Doctor Web’s September 2016 virus activity review
September 30, 2016
In September 2016, Doctor Web’s analysts examined several malicious programs for Linux. The month began with the discovery of a Trojan written in the Rust language, and then a Trojan designed to carry out DDoS attacks was found. Some time later, the whole family of DDoS Trojans for Linux was investigated by security researchers, together with a malware program for Android capable of performing injections into system processes.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN SEPTEMBER
- The emergence of a Linux Trojan written in Rust
- Distribution of new Linux Trojans designed to carry out DDoS attacks
- The emergence of a Trojan for Android capable to perform injections into system processes
Threat of the month
Trojans designed to carry out DDoS attacks is nothing new. Some of them can infect computers running not only Microsoft Windows but also Linux. Linux.Mirai is one of them.
The first version of Linux.Mirai appeared in May 2016 and was added to the Doctor Web virus database under the name Linux.DDoS.87. This Trojan, designed to carry out DDoS attacks, can work with the SPARC, ARM, MIPS, SH-4, M68K architectures and Intel x86 computers. It also shares a few features with the Linux.BackDoor.Fgt family, one of whose representatives we described in 2014. Once launched on an infected computer, Linux.DDoS.87 searches the memory for the processes of other Trojans and terminates them. Linux.DDoS.87 can launch the following DDoS attacks:
- UDP flood;
- UDP flood over GRE;
- DNS flood;
- TCP flood (several types);
- HTTP flood.
August 2016 began with the discovery of a new version of this dangerous Trojan, which was dubbed Linux.DDoS.89. It shares many of its predecessor’s features, although there are some notable differences from Linux.DDoS.87. For example, the newer version has another procedure for launching the Trojan and the mechanism for protecting itself from being self-removed. Moreover, HTTP flood attacks are no longer carried out. Finally, Linux.DDoS.89 includes a new component—the telnet scanner that is designed to search for vulnerable computers on the Internet and connect to them using the telnet protocol.
In the end of September, one more representative—Linux.Mirai—was discovered by Doctor Web’s specialists. The Trojan has learned how to turn off the watchdog timer (which protects against system hangs and reboots), and once again it is carrying out HTTP flood attacks. For more information about this family of Linux Trojans, refer to the review.
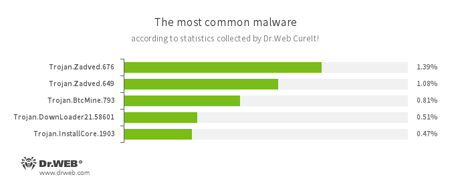
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web CureIt!
- Trojan.Zadved
This Trojan displays fake search results in the browser window and imitates pop-up messages from social networking sites. In addition to this, the malware can replace advertisements displayed on different Internet resources. - Trojan.BtcMine.793
A Trojan designed to covertly use the infected computer’s resources in order to generate cryptocurrency—for example, Bitcoin. - Trojan.DownLoader
A family of malicious programs designed to download other malware to the compromised computer. - Trojan.InstallCore.1903
A Trojan that can install unwanted and malicious applications.
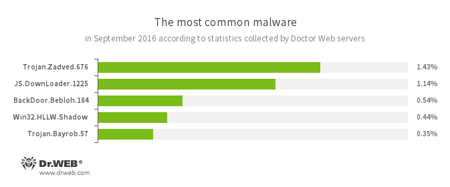
According to Doctor Web’s statistics servers
- Trojan.Zadved
This Trojan displays fake search results in the browser window and imitates pop-up messages from social networking sites. In addition to this, the malware can replace advertisements displayed on different Internet resources. - JS.Downloader
A family of malicious scripts written in JavaScript and designed to download and install other malware programs on a computer. - BackDoor.Bebloh.184
A backdoor Trojan that is capable of performing injections into other applications and executing cybercriminals’ commands. - Win32.HLLW.Shadow
A worm that replicates itself through removable media and network drives. In addition, it can be spread via a network using a standard SMB protocol. It is designed to download executable files from the C&C server and run them. - Trojan.Bayrob.57
A Trojan that can steal confidential information from a compromised computer and perform other malicious actions.
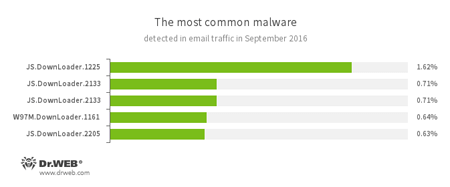
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in email traffic
- JS.Downloader
A family of malicious scripts written in JavaScript and designed to download and install other malware programs on a computer. - W97M.DownLoader
A family of downloader Trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in office applications and can download other malicious programs to the compromised computer.
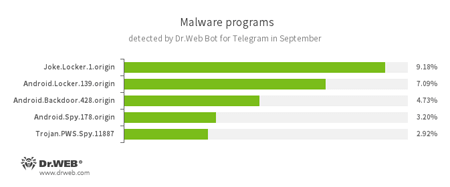
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web Bot for Telegram
- Joke.Locker.1.origin
A joke program for Android that locks the home screen of a device and displays a BSOD (Blue Screen of Death) error of Microsoft Windows. - Android.Locker.139.origin
A ransomware Trojan for Android. Its different modifications can lock the device displaying a warning about some violation of law. To unlock the device, the user has to pay a ransom. - Android.Backdoor.428.origin
A Trojan for Android that executes instructions received from cybercriminals. Depending on a modification, the Trojan can send SMS messages, open URLs in a browser, collect information about a device and a user’s contacts, download other applications, and so on. - Android.Spy
A family of multifunctional Trojans for Android that are designed to read and save contacts, receive and send SMS messages, determine GPS coordinates, read and save bookmarks in a browser, and get a device’s IMEI and telephone number. - Trojan.PWS.Spy.11887
A Trojan for Windows that steals private information including user passwords.
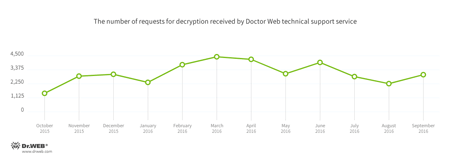
Encryption ransomware
In September, cases involving the following ransomware modifications were registered by Doctor Web’s technical support service:
- Trojan.Encoder.717 — 25.64% of requests
- Trojan.Encoder.602 — 21.53% of requests
- Trojan.Encoder.143 — 5.11% of requests
- Trojan.Encoder.126 — 4.51% of requests
- Trojan.Encoder.126 — 4.26% of requests
Dr.Web Security Space 11.0 for Windows
protects against encryption ransomware
This feature is not available in Dr.Web Anti-virus for Windows.
| Data Loss Prevention | |
|---|---|
 |  |
Dangerous websites
During September 2016, 298,985 URLs of non-recommended websites were added to Dr.Web database.
| August 2016 | September 2016 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| +245,394 | +298,985 | +21.8% |
Linux
Doctor Web’s specialists have discovered a new Linux Trojan written in the Rust programming language. The Trojan has been named Linux.BackDoor.Irc.16. It is a typical backdoor program that executes commands issued by cybercriminals via the IRC (Internet Relay Chat) protocol. For more information about this Trojan, refer to the news article.
Some time later, yet another Linux Trojan was detected—Linux.DDoS.93. The Linux.DDoS.93 is designed to carry out DDoS attacks and can execute the following commands:
- Update the malicious program
- Download and run the file specified in the command
- Remove itself
- Launch a UDP flood attack on a specified port
- Launch a UDP flood attack on a random port
- Launch a Spoofed UDP flood attack
- Launch a TCP flood attack
- Launch a TCP flood attack (random data up to 4096 B long is added to the packages)
- Launch an HTTP flood attack using GET requests
- Launch an HTTP flood attack using POST requests
- Launch an HTTP flood attack using HEAD requests
- Send HTTP requests with the parameters specified to 255 random IP addresses
- Terminate execution
- Send a PING command
You can learn more about Linux.DDoS.93 in the news article published by Doctor Web.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In September, Doctor Web analysts have detected, within the Android.Xiny family, new species of Trojans designed to download and install various programs without user knowledge. These Trojans can now infect the processes of system applications and run malicious plugins.
Among the most notable September events related to mobile malware:
- The discovery of Trojans belonging to the Android.Xiny family that can inject themselves into processes of system applications and launch malicious plugins.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.