Doctor Web’s overview of malware detected on mobile devices in August 2018
August 31, 2018
In August 2018, Doctor Web specialists detected an Android Trojan capable of changing e-wallet numbers on the clipboard. In addition, security researchers detected numerous Trojans on Google Play. Cybercriminals used them in different schemes to generate illegal revenue. Also in August, several Android banking Trojans and downloader Trojans were detected on Google Play. The latest downloaded other malicious software to mobile devices. Security researchers also detected a dangerous spying Trojan, which cybercriminals could incorporate into benign programs and distribute under the guise of original applications.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN AUGUST
- Detection of an Android Trojan capable to change e-wallet numbers on the clipboard
- Distribution of Trojan bankers
- Detection of numerous malicious programs on Google Play
- Detection of a dangerous spying Trojan, which cybercriminals could incorporate into any application
Mobile threat of the month
In early August, Doctor Web security researchers detected the Android.Clipper.1.origin Trojan that monitored the clipboard and changed copied the e-wallet numbers of popular payment systems and cryptocurrencies. The malicious program targeted e-wallet numbers from Qiwi, Webmoney, Yandex.Money, Bitcoin, Monero, zCash, DOGE, DASH, Etherium, Blackcoin, and Litecoin. When a user copies the number to the clipboard, the Trojan intercepts it and sends it to a command and control (C&C) server. Android.Clipper.1.origin receives information about the cybercriminals’ e-wallet number, which then replaces the victim’s e-wallet number. Thus, owners of the infected device is at risk of transferring money to cybercriminals’ account. More information about this Trojan can be found in the news article on our website.
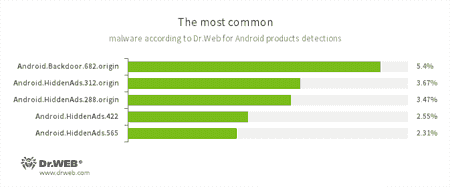
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android
- Android.Backdoor.682.origin
- The Trojan that executes cybercriminals’ commands and helps them control infected mobile devices.
- Android.HiddenAds
- The Trojans, designed to display intrusive advertising. They are distributed under the guise of popular applications by other malicious programs, which in some cases quietly, install themselves in the system catalog.
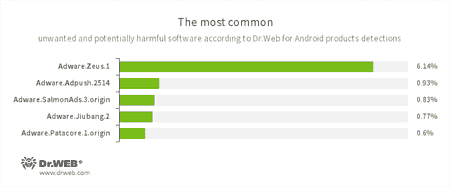
- Adware.Zeus.1
- Adware.Adpush.2514
- Adware.SalmonAds.3.origin
- Adware.Jiubang.2
- Adware.Patacore.1.origin
- Unwanted program modules incorporated into Android applications and designed to display obnoxious ads on mobile devices.
Trojans on Google Play
In August, numerous Trojans were detected on Google Play. During the month, Doctor Web security researchers monitored the distribution of the Android.Click Trojan family on Google Play. Our specialists detected 127 such malicious applications that were spread by cybercriminals under the guise of official bootmaker applications.
Once launched, these Trojans display a website specified by the C&C server to a user. When the Android.Click Trojans were detected, they all displayed bookmakers’ Internet portals. However, at any moment, they can receive a command to load an arbitrary website that can distribute other malicious software or can be used in phishing attacks.
Android.Click.265.origin was another clicker Trojan detected on Google Play in August. Cybercriminals used it to subscribe users to chargeable mobiles services. Cybercriminals distributed this malicious program under the guise of an official application designed to work with the “Eldorado” Internet store.
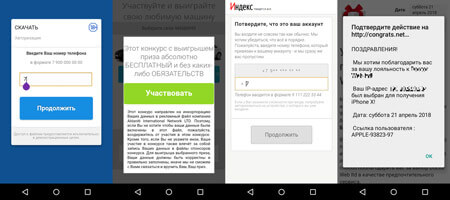
The Android.Click.248.origin Trojan that Doctor Web security researchers came across in April, appeared again on Google Play in August. As before, it was spread under the guise of well-known software. Android.Click.248.origin loads fraudulent websites where a user is invited to download different programs or to receive a reward. To receive a reward or download a program, the potential victim is asked to enter a phone number, which is then used to receive a confirmation code. After entering this code, the user is subscribed to a chargeable service. At that, if an infected device uses a mobile network to connect to the Internet, the user is subscribed to a chargeable service automatically after cybercriminals receive the number.
For more information about these clicker Trojans, refer to the news article on our website.
At the end of August, Doctor Web security researchers detected the Android.FakeApp.110 Trojan on Google Play. Cybercriminals used the Trojan to generate illegal profit. This malicious program loaded a fraudulent website, where a potential victim was invited to take a survey. After answering all questions, the victim was prompted to make an identification payment of 100–200 rubles. Once the payment was made, however, the victim did not receive any reward.
Among the malicious programs detected on Google play in August were new banking Trojans. One of them was given the name Android.Banker.2843. It was distributed under the guise of an official application of a Turkish credit organization. Android.Banker.2843 stole logins and passwords to access users’ bank account information and sent it to cybercriminals.
Another banking Trojan added to the Dr.Web virus database as Android.Banker.2855 was distributed as different service tools. This malicious program extracted from its file resources and launched the Android.Banker.279.origin Trojan. This Trojan stole the bank’s user authentication credentials.
Some Android.Banker.2855 modifications attempted to hide its presence on a mobile device showing fake error message after launching and deleting their shortcuts on the main screen.
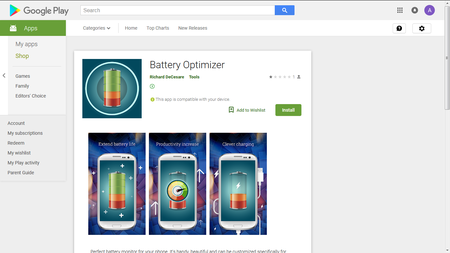
Another Android banking Trojan named Android.BankBot.325.origin was downloaded to infected devices by the Android.DownLoader.772.origin Trojan. Cybercriminals distributed this downloader on Google Play under the guise of useful applications, for example, a battery operation optimizer.
In addition, Doctor Web security researchers detected Android.DownLoader.768.origin on Google Play. This downloader was distributed under the guise of a Shell corporation application. Android.DownLoader.768.origin downloaded various banking Trojans to mobile devices.
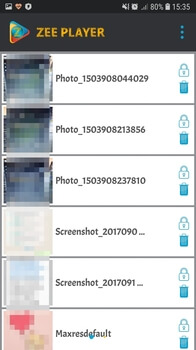
Also in August, the Android.DownLoader.784.origin downloader Trojan was detected on Google Play and added to the Dr.Web virus database. It was embedded into an application called “Zee Player.” This application allowed the Trojan to hide photos and videos stored in mobile devices’ memory.
Android.DownLoader.784.origin downloaded the Android.Spy.409.origin Trojan, which can be used for cyber spying by criminals.
Android spyware
In August, the Dr.Web virus database was updated with an entry for the Android.Spy.490.origin Trojan designed for cyber spying. Cybercriminals can incorporate it to any benign application and distribute their modified copies under the guise of the original software without arousing user suspicion. Android.Spy.490.origin is capable of monitoring SMS communication and the location of an infected device, intercept and record phone conversations, send information on conversations to a remote server as well as photos and videos made by the device owner.
Google Play is the most secure Android app resource. However, cybercriminals are still able to distribute various malicious programs on it. To protect Android smartphones and tablets, it is recommended that users install Dr.Web anti-virus products for Android.
Your Android needs protection
Use Dr.Web
- The first Russian Anti-virus for Android
- More than 135 million downloads on Google Play alone
- Free for users of Dr.Web home products