Doctor Web’s overview of malware detected on mobile devices in September 2017
September 29, 2017
In September, it became widely known that some information security specialists had discovered a group of BlueBorne vulnerabilities in the Bluetooth protocol stack. These vulnerabilities let cybercriminals gain full control over Bluetooth-compatible devices, spread malicious programs among them, and covertly steal confidential information. In addition, in the past month, yet another banking Trojan was detected on Google Play.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN SEPTEMBER
- The emergence of information about dangerous vulnerabilities in an implementation of the Bluetooth protocol that could affect many devices, including Android smartphones and tablets;
- The detection on Google Play of a banking Trojan built into a benign game.
Mobile threat of the month
In September, a whole series of vulnerabilities was detected in the Bluetooth protocol stack. Dubbed BlueBorne, they allow cybercriminals to gain complete control over a wide range of attacked devices, execute arbitrary code, and steal confidential information. The vulnerabilities also pose a threat to Android smartphones and tablets that have not yet had OS “patches” installed on them.
Doctor Web specialists are working on an update for Dr.Web Security Space for Android that will allow it to detect not only known vulnerabilities but also program errors.
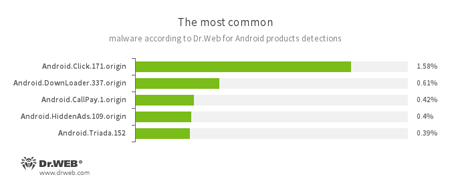
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android
- Android.Click.171.origin
- A Trojan designed to inflate traffic numbers on websites specified by cybercriminals.
- Android.DownLoader.337.origin
- A Trojan designed to download other applications.
- Android.CallPay.1.origin
- A Trojan that provides access to adult content while covertly making phone calls to premium numbers as payment for this service.
- Android.HiddenAds.109.origin
- Trojans designed to display unwanted ads on mobile devices. They are distributed under the guise of popular apps by other malicious programs that sometimes covertly install them in the system directory.
- Android.Triada.152
- A multi-functional Trojan that performs different malicious actions.
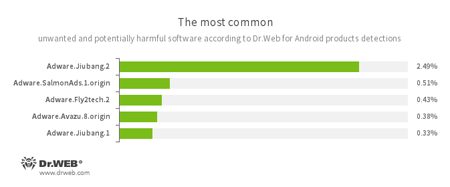
- Adware.Jiubang.2
- Adware.SalmonAds.1.origin
- Adware.Fly2tech.2
- Adware.Avazu.8.origin
- Adware.Jiubang.1
- Unwanted program modules incorporated into Android applications and designed to display annoying ads on mobile devices.
Trojan on Google Play
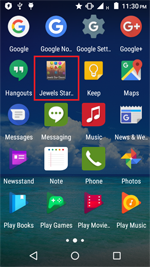
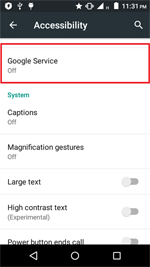
In September, the banking Trojan Android.BankBot.234.origin was detected on Google Play. It was hidden in a benign game called Jewels Star Classic. Some time after its launch, it requests access to the Android Accessibility Service. The malicious program uses it to covertly install and launch Android.BankBot.233.origin, which is hidden in its resources. Then Android.BankBot.233.origin tracks the launch of Google Play and displays a phishing form of a payment service settings with a request to input a bank card information. Input data is sent to cybercriminals who can subsequently steal money from a victim’s bank account because the Trojan intercepts all SMS messages containing verification codes.
Features of Android.BankBot.234.origin:
- Injected into a benign game;
- To avoid arousing suspicion, it commences with its malicious activities at some point after its installation and launch;
- Attempts to gain access to the Accessibility Service on devices in order to independently tap buttons in dialogs, turn on required system parameters, and install applications;
- Contains within its resources a Trojan called Android.BankBot.233.origin, which is covertly installed on infected smartphones or tablets and used to steal bank card details.
Android device owners are exposed to danger not only from malicious applications that are spread on the Internet and Google Play but also from vulnerabilities in the operating system and its components. Doctor Web recommends that device owners install all available updates in a timely manner and use Dr.Web anti-virus products for Android.
Your Android needs protection
Use Dr.Web
- The first Russian Anti-virus for Android
- More than 100 million downloads on Google Play alone
- Free for users of Dr.Web home products