June 2018 virus activity review from Doctor Web
July 3, 2018
The first month of summer appeared to be a quiet month in terms of information security. In the second half of June, Doctor Web security researchers registered a mass mailing used by network fraudsters to trick Internet users. During the month, new versions of malware programs for Android were also discovered.
Principal Trends in June
- Fraudulent mailings
- Distribution of new malicious programs for Android
Threat of the month
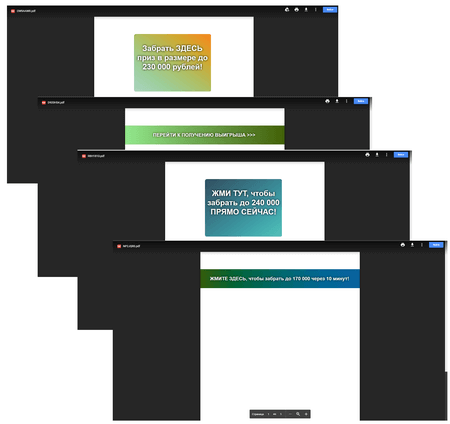
In the second half of June, several mass mailings were detected. These mailings were used by cybercriminals to get gullible potential victims to visit fraudulent websites. Apart from mailings, cybercriminals also used feedback forms at various Internet resources, even those using captcha. In the messages, it appeared that the user had received a transaction or a money transfer. Here are some examples of these messages: “Hello. We have made a payment of $33.50 USD. Invoice code for payment: 2478347616. We inform you that there is enough money on your account balance for automatic renewal”, “The current personal account balance is 13,300 R. We inform you about receiving payment of 1,017 rubles according to invoice №97724”, “We inform you about receiving an invoice payment of 0 031 rub. Your current account balance is 37,561 rub”, “You order details: Balance increase—2 items, 379. 03 $. Thank you for using secure online ordering system. It is worth mentioning that all links in such messages directed to the free Google Docs service, where cybercriminals had already published a PDF document, offered to take a cash prize.
Once a potential victim clicked the link in this PDF document, they were redirected to one of the fraudulent websites offering to take some winnings or reward.
The next fraudulent scheme was quite simple. Cybercriminals have used it for years. A website visitor is required to send a sum of money to cybercriminals to get a prize. After, the visitor, of course, doesn’t receive any prize. Doctor Web analysts detected the addresses of fraudulent Internet resources and added all of them to the Dr.Web Parental Control and Office Control’s databases of non-recommended websites.
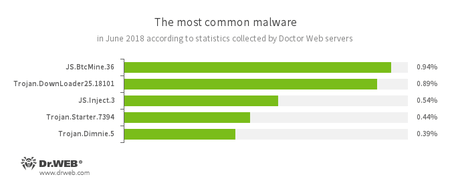
According to Doctor Web’s statistics servers
- JS.BtcMine.36
- A JavaScript designed to stealthily mine cryptocurrencies.
- Trojan.DownLoader
- A family of malicious programs designed to download other malware to the compromised computer.
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts that injects a malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- Trojan.Starter.7394
- A Trojan whose main purpose is to launch in an infected system with an executable file possessing a specific set of malicious functions.
- Trojan.Dimnie.5
- A spyware Trojan capable of stealing confidential information from an infected device and providing illegal access to an infected computer. It also has a built-in banking module.
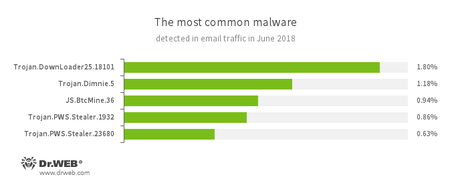
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in email traffic.
- Trojan.DownLoader
- A family of malicious programs designed to download other malware to the compromised computer.
- Trojan.Dimnie.5
- A spyware Trojan capable of stealing confidential information from an infected device and providing illegal access to an infected computer. It also has a built-in banking module.
- JS.BtcMine.36
- A JavaScript designed to stealthily mine cryptocurrencies.
- Trojan.PWS.Stealer
- A family of Trojans designed to steal passwords and other confidential information stored on an infected computer.
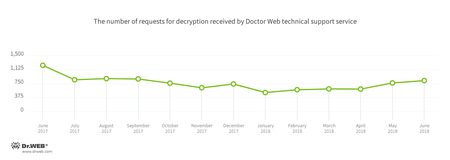
Encryption ransomware
In June, cases involving the following ransomware modifications were registered by Doctor Web’s technical support service:
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 15.47% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.25574 — 12.31% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.11464 — 8.32% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.13671 — 5.99% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.24249 — 4.33% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.10700 — 2.32% requests;
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
During June 2018, 395,477 URLs of non-recommended sites were added to Dr.Web database.
| May 2018 | June 2018 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 1,388,093 | + 395,477 | -71.5% |
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In the last month, Doctor Web security researchers detected many programs with unwanted embedded advertising modules Adware.Appalytic.1.origin on Google Play. These modules displayed obnoxious notifications offering to download different software and opened the pages of advertised programs in Play Store. Later, our specialists detected several new representatives of the Trojan family Android.FakeApp on Google Play. These Trojans displayed various websites upon cybercriminals’ request. Also in June, cybercriminals distributed the Android.Spy.461.origin Trojan, that was used for spying purposes. In addition, the Android.SmsSend.1989.origin SMS Trojan imposed a threat for Android smartphone and tablet users. This Trojan subscribed users to chargeable services.
Among the most notable June events related to mobile malware, we can mention:
- The detection of new Android Trojans on Google Play;
- Distribution of a dangerous spyware.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.