February 2016 virus activity review from Doctor Web
February 29, 2016
February was quite eventful in terms of information security. At the beginning of the month, Doctor Web specialists detected a dangerous Trojan for Android that was capable to inject itself into system processes. In addition, a number of malicious programs for Windows were discovered at the end of February.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN FEBRUARY
- Emergence of a Trojan for Android capable to perform injections into system processes
- Distribution of a banking Trojan targeting Russian bank customers
- New backdoor for Windows that has geographical restrictions
Threat of the month
A group of three associated Trojans for Android named Android.Loki.1.origin, Android.Loki.2.origin and Android.Loki.3 is considered to be the most sophisticated threat detected during the past month. To perform their malicious activity, they use the liblokih.so library, which Dr.Web detects as Android.Loki.6. This library is incorporated into system processes by Android.Loki.3. Thus, Android.Loki.1.origin—the Trojan’s main module—gains the system privileges.
It is noteworthy that security researchers have not previously encountered Android malware that could perform injections into system processes, which makes this Trojan really noticeable. Android.Loki.1.origin can execute a wide range of functions. For instance, it is able to
- Download and delete applications.
- Enable and disable applications and their components.
- Kill processes.
- Display notifications.
- Register any application as the Accessibility Service application.
- Update its components and download plug-ins from the server.
The next element of the Trojan—Android.Loki.2.origin—is designed to display advertisements and install different software on the infected device upon receiving cybercriminals’ instructions. Yet, it can also act as a spyware program by sending detailed information about the machine to the server. To read more about this incident, refer to the news article.
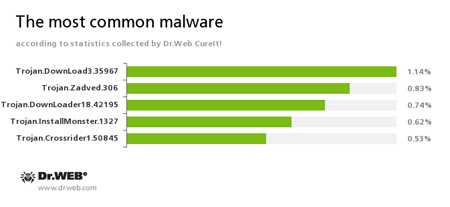
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web CureIt!
Trojan.DownLoad3.35967
A Trojan that can download other malicious programs from the Internet and install them on the infected computer.Trojan.Zadved
This Trojan displays fake search results in the browser window and imitates pop-up messages from social networking sites. In addition to this, the malware can replace advertisements displayed on different Internet resources.Trojan.DownLoader
A family of malicious programs designed to download other malware to the compromised computer.Trojan.Installmonster
A family of malicious programs created using the Installmonster affiliate program. These programs install various unwanted software on the victim's computer.Trojan.Crossrider1.50845
Trojans designed to display various advertisements.
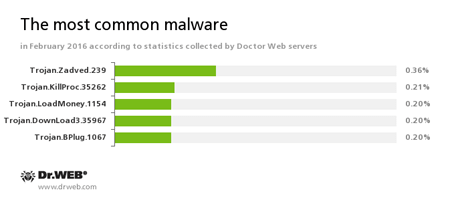
According to Doctor Web statistics servers
Trojan.Zadved
This Trojan displays fake search results in the browser window and imitates pop-up messages from social networking sites. In addition to this, the malware can replace advertisements displayed on different Internet resources.Trojan.KillProc.35262
Trojans designed to kill running processes of other applications and to perform other malicious functions on the infected device.Trojan.LoadMoney
A family of downloader programs generated by servers belonging to the LoadMoney affiliate program. These applications download and install unwanted software on the victim's computer.Trojan.DownLoad3.35967
A Trojan that can download other malicious programs from the Internet and install them on the infected computer.Trojan.BPlug
These plug-ins for popular browsers display annoying advertisements to users as they browse webpages.
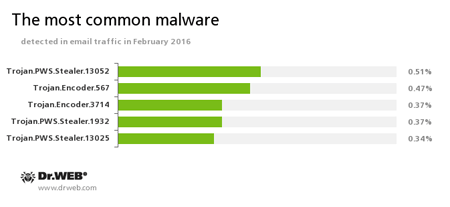
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in email traffic
Trojan.PWS.Stealer
A family of Trojans designed to steal passwords and other confidential information stored on the infected computer.Trojan.Encoder.567
A malicious program belonging to the family of encryption ransomware Trojans that encrypt files and demand a ransom for decryption of compromised data. This program can encrypt important user files, for example, of the following types: .jpg, .jpeg, .doc, .docx, .xls, xlsx, .dbf, .1cd, .psd, .dwg, .xml, .zip, .rar, .db3, .pdf, .rtf, .7z, .kwm, .arj, .xlsm, .key, .cer, .accdb, .odt, .ppt, .mdb, .dt, .gsf, .ppsx, .pptx.Trojan.Encoder.3714
A malicious program belonging to the family of encryption ransomware Trojans that encrypt files and demand a ransom for decryption of compromised data.
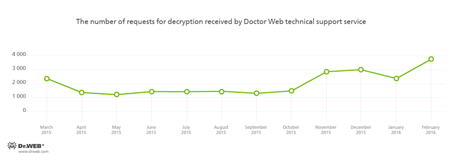
Encryption ransomware
The most common ransomware programs in February 2016:
It should be noted that almost half of the requests for decryption received by the Doctor Web technical support service were from foreign users.
Dr.Web Security Space 11.0 for Windows
protects against encryption ransomware
This feature is not available in Dr.Web Anti-virus for Windows.
| Data Loss Prevention | |
|---|---|
 |  |
Other malicious applications
Trojans belonging to the Trojan.Dyre family were first spotted in the middle of 2014. Since then, mass media has regularly published materials about new attacks involving this Trojan. To distribute different variants of Trojan.Dyre, attackers used affiliate programs, implementing the CaaS (crime-as-a-service) model. The “clients of this service” received a builder that was used to generate samples of the Trojan. In addition, attackers provided “users” with a special bot control panel. To learn more about how Doctor Web specialists fight against virus makers responsible for creation and distribution of Trojan.Dyre, read the article published by Doctor Web.
In mid-February, security researchers registered a new malware program—Trojan.Proxy2.102—that threatened customers of several Russian banks by stealing money from victims’ bank accounts. Once launched, it installed a root digital certificate and changed the Internet connection settings specifying a proxy server that belonged to virus makers.
This server was also applied to inject arbitrary content into websites once a user opened them on the infected computer. Therefore, a victim was tricked into transferring money from their accounts to cybercriminals’. For more information about Trojan.Proxy2.102, refer to the news article.
At the end of February, Doctor Web reported on detection of a backdoor Trojan named BackDoor.Andromeda.1407. Its key feature lay in the fact that this Trojan deleted itself from computers that used Russian, Ukrainian, Belorussian, or Kazakh keyboard layouts. The backdoor is currently known to distribute several malicious applications.
Dangerous websites
During February 2016, 453,623 URLs of non-recommended websites were added to the Dr.Web database.
| January 2016 | February 2016 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| +625,588 | +453,623 | -27.5% |
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
The past month was marked by several incidents involving Trojans for Android. At the beginning of the month, Doctor Web security researchers examined a group of Trojans belonging to the Android.Loki family. Its representatives were designed to download and install software, display advertising, and collect confidential information. In addition, attackers continued distributing banking Trojans among Android devices users in February.
Among the most noticeable February events related to mobile malware, we can mention
- Emergence of multicomponent Trojans injected into system processes and capable to perform a wide variety of function.
- New cases of mobile devices being infected by banking Trojans.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.