April 2018 virus activity review from Doctor Web
April 28, 2018
In early April Doctor Web virus analysts detected a new version of a dangerous banking Trojan, which infected Android mobile devices. In mid-April, distribution of the Windows encryption Trojan was also detected. Due to virus writers’ error, it corrupted files without the possibility of decrypting them.
Principal Trends in April
- Detection of the dangerous Android banking Trojan
- Spreading of the encryption Trojan that infected Windows devices
Threat of the month
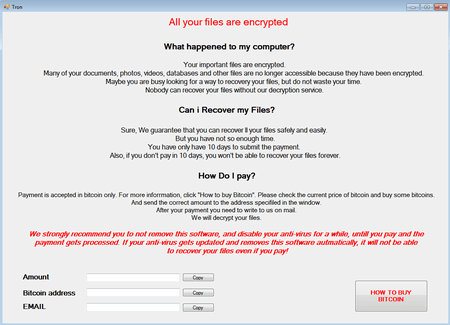
The encryption Trojan, which was dubbed Trojan.Encoder.25129, is detected by the preventive protection of Dr.Web Anti-virus as DPH:Trojan.Encoder.9. Virus writers designed the malicious program so that it does not encrypt files if the infected device is located in Russia, Belarus and Kazakhstan, or if the Russian language and Russian regional parameters are set in the system preferences. However, the encoder encrypts files regardless of the IP address’s geographical location due to the code error.
Using the AES-256-CBC algorithms, Trojan.Encoder.25129 encrypts the folder contents of the current user’s folders, Windows Desktop, the AppData and LocalAppData system folders. The encrypted files are appended the TRON extension. The ransom amount that cybercriminals demand ranges from 0.007305 to 0.04 Btc.
The Trojan’s creators have made an error in its code, so in most cases they will not be able to decrypt files encrypted by the encoder. For more information on the operation of Trojan.Encoder.25129 and its features, refer to this article published on our website.
According to Doctor Web’s statistics servers
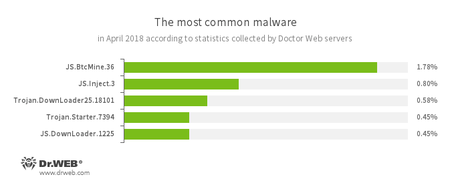
- JS.BtcMine.36
- A JavaScript designed to stealthily mine cryptocurrencies (mining).
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts. They inject malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- Trojan.DownLoader
- A family of malicious programs designed to download other malware to the compromised computer.
- Trojan.Starter.7394
- A Trojan whose main purpose is to launch in an infected system with an executable file possessing a specific set of malicious functions.
- JS.DownLoader
- A family of malicious JavaScripts. They download and install malicious software on a computer.
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in email traffic
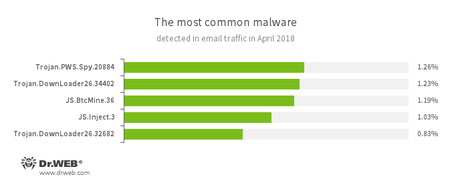
- Trojan.PWS.Spy.20884
- A spying Trojan for Windows that steals confidential information, including user passwords.
- Trojan.DownLoader
- A family of malicious programs designed to download other malware to the compromised computer.
- JS.BtcMine.36
- A JavaScript designed to stealthily mine cryptocurrencies (mining).
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts. They inject malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- Trojan.Encoder.11464 — 10.56% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.11539 — 9.73% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 8.70% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.25064 — 7.66% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.24249 — 4.76% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.761 — 2.28% requests.
- Spreading of a dangerous banking Trojan, which infected over 60,000 mobile devices of Russian users;
- The emergence of new spyware Trojans;
- The detection of malicious programs and riskware on Google Play.
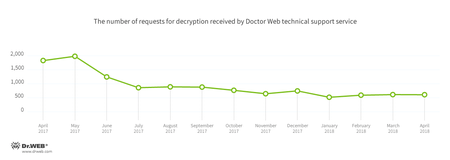
Encryption ransomware
In April, cases involving the following ransomware modifications were registered by Doctor Web’s technical support service:
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
During April 2018, Doctor Web added 287,661 URLs to the Dr.Web database of non-recommended sites.
| March 2018 | April 2018 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 624,474 | + 287,661 | - 53.9% |
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In April, Doctor Web specialists detected a new modification of a dangerous Android Trojan, which was named Android.BankBot.358.origin. It attacked clients of a major bank and infected over 60,000 mobile devices. In the past month, virus analysts also detected numerous malicious programs on Google Play. They all belonged to the Android.Click family. Among them are Android.Click.245.origin, Android.Click.246.origin and Android.Click.458. Once launched, they downloaded websites specified by cybercriminals. These websites were used to trick users into signing up for expensive content services. Later riskware Program.PWS.2 was detected on Google Play. It allowed connection to Telegram that was blocked in Russia. This application did not encrypt the transferred confidential information, which could lead to Android smartphone and tablet owners’ confidential data being leaked. In late April Doctor Web specialists detected Android.RemoteCode.152.origin on Google Play. It downloaded and launched additional modules, and used them to create advertising banners. Then the malicious program tapped on them, generating income for cybercriminals. New spyware that tracked users was also detected in April. According to Doctor Web classification, these malicious programs were named Android.Spy.443.origin and Android.Spy.444.origin.
Among the most noticeable April events related to mobile malware, we can mention:
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.