Doctor Web’s March 2023 virus activity review
May 17, 2023
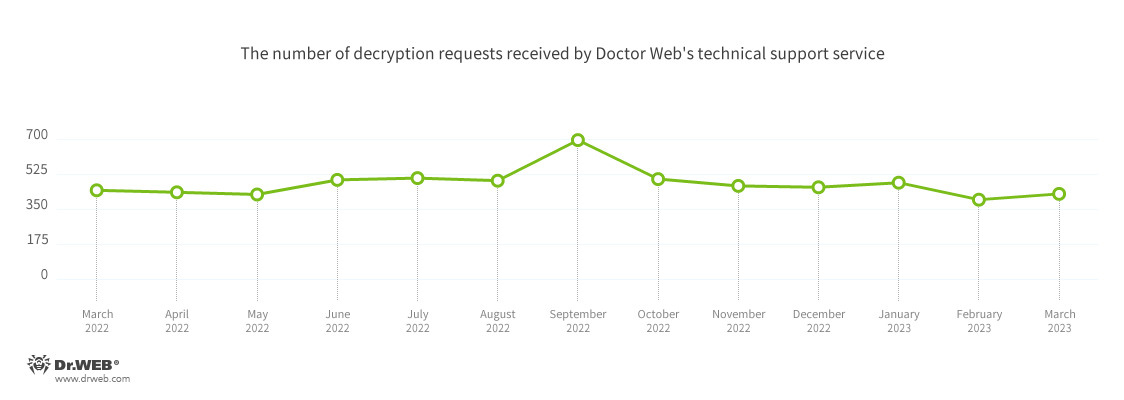
The number of user requests to decrypt files damaged by encoder trojans increased by 7.3%, compared to the previous month. Most often users were attacked by Trojan.Encoder.26996, Trojan.Encoder.3953, and Trojan.Encoder.35534 ransomware.
At the same time, Doctor Web’s specialists discovered over 60 malicious apps from the Android.FakeApp family on Google Play. Threat actors used these in various fraudulent schemes.
Principal trends in March
- An increase in the total number of detected threats
- An increase in the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans
- The emergence of other malicious apps on Google Play
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
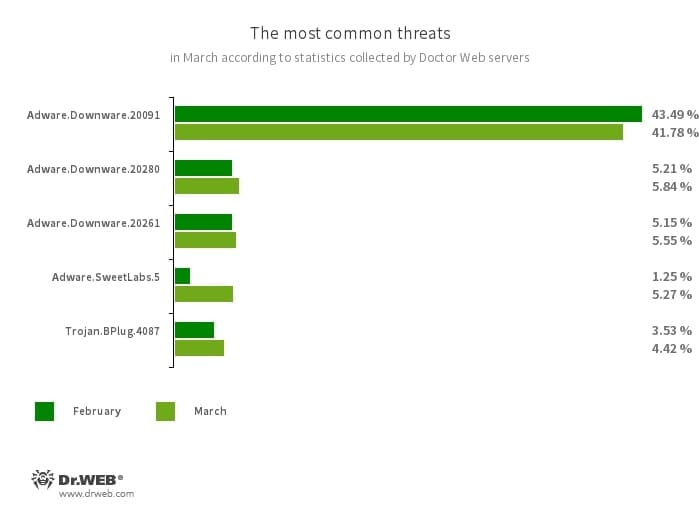
The most common threats of the month:
- Adware.Downware.20091
- Adware.Downware.20280
- Adware.Downware.20261
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirated software.
- Adware.SweetLabs.5
- An alternative app store and an add-on for Windows GUI (graphical user interface) from the creators of “OpenCandy” adware.
- Trojan.BPlug.4087
- The detection name for a malicious component of the WinSafe browser extension. This component represents a JavaScript file that displays intrusive ads in browsers.
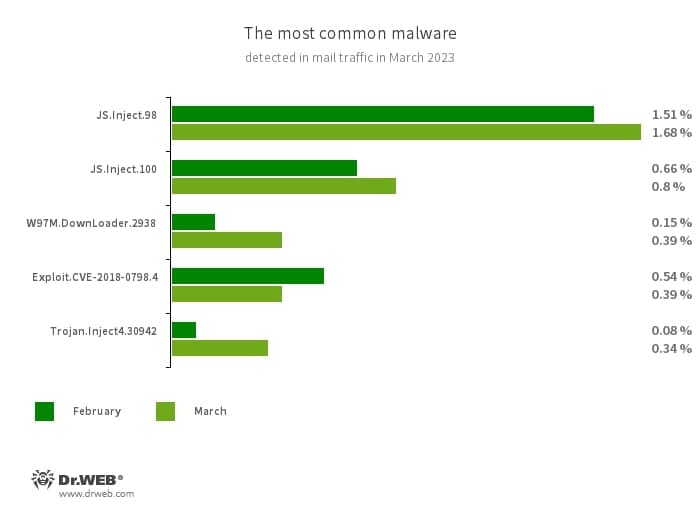
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts that inject a malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents. They can also download other malicious programs to a compromised computer.
- Exploit.CVE-2018-0798.4
- An exploit designed to take advantage of Microsoft Office software vulnerabilities and allow an attacker to run arbitrary code.
- Trojan.Inject4.30942
- The detection name for a software packer used to protect a malicious keylogger app.
Encryption ransomware
In March, the number of requests to decrypt files damaged by encoder trojans increased by 7.3%, compared to February.
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 20.00%
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 15.82%
- Trojan.Encoder.35534 — 10.15%
- Trojan.Encoder.35209 — 2.99%
- Trojan.Encoder.34027 — 2.39%
Dangerous websites
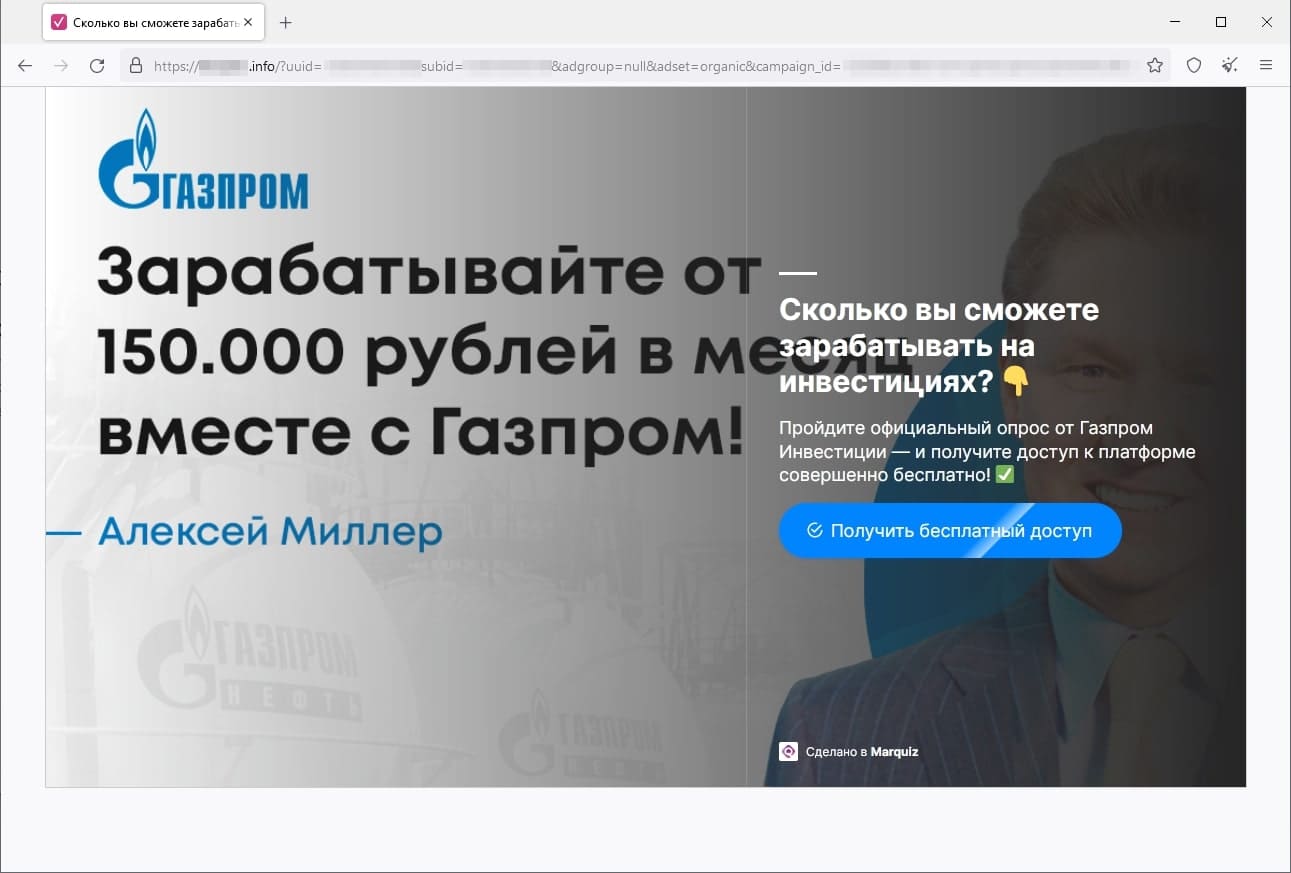
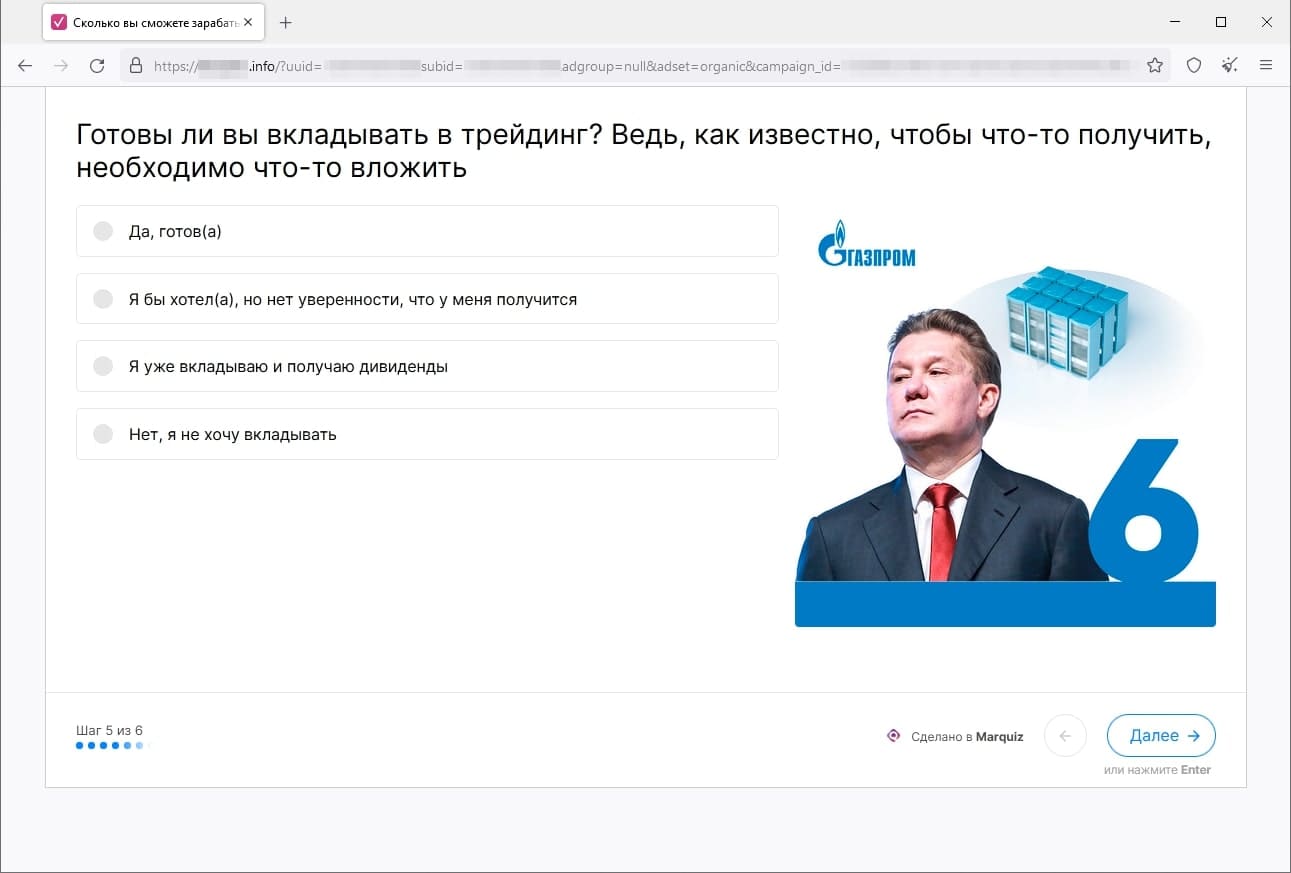
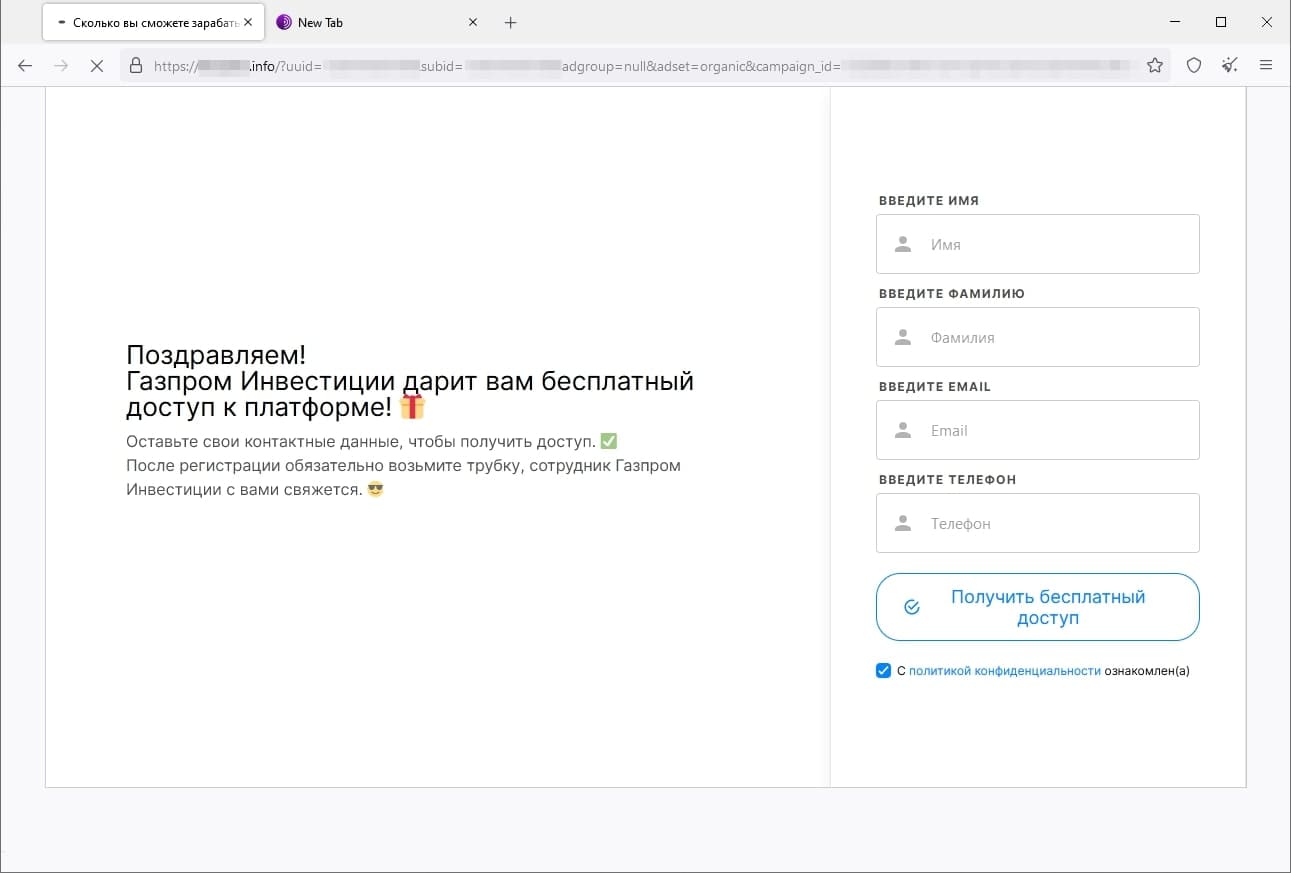
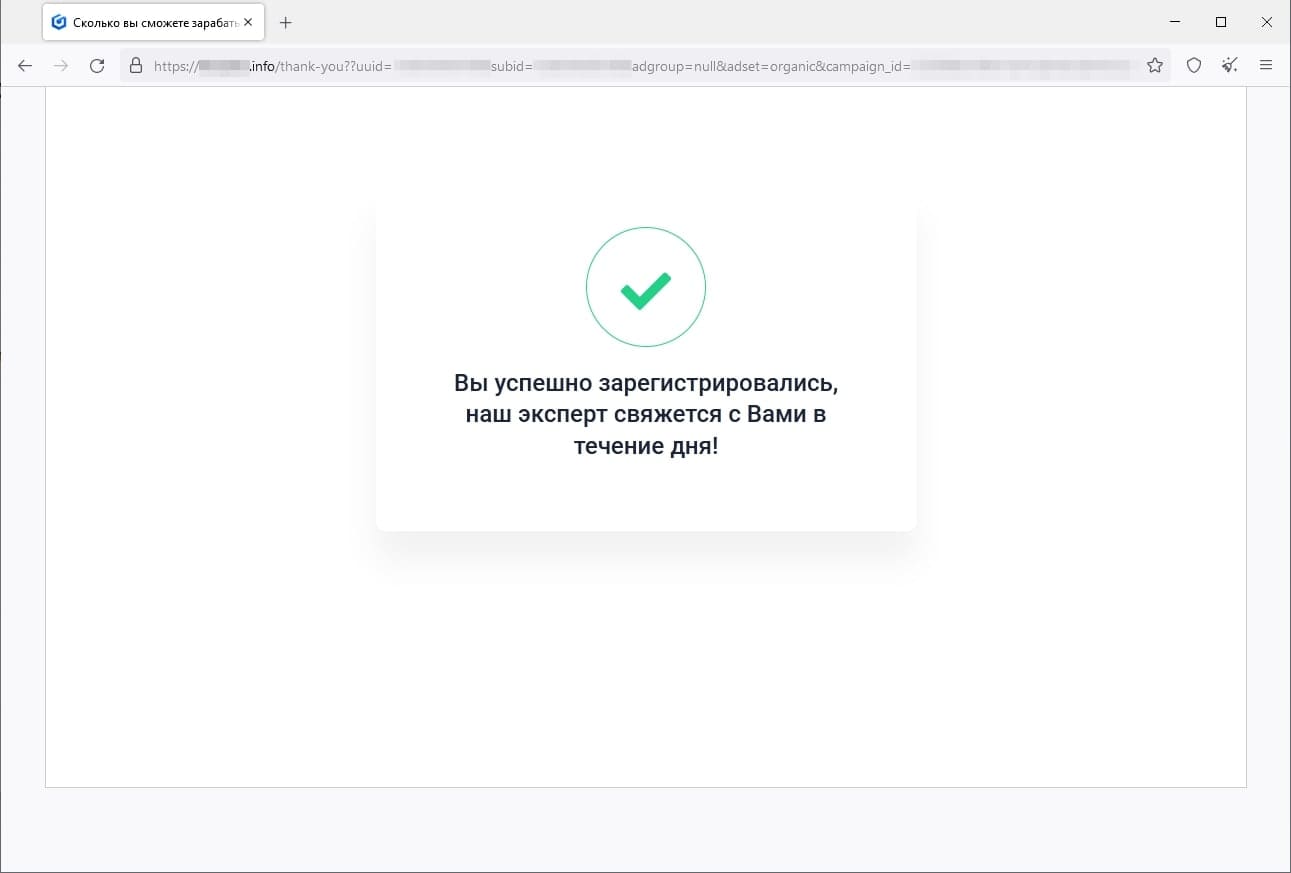
In March, Doctor Web’s Internet analysts again observed the activity of fraudsters who tried luring users to fake investment-related websites, such as web resources allegedly affiliated with famous companies. When potential victims visit such sites, they are offered the opportunity to gain access to certain investing platforms that allegedly allow people to make money from their investments quickly and without any risks. In reality, the malicious actors are misleading users: they collect their personal information and involve them in various fraudulent schemes, participation in which could lead to financial losses.
The screenshots above depict examples of one such site’s page. First, the visitor is offered “access” to the platform, but they must participate in a formal survey beforehand. Next, the potential victim is requested to provide personal information. Finally, the website displays a message stating that the user has successfully registered an account and that they will be contacted by an “expert” that same day.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
According to the detection statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android, in March, adware trojans from the Android.HiddenAds family remained among the most widespread threats. In addition, users encountered banking trojans and ransomware malware more often. With that, spyware trojans infected protected Android devices less frequently.
During March, our virus analysts discovered dozens of trojan apps from the Android.FakeApp family on Google Play. Threat actors distributed these fake apps under the guise of harmless games and programs. However, their primary functionality was to load different websites, including fraudulent ones. Moreover, our specialists identified cases of Android-based TV box models being infected. The dangerous Android.Pandora.2 backdoor was involved in this attack where the protected system partition was infected. This trojan is capable of performing various malicious actions on the command of threat actors.
The following March events involving mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- An increase in the activity of adware trojans.
- An increase in the number of banking trojans and ransom malware attacks.
- Detected cases of an Android TV box model’s system partition being infected with a dangerous backdoor.
- The discovery of other threats on Google Play.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.
[% END %]