Doctor Web’s June 2022 review of virus activity on mobile devices
July 26, 2022
Over the month, Doctor Web’s malware analysts discovered dozens of malicious apps on Google Play. Among them were adware trojans, fake apps used by scammers, info-stealers targeting confidential data, and others.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN JUNE
- The continued decline in Android.Spy.4498 activity
- Decreased adware trojan activity
- The discovery of numerous trojan apps on Google Play
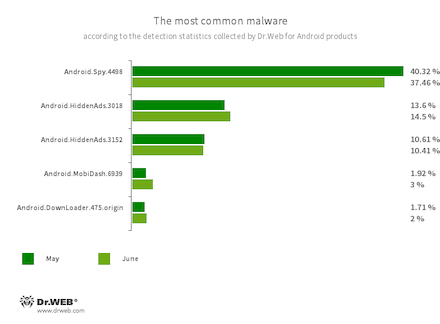
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android
- Android.Spy.4498
- A trojan that steals the contents of other apps’ notifications. In addition, it can download apps and prompt users to install them, and it can also display various dialog boxes.
- Android.HiddenAds.3018
- Android.HiddenAds.3152
- Trojans designed to display intrusive ads. Trojans of this family are often distributed as popular and harmless applications. In some cases, other malware can install them in the system directory. When these trojans infect Android devices, they typically conceal their presence from the user. For example, they “hide” their icons from the home screen menu.
- Android.MobiDash.6939
- A trojan that displays obnoxious ads. It is a special software module that developers incorporate into applications.
- Android.DownLoader.475.origin
- A trojan that downloads other malware and unwanted software. It can be hidden inside seemingly harmless apps found on Google Play or malicious websites.
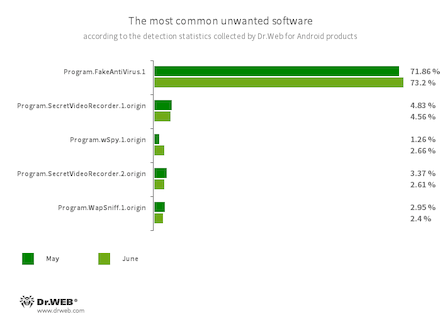
- Program.FakeAntiVirus.1
- The detection name for adware programs that imitate anti-virus software. These apps inform users of non-existing threats, mislead them, and demand that they purchase the software’s full version.
- Program.SecretVideoRecorder.1.origin
- Program.SecretVideoRecorder.2.origin
- The detection name for various modifications of an application that is designed to record videos and take photos in the background using built-in Android device cameras. It can operate covertly by allowing notifications about ongoing recordings to be disabled. It also allows an app’s icon and name to be replaced with fake ones. This functionality makes this software potentially dangerous.
- Program.wSpy.1.origin
- A commercial spyware app designed to covertly monitor Android device user activity. It allows intruders to read SMS and chats in popular messaging software, listen to the surroundings, track device location and browser history, gain access to a phonebook and contacts, photos and videos, and take screenshots and pictures through a device’s built-in camera. In addition, it has keylogger functionality.
- Program.WapSniff.1.origin
- An Android program designed to intercept WhatsApp messages.
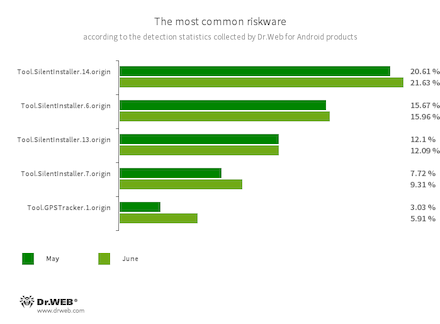
- Tool.SilentInstaller.14.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.6.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.13.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.7.origin
- Riskware platforms that allow applications to launch APK files without installing them. They create a virtual runtime environment that does not affect the main operating system.
- Tool.GPSTracker.1.origin
- A specialized software platform designed to covertly track user location and movement. It can be built into various apps and games.
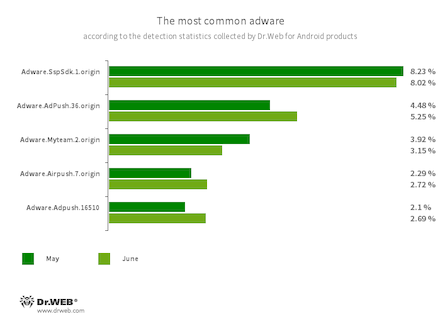
Program modules incorporated into Android applications. These are designed to display obnoxious ads on Android devices. Depending on their family and modifications, they can display full-screen ads and block other apps’ windows, show various notifications, create shortcuts, and load websites.
- Adware.SspSdk.1.origin
- Adware.AdPush.36.origin
- Adware.Adpush.16510
- Adware.Myteam.2.origin
- Adware.Airpush.7.origin
Threats on Google Play
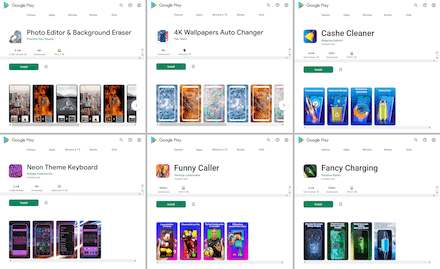
In June, Doctor Web’s virus laboratory uncovered almost 30 adware trojans from the Android.HiddenAds family, with more than 9,890,000 downloads combined. These included both new members of the family (like Android.HiddenAds.3168, Android.HiddenAds.3169, Android.HiddenAds.3171, Android.HiddenAds.3172, and Android.HiddenAds.3207), and new modifications of the already known Android.HiddenAds.3158 malware, which was covered in our May review.
All of them were built into various programs, including image-editing software, virtual keyboards, system tools and utilities, calling apps, wallpaper collection apps, and others.
Below is a list of the names of the apps containing these trojans:
- Photo Editor: Beauty Filter (gb.artfilter.tenvarnist)
- Photo Editor: Retouch & Cutout (de.nineergysh.quickarttwo)
- Photo Editor: Art Filters (gb.painnt.moonlightingnine)
- Photo Editor - Design Maker (gb.twentynine.redaktoridea)
- Photo Editor & Background Eraser (de.photoground.twentysixshot)
- Photo & Exif Editor (de.xnano.photoexifeditornine)
- Photo Editor - Filters Effects (de.hitopgop.sixtyeightgx)
- Photo Filters & Effects (de.sixtyonecollice.cameraroll)
- Photo Editor : Blur Image (de.instgang.fiftyggfife)
- Photo Editor : Cut, Paste (de.fiftyninecamera.rollredactor)
- Emoji Keyboard: Stickers & GIF (gb.crazykey.sevenboard)
- Neon Theme Keyboard (com.neonthemekeyboard.app)
- Neon Theme - Android Keyboard (com.androidneonkeyboard.app)
- Cashe Cleaner (com.cachecleanereasytool.app)
- Fancy Charging (com.fancyanimatedbattery.app)
- FastCleaner: Cashe Cleaner (com.fastcleanercashecleaner.app)
- Call Skins - Caller Themes (com.rockskinthemes.app)
- Funny Caller (com.funnycallercustomtheme.app)
- CallMe Phone Themes (com.callercallwallpaper.app)
- InCall: Contact Background (com.mycallcustomcallscrean.app)
- MyCall - Call Personalization (com.mycallcallpersonalization.app)
- Caller Theme (com.caller.theme.slow)
- Caller Theme (com.callertheme.firstref)
- Funny Wallpapers - Live Screen (com.funnywallpapaerslive.app)
- 4K Wallpapers Auto Changer (de.andromo.ssfiftylivesixcc)
- NewScrean: 4D Wallpapers (com.newscrean4dwallpapers.app)
- Stock Wallpapers & Backgrounds (de.stockeighty.onewallpapers)
- Notes - reminders and lists (com.notesreminderslists.app)
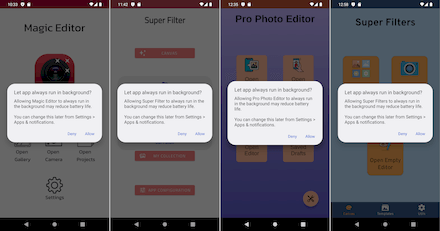
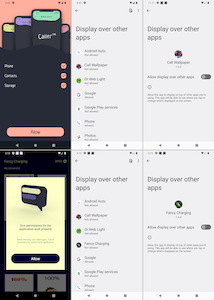
To display ads, some of them request permission to show windows over other apps; the rest ask users to add them to the exclusion list of the battery-saving feature. In addition, to make it more difficult for users to detect malicious apps in the future, the trojans hide their icons from the list of installed apps in the home screen menu—or, they replace the icons with less noticeable ones. Take, for example, the icon named “SIM Toolkit”, which when selected, launches an eponymous system app for working with SIM cards—instead of the original app.
Below are examples of how these trojans try to gain access to needed functions:
An example of how one of the trojans replaces its icon:
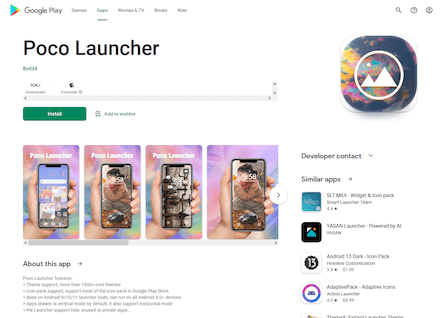
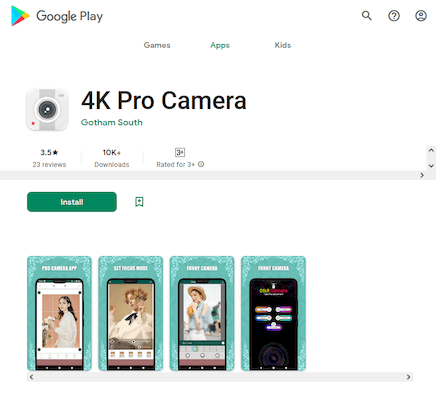
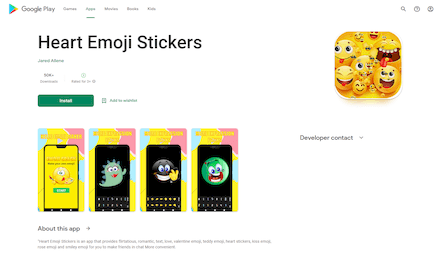
Moreover, our specialists discovered yet other trojans from the Android.Joker family which are capable of downloading and executing arbitrary code and subscribing victims to paid mobile services without their knowledge. One of them was hidden in third-party launcher “Poco Launcher”, while another was in the “4K Pro Camera” app. A third was in the ‘Heart Emoji Stickers” stickers collection app. They were added to the Dr.Web virus database as Android.Joker.1435, Android.Joker.1461, and Android.Joker.1466, respectively.
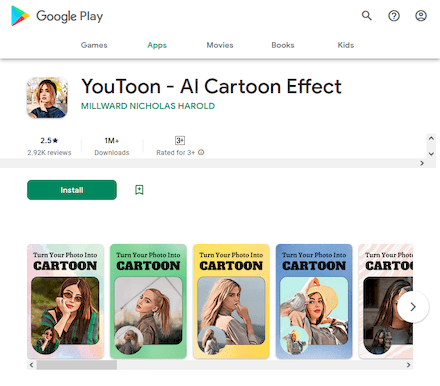
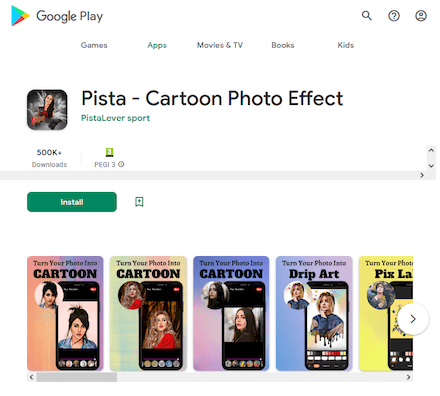
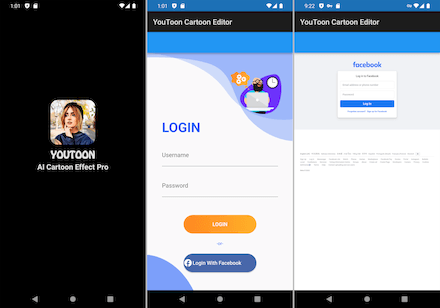
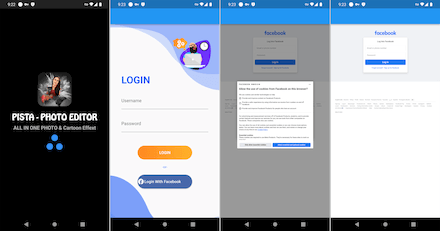
New malware from the Android.PWS.Facebook family were also among the threats we discovered. Dubbed Android.PWS.Facebook.149 and Android.PWS.Facebook.151, they are designed to steal data that can be used to hack Facebook accounts. The trojans were distributed as image editing software under the names “YouToon - AI Cartoon Effect” and “Pista - Cartoon Photo Effect”.
Upon launching, they asked potential victims to log in to their accounts and then loaded a genuine Facebook authorization page. Next, they hijacked the authentication data and sent it to malicious actors.
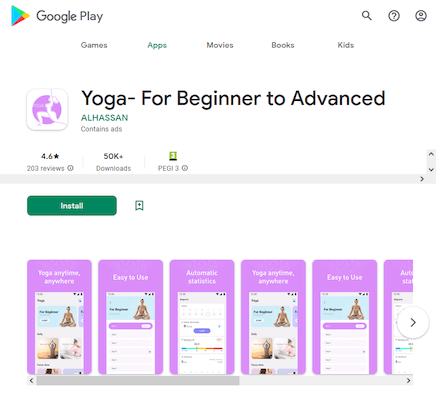
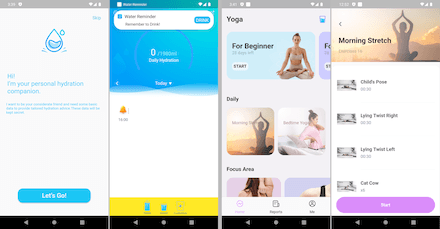
Doctor Web’s specialists also discovered an Android.Click.401.origin trojan. It was hiding in two apps: “Water Reminder- Tracker & Reminder”, which helped users drink more water and stay hydrated, and “Yoga- For Beginner to Advanced”, a yoga curriculum app. Both were fully functional software, so users had no reasons to suspect that they were malicious.
This trojan decrypts and launches the main malicious component (detected by Dr.Web as Android.Click.402.origin) hidden inside its file resources, which covertly loads various websites in WebView. Next, this component simulates user actions, automatically clicking on interactive elements located on these sites—for example, banners and advertisement links.
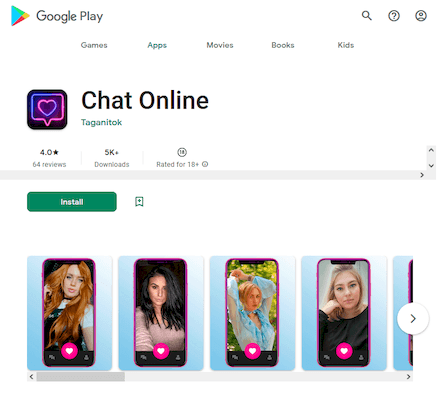
Another uncovered threat was a fake app for online communication called “Chat Online”. Several modifications of this malware were added to the Dr.Web virus database as Android.FakeApp.963 and Android.FakeApp.964.
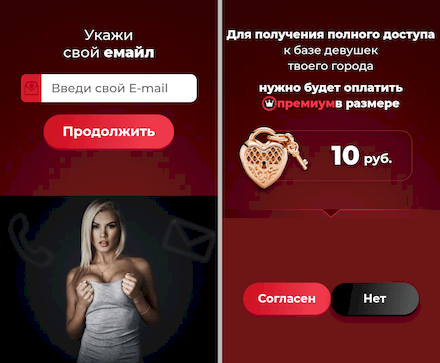
This trojan does not provide any of its declared functionality. It only loads different websites, including fraudulent ones. On some of them, the process of registering for online dating services is simulated. And this is when potential victims are asked to provide their mobile phone number, email, and other personal data. This information could subsequently end up on the black market and be used by scammers.
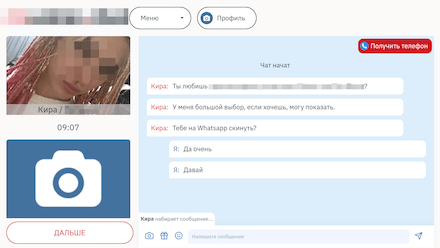
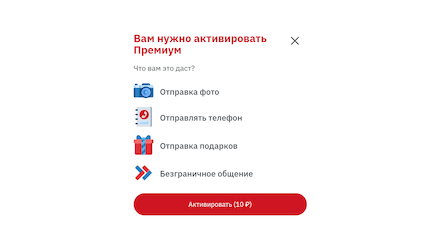
On other websites, a dialog with a real person is imitated, and the user is then asked to pay for full premium access to continue “chatting”. Any user agreeing to this can end up not only having their account debited for a one-time set amount or being subscribed to a paid service they don’t need, but also losing all their money—if cybercriminals get hold of their bank card details.
Doctor Web informed Google about the discovered threats. At the time of this review’s release, some of the malicious apps were still available for download.
To protect your Android device from malware and unwanted programs, we recommend installing Dr.Web anti-virus products for Android.

Your Android needs protection.
Use Dr.Web
- The first Russian anti-virus for Android
- Over 140 million downloads—just from Google Play
- Available free of charge for users of Dr.Web home products