Doctor Web’s February 2024 review of virus activity on mobile devices
April 1, 2024
The activity of banking trojans from various families decreased by 18.77%, while Android.Spy spyware trojan activity decreased by 27.33%. In contrast, the number of Android.Locker ransomware trojan detections increased by 29.85%.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN FEBRUARY
- A significant increase in activity on the part of advertising tojan programs from the Android.HiddenAds family
- Fewer attacks carried out by banking trojans and malicious spyware
- An increase in the number of malicious ransomware programs detected on protected devices
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android
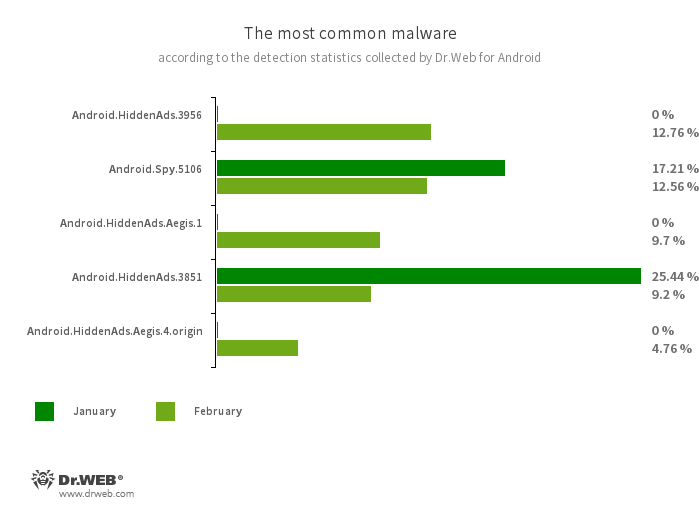
- Android.HiddenAds.3956
- Android.HiddenAds.3851
- Trojan apps designed to display intrusive ads. Trojans of this family are often distributed as popular and harmless applications. In some cases, other malware can install them in the system directory. When these infect Android devices, they typically conceal their presence from the user. For example, they “hide” their icons from the home screen menu.
- Android.Spy.5106
- The detection name for a trojan that presents itself as modified versions of unofficial WhatsApp messenger mods. This malicious program can steal the contents of notifications and offer users other apps from unknown sources for installation. And when such a modified messenger is used, it can also display dialog boxes containing remotely configurable content.
- Android.HiddenAds.Aegis.1
- Android.HiddenAds.Aegis.4.origin
- These are the trojan apps that conceal their presence on Android devices and display intrusive ads. They have a number of characteristics that differentiate them from other members of the Android.HiddenAds family. For example, these trojans can run automatically after they are installed. Moreover, they implement a mechanism that allows their services to remain constantly running. And, in some cases, they can also use hidden Android operating system functions.
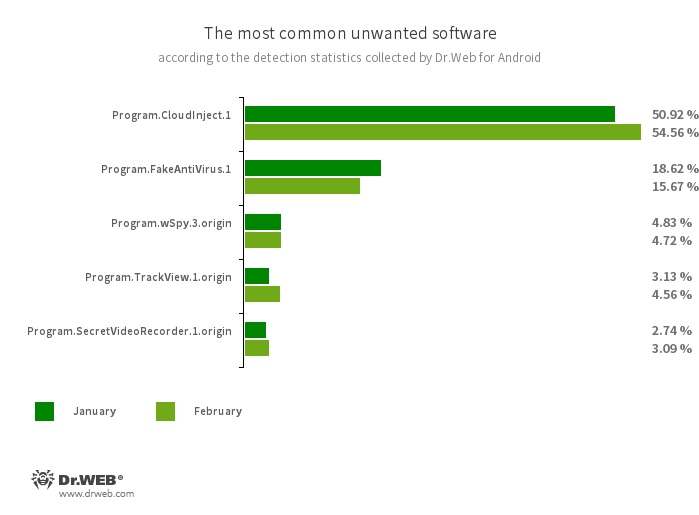
- Program.CloudInject.1
- The detection name for Android programs that have been modified using the CloudInject cloud service and the eponymous Android utility (the latter was added to the Dr.Web virus database as Tool.CloudInject). Such programs are modified on a remote server; meanwhile, the modders (users) who are interested in such modifications cannot control exactly what will be added to the apps. Moreover, these programs receive a number of dangerous system permissions. Once modification is complete, users can remotely manage these apps. They can block them, display custom dialogs, and track when other software is being installed or removed from a device, etc.
- Program.FakeAntiVirus.1
- The detection name for adware programs that imitate anti-virus software. These apps inform users of nonexistent threats, mislead them, and demand that they purchase the software’s full version.
- Program.wSpy.3.origin
- A commercial spyware app designed to covertly monitor Android device user activity. It allows intruders to read SMS and chats in popular messaging software, listen to the surroundings, track device location and browser history, gain access to the phonebook and contacts, photos and videos, and take screenshots and pictures through a device’s built-in camera. It also has keylogger functionality.
- Program.TrackView.1.origin
- The detection name for a program that allows users to be monitored via their Android devices. Malicious actors can utilize it to track a target device’s location, use the camera to record video and take photos, eavesdrop via the microphone, record audio, etc.
- Program.SecretVideoRecorder.1.origin
- The detection name for various modifications of an application that is designed to record videos and take photos in the background using built-in Android device cameras. It can operate covertly by allowing notifications about ongoing recordings to be disabled. It also allows an app’s icon and name to be replaced with fake ones. This functionality makes this software potentially dangerous.
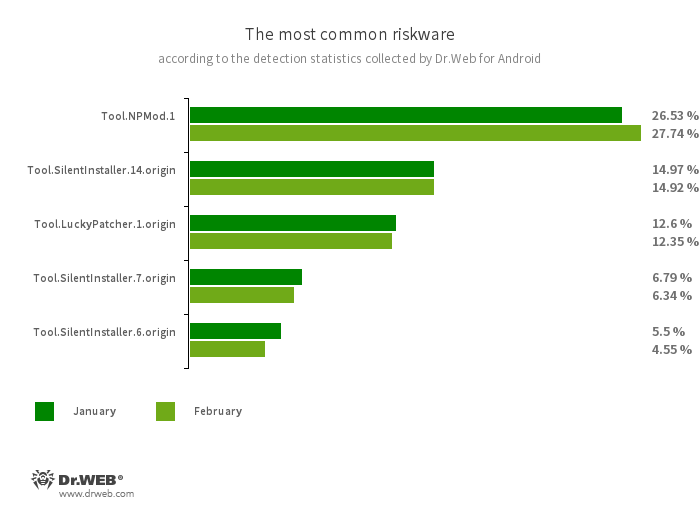
- Tool.NPMod.1
- The detection name for Android programs that have been modified using the NP Manager utility. A special module is embedded in such apps, and it allows them to bypass digital signature verification once they have been modified.
- Tool.SilentInstaller.14.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.7.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.6.origin
- Riskware platforms that allow applications to launch APK files without installing them. They create a virtual runtime environment in the context of the apps in which they are integrated. The APK files, launched with the help of these platforms, can operate as if they are part of such programs and can also obtain the same permissions.
- Tool.LuckyPatcher.1.origin
- A tool that allows apps installed on Android devices to be modified (i.e., by creating patches for them) in order to change the logic of their work or to bypass certain restrictions. For instance, users can apply it to disable root-access verification in banking software or to obtain unlimited resources in games. To add patches, this utility downloads specially prepared scripts from the Internet, which can be crafted and added to the common database by any third party. The functionality of such scripts can prove to be malicious; thus, patches made with this tool can pose a potential threat.
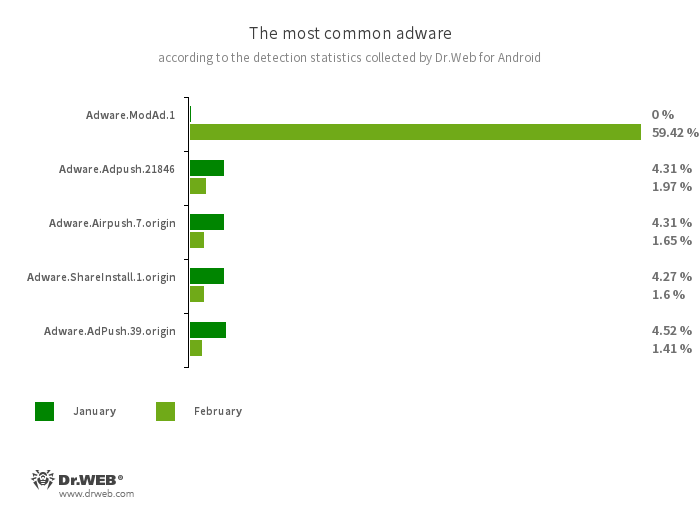
- Adware.ModAd.1
- The detection name for some modified versions (mods) of the WhatsApp messenger whose functions have been injected with a specific code. This code is responsible for loading target URLs by displaying web content (via the Android WebView component) during the messenger’s operation. Such web addresses perform redirects to advertised sites, including online casino, bookmaker, and adult sites.
- Adware.Adpush.21846
- Adware.AdPush.39.origin
- Adware modules that can be built into Android apps. They display notifications containing ads that mislead users. For example, such notifications can look like messages from the operating system. In addition, these modules collect a variety of confidential data and are able to download other apps and initiate their installation.
- Adware.Airpush.7.origin
- A member of a family of adware modules that can be built into Android apps and display various ads. Depending on the modules’ version and modification, these can be notifications containing ads, pop-up windows or banners. Malicious actors often use these modules to distribute malware by offering their potential victims diverse software for installation. Moreover, such modules collect personal information and send it to a remote server.
- Adware.ShareInstall.1.origin
- An adware module that can be built into Android applications. It displays notifications containing ads on the Android OS lock screen.
To protect your Android device from malware and unwanted programs, we recommend installing Dr.Web anti-virus products for Android.