Doctor Web’s August 2022 virus activity review
September 15, 2022
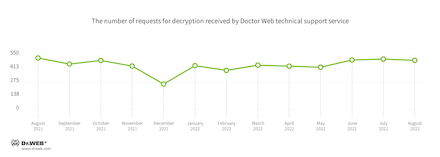
Last month, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders decreased by 2.57%. Once again, the leading encoder trojan was Trojan.Encoder.26996, which accounted for 32.24% of all incidents recorded.
We also observed high trojan activity and shady apps designed to display intrusive ads on Android devices.
Principal trends in August
- An increase in the total number of detected threats
- Adware remains among the most widespread threats
- The number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoder trojans decreased
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service»
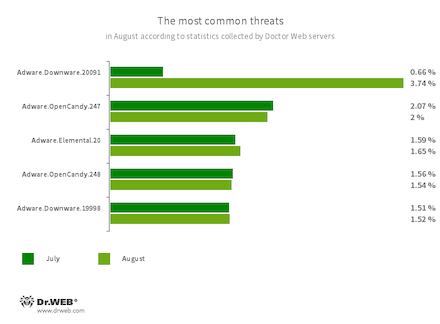
The most common threats of the month:
- Adware.Downware.20091
- Adware.Downware.19998
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirated software.
- Adware.OpenCandy.247
- Adware.OpenCandy.248
- A family of applications that install other software on a system, including other adware.
- Adware.Elemental.20
- Adware that spreads through file sharing services as a result of link spoofing. Instead of normal files, victims receive applications that display advertisements and install unwanted software.
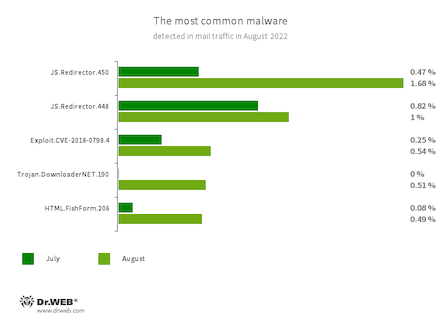
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- JS.Redirector.448
- JS.Redirector.450
- Malicious scripts that redirect users to webpages controlled by fraudsters.
- Exploit.CVE-2018-0798.4
- An exploit designed to take advantage of a Microsoft Office software vulnerability and allow an attacker to run arbitrary code.
- Trojan.DownloaderNET.190
- A trojan app that downloads other malware on targeted computers.
- HTML.FishForm.206
- A webpage spread via phishing emails. It is a bogus authorization page that mimics well-known websites. The credentials a user enters on the page are sent to the attacker.
Encryption ransomware
In August, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders decreased by 2.57% compared to July.
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 32.24%
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 12.17%
- Trojan.Encoder.30356 — 3.95%
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 2.96%
- Trojan.Encoder.11539 — 1.97%
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
Internet scammers remained highly active in August. For example, they continued luring potential victims to pseudo-investing sites that were allegedly tied to large Russian financial and oil and gas sector companies. When visiting such websites, users are often asked to participate in a simple test, register an account by providing personal information, and wait for the “manager” to call back. If they believe such offers and proceed, these users are willingly providing an unknown third-party with their confidential data. On top of that, they might start receiving unwanted phone calls—both from scammers pretending to be bank employees and from some other dubious people, like company representatives advertising their services.
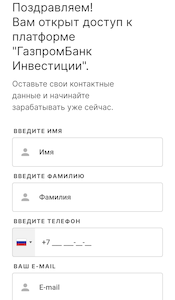
An example of one such site is shown below. First, visitors are invited to take a test, which is scripted and the answers do not affect the final result in any way. Next, users are allegedly granted access to the investing platform of a large Russian bank. Last, they are asked to provide their contact data: first and last names, mobile phone number, and email. When they do that, they receive a message stating that the registration was successful and that soon they will be contacted by an “expert”.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In August, an increase was observed in trojan activity and apps designed to display unwanted and intrusive ads on Android devices. The activity of specialized software platforms that allow applications to launch other apps without installing them also increased. At the same time, the activity of the Android.Spy.4498 trojan, designed to steal information from other apps’ notifications, continued to decrease.
The following August events involving mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- An increase in the activity of malware and dubious apps designed to display intrusive ads;
- A decrease in Android.Spy.4498 trojan activity.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.