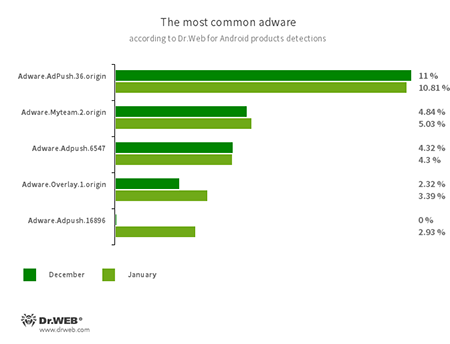
Program modules incorporated into Android applications and designed to display obnoxious ads on Android devices. Depending on their family and modifications, they can display full screen ads and block other apps’ windows, show various notifications, create shortcuts and load websites.
- Adware.Adpush.36.origin
- Adware.Adpush.6547
- Adware.Adpush.16896
- Adware.Myteam.2.origin
- Adware.Overlay.1.origin
Threats on Google Play
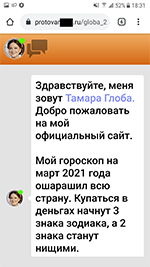
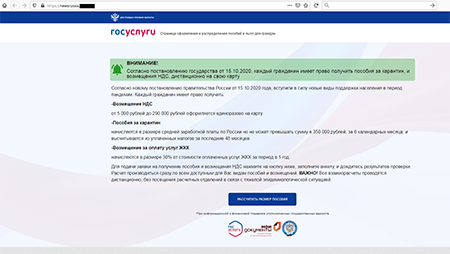
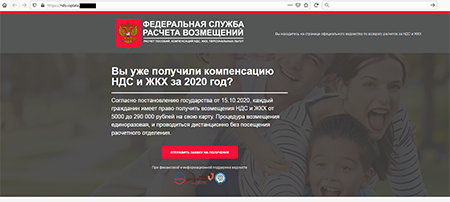
In addition to apps with built-in Adware.NewDich adware modules, Doctor Web specialists discovered a large number of trojans from the Android.FakeApp family, which were spread as reference software and handbooks with information about tax refunds and the availability of welfare payouts and other social compensations. There were also other modifications of these trojans disguised, for instance, as programs designed to search information about lotteries and receiving gifts from popular bloggers.
Similar to other trojans of this type, which were discovered earlier, current modifications loaded fraudulent websites where potential victims were informed about the supposed payouts from the government. To “receive” the money, users were asked to provide their personal information, as well as to pay for the lawyers’ time, document preparation, and tax or fees for transferring the money to the bank account. In fact, victims didn’t receive any funds, but cybercriminals did steal their confidential information and money.
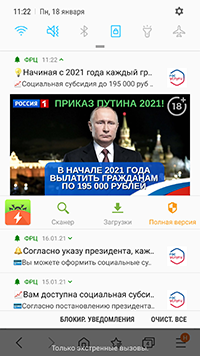
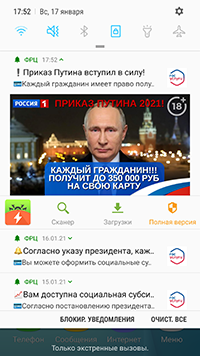
In addition, some modifications of these malicious apps periodically displayed notifications where users were also informed about available “payouts” and “compensations”. In this way, malicious actors tried to attract additional attention from potential victims so they would visit the fraudulent websites more often.
Examples of websites various modifications of the Android.FakeApp trojans load:
The examples of fraudulent notifications with the information about “payouts” and “compensations” displayed by these malicious apps:
Moreover, other multifunctional trojans from the Android.Joker family were also found—they were dubbed Android.Joker.496, Android.Joker.534, and Android.Joker.535. These trojans were spread under the guise of harmless apps, such as translation software and multimedia editing software designed to create gif animations. Their real functionality, however, was to download and execute arbitrary code, as well as to intercept the contents of incoming notifications and subscribe users to premium services.
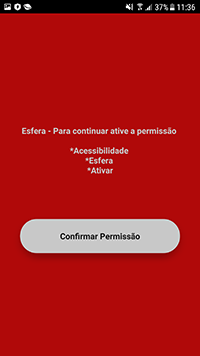
A new banking trojan dubbed Android.Banker.3679 was also among the uncovered threats. It was spread as an application designed to work with Santander bank’s Esfera rebate and bonus program for Brazilian users. Android.Banker.3679’s main functions were phishing and confidential data stealing, while its primary target was the Santander Empresas banking application.
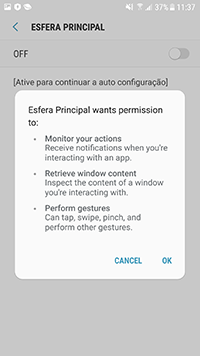
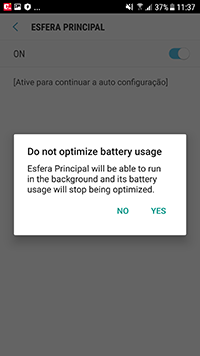
Upon installation and launch, the trojan requested access to the Accessibility Service function of the Android OS—allegedly to continue working with the app. In fact, it needed the requested functionality to automatically perform malicious actions. If a victim agreed to provide the necessary system privileges, the banker received control over the infected device and could click on various menu elements, buttons, read the contents of other apps’ windows, etc.
Banking trojans
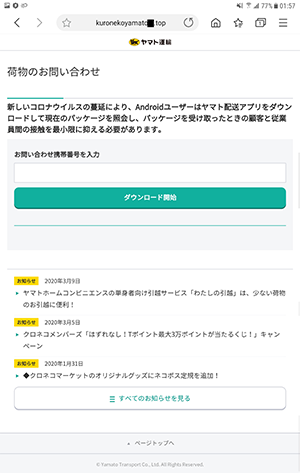
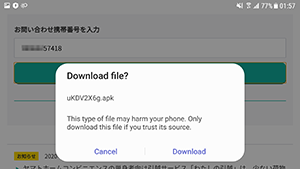
Alongside banking trojans found on Google Play, Android device owners were targeted by bankers that spread through the malicious websites. For example, Doctor Web specialists observed other attacks on Japanese users where trojans from various banking malware families were involved. The Android.BankBot.3954, Android.SmsSpy.833.origin, Android.SmsSpy.10809, and Android.Spy.679.origin trojans were among them. They were downloaded from fake postal and delivery service websites under the guise of updates for Chrome, Play Market and other legitimate software.
To protect your Android device from malware and unwanted programs, we recommend installing Dr.Web for Android.

Your Android needs protection.
Use Dr.Web
- The first Russian anti-virus for Android
- Over 140 million downloads—just from Google Play
- Available free of charge for users of Dr.Web home products