February 2017 virus activity review from Doctor Web
February 28, 2017
The last month of winter was marked by the emergence of a new banking Trojan that inherited fragments of the source code of another widespread banker family—Zeus (Trojan.PWS.Panda). This malware injects arbitrary content into user-loaded web pages and runs a VNC server on the infected computer. Also in February, Doctor Web security researchers detected a new Trojan for Linux. New entries were also added to the Dr.Web virus databases for Android.
Principal trends in February
- The distribution of a new banking Trojan
- The detection of a new malicious program for Linux
- The emergence of new malware for Android
Threat of the month
Banking Trojans are considered one of the most dangerous types of malware programs since they are capable of stealing money directly from the bank accounts of their victims. The new banking Trojan examined by Doctor Web security researchers was dubbed Trojan.PWS.Sphinx.2. It performs web injections, i.e., it injects arbitrary content into user-loaded web pages. Thus, it can, for example, send cybercriminals user login credentials to access online banking services. The user enters this data into fake forms created by the Trojan. Below is an example of the code that Trojan.PWS.Sphinx.2 embeds in the pages of the bankofamerica.com website:
Furthermore, Trojan.PWS.Sphinx.2 can run a VNC server on an infected computer, and cybercriminals can use it to connect to the infected device and install digital certificates in the system for organizing attacks based on MITM (Man-in-the-middle) technology. The Trojan has a grabber—a module that intercepts and sends data entered by the user into various forms to a remote server. It is notable that the automatic launch of Trojan.PWS.Sphinx.2 is executed via a special PHP script. More information about this malicious program can be found in the corresponding review published by Doctor Web.
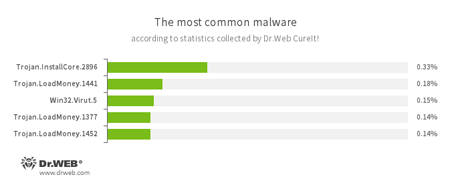
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web CureIt!
- Trojan.InstallCore
A family of installers of unwanted and malicious applications. - Trojan.LoadMoney
A family of downloader programs generated by servers belonging to the LoadMoney affiliate program. These applications download and install unwanted software on the victim's computer. - Win32.Virut.5
A complex polymorphic virus that infects executable files and contains functions that allow infected computers to be controlled remotely.
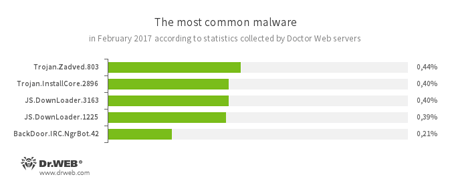
- Trojan.Zadved
This Trojan displays fake search results in the browser window and imitates pop-up messages from social networking sites. In addition to this, the malware can replace advertisements displayed on different Internet resources. - Trojan.InstallCore
A family of installers of unwanted and malicious applications. - JS.DownLoader
A family of malicious JavaScripts. Download and install malicious software. - BackDoor.IRC.NgrBot.42
A fairly common Trojan which is known to the information security researchers since 2011. Malicious programs of this family are able to execute intruder-issued commands on infected machines, and cybercriminals use the IRC (Internet Relay Chat) text-messaging protocol to control those PCs.
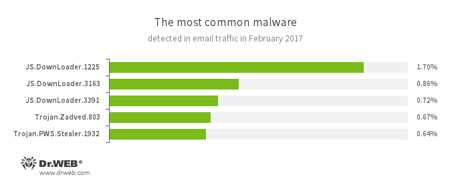
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in email traffic
- JS.DownLoader
A family of malicious JavaScripts. Download and install malicious software. - Trojan.Zadved
This Trojan displays fake search results in the browser window and imitates pop-up messages from social networking sites. In addition to this, the malware can replace advertisements displayed on different Internet resources. - Trojan.PWS.Stealer
A family of Trojans designed to steal passwords and other confidential information stored on an infected computer.
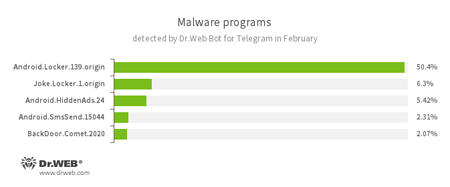
According to Dr.Web Bot for Telegram data
- Android.Locker.139.origin
A ransomware Trojan for Android. Different modifications of these malicious programs can lock a device after alleging, via an on-screen warning, that the device owner has done something illegal. To unlock the device, the owner has to pay a ransom. - Joke.Locker.1.origin
A joke program for Android that blocks a mobile device’s screen and displays the Windows BSOD (“Blue Screen of Death”). - Android.HiddenAds.24
A Trojan designed to display unwanted ads on mobile devices. - Android.SmsSend.15044
One of the Trojans belonging to the family of malicious programs that are designed to send SMS messages to premium numbers and subscribe users to chargeable services and services providing paid content. - BackDoor.Comet.2020
A representative of the malware family that executes commands received from cybercriminals on an infected device and provides them with unauthorized access to it.
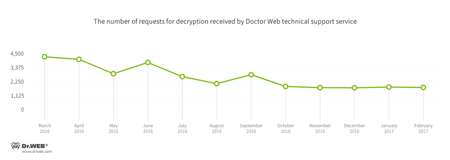
Encryption ransomware
In February, Doctor Web’s technical support was most often contacted by victims of the following modifications of encryption ransomware:
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 31.16% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 6.70% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 4.70% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.761 — 3.31% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.3976 — 1.91% requests.
Dr.Web Security Space 11.0 for Windows
protects against encryption ransomware
This feature is not available in Dr.Web Anti-virus for Windows
| Data Loss Prevention | |
|---|---|
 |  |
During February 2017, 134,063 URLs of non-recommended websites were added to the Dr.Web database.
| January 2017 | February 2017 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 223,127 | + 134,063 | -39.9% |
Linux malware
Trojans that infect Linux devices are no longer considered rare. However, in February Doctor Web security researchers detected an unusual malicious program. Once launched on a Microsoft Windows computer, it attempts to find and infect various Linux devices.
This Trojan was dubbed Trojan.Mirai.1. After downloading the list of IP addresses from its command and control server, it launches a scanner on the infected machine. The scanner that checks these addresses and attempts to log into them using the login and password combination indicated in the configuration file. While connecting to the Linux device via Telnet protocol, the Trojan downloads a binary file onto the compromised device, and this file subsequently downloads and launches Linux.Mirai. In addition, Trojan.Mirai.1 can execute cybercriminals’ commands and perform other malicious functions. For more information, refer to this news article.
Also in February, Doctor Web security researchers examined the Trojan Linux.Aliande.4. Written in the language Go, it is designed to hack into remote network server login systems by engaging in dictionary attacks (brute-force attacks). For its operation, Linux.Aliande.4 uses the list of IP addresses obtained from the command and control server. The SSH protocol is used to access the remote devices. The Trojan sends the list of successfully generated login and password combinations to the cybercriminals.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In February, Android.Click.132.origin was detected. It was spread via Google Play. This malicious program covertly opened websites and could independently tap on advertisements. Cybercriminals were remunerated for that activity.
The most noticeable February event related to mobile malware:
- the detection of an Android Trojan that covertly loaded advertising websites and tapped on advertisements.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.