February 2015 Android malware overview
March 4, 2015
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN FEBRUARY
- New versions of dangerous Trojans that encrypt files on Android devices
- The increase in the number of aggressive advertising modules used by software developers to monetize
- The increase in the number of SMS Trojans
- New banking Trojans
The number of entries for malicious and unwanted software in the Dr.Web for Android virus database
| January 2015 | February 2015 | Movement |
|---|---|---|
| 6087 | 6665 | +9,5% |
Mobile threat of the month
At the beginning of February, a number of applications containing a new aggressive advertising module, Adware.MobiDash.1.origin, were detected in the Google Play digital content catalogue. Some of these programs were downloaded by users tens of millions of times. Adware.MobiDash.1.origin incorporates the following features:
- It can be embedded in a wide variety of games and programs hosted on Google Play—the official Android applications' catalogue—as well as on other popular sites.
- Every time the compromised device's screen is unlocked, the program loads webpages with various ads in the browser and also displays suspicious messages about allegedly found problems and prompts the user to install updates or certain applications etc.
- It can also show ads or other messages in the status bar or display advertisements on top of the OS interface and windows, which makes working with the device difficult.
- A great period of time passes after installation and launching of the application containing the module, before it becomes operational. It makes it harder for the user to define the source of annoying ads.
Aggressive advertising modules
In the past month Doctor Web security researchers registered the emergence of several new advertising modules with rather aggressive features. Adware.MobiDash.1.origin, which was incorporated in a number of applications on Google Play, became one of them.
Other "unpleasant" advertising modules:
Adware.HiddenAds.1
- It can be installed onto a mobile device by a variety of malware.
- It does not have an icon or the GUI, and runs in a stealth mode.
- It displays various advertising messages in the status bar.
Adware.Adstoken.1.origin
- It is embedded into popular applications modified by third parties
- It displays an advertising banner on mobile devices' screens
- It shows various messages in the status bar
- It loads advertising web pages in the browser
Ransomware
The number of entries of Android.Locker in the Dr.Web virus database:
| January 2015 | February 2015 | Movement |
|---|---|---|
| 159 | 174 | +9,4% |
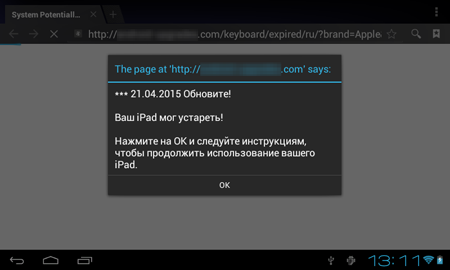
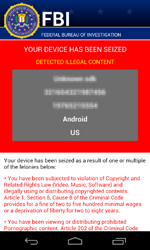
In February, a dangerous ransomware locker named Android.Locker.71.origin was discovered. The program encrypts files, locks the infected device, and demands a $200 ransom.
 |
 |
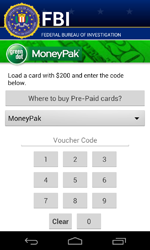 |
Android.Locker.71.origin uses a unique encryption key to encrypt files on each infected device—this complicates restoring data compromised by the Trojan.
Currently, decryption of the files affected by the actions of this malware is not possible, however, all versions of Android.Locker.71.origin are successfully detected and removed by Dr.Web for Android and, thus, users are protected from this Trojan’s activities.
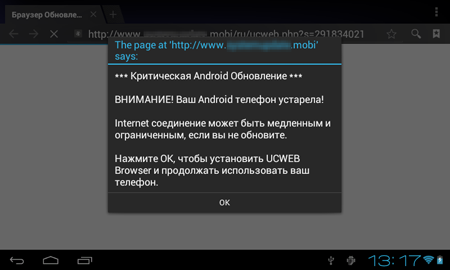
SMS Trojans
Last month there was a significant increase in the number of new SMS Trojans sending short messages at premium numbers and subscribing users to chargeable services. The number of enentries of Android.SmsSend in the Dr.Web virus database:
| January 2015 | February 2015 | Movement |
|---|---|---|
| 2870 | 3264 | +13,7% |
Banking Trojans
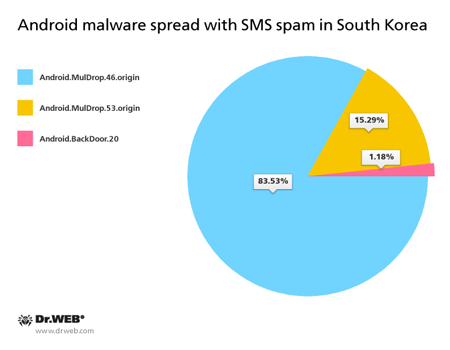
Once again, there was a splash in activity of various mobile banking Trojans in February. In particular, such malicious applications were spread in South Korea, where cybercriminals launched an SMS mailing again to distribute Trojan download links.
Over 80 spam campaigns involving several malicious programs were registered. Most of them were dropper Trojans.
Android.MulDrop malware
Hides inside other Trojans, which in this case are banking Trojans—the main tools of South Korean criminals.
Android.BackDoor.20
A malicious program that allows attackers to perform various actions on infected mobile devices.
The following banking Trojans were used by South Korean cybercriminals:
- Android.BankBot.39.origin
- Android.BankBot.47.origin
- Android.BankBot.48.origin
All these programs enable virus writers to gain access to users' bank accounts.
[% END %]