Doctor Web’s May 2022 virus activity review
June 14, 2022
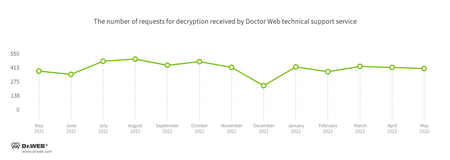
In May, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders decreased by 2.53%, compared to the previous month. Trojan.Encoder.26996 was the most active, accounting for almost 37.47% of all incidents.
Principal trends in May
- The spread of malware in email traffic
- Adware remains the top threat
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
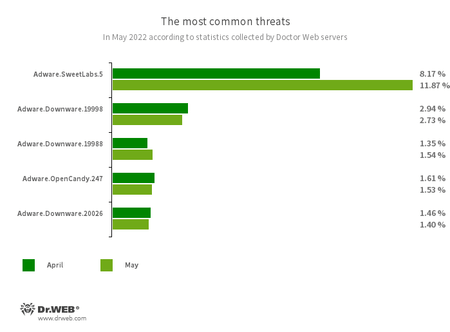
The most common threats of the month:
- Adware.SweetLabs.5
- An alternative app store and an add-on for Windows GUI (graphical user interface) by the creators of “OpenCandy” adware.
- Adware.Downware.19998
- Adware.Downware.19988
- Adware.Downware.20026
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirate software.
- Adware.OpenCandy.247
- A family of applications that install other software on a system.
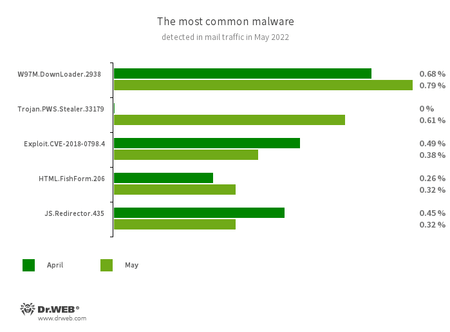
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents. They can also download other malicious programs to a compromised computer.
- Trojan.PWS.Stealer.33179
- A trojan designed to steal passwords and other confidential user data.
- Exploit.CVE-2018-0798.4
- An exploit designed to take advantage of a Microsoft Office software vulnerability and allow an attacker to run arbitrary code.
- HTML.FishForm.206
- A web page spread via phishing emails. It is a bogus authorization page that mimics well-known websites. The credentials a user enters on the page are sent to the attacker.
- JS.Redirector.435
- A malicious script that redirects users to a web page controlled by fraudsters.
Encryption ransomware
User requests to decrypt files affected by encoders decreased by 2.53%, compared to the previous month.
- Trojan.Encoder.26996—37.47%
- Trojan.Encoder.3953—13.93%
- Trojan.Encoder.567—3.72%
- Trojan.Encoder.11539—2.17%
- Trojan.Encoder.33749—1.86%
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
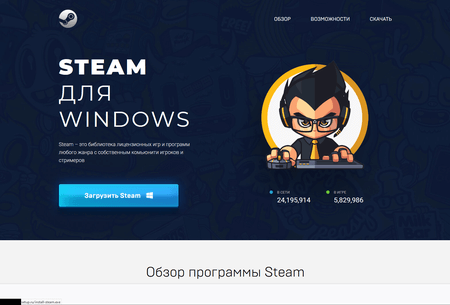
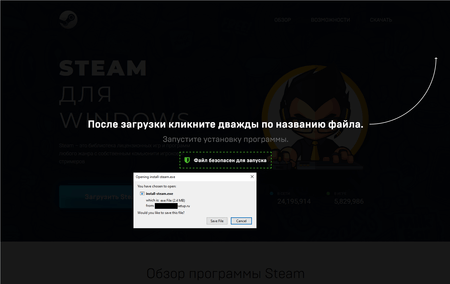
In May 2022, the number of sites masquerading as official download pages of various popular software continued to grow. Cybercrooks continued to use these websites to spread bogus installers that delivered adware and malware to users’ computers.
The snapshot above shows an example of such a website and the launch of such an installer. The website has a certificate with a valid digital signature and additionally notifies the user that the file is allegedly safe to run.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In May, Android.Spy.4498, which steals information from other apps’ notifications, was again the most common mobile threat. That said, its activity continued to decrease. Advertisement trojans from the Android.HiddenAds family also remained among the most widespread Android threats. Their activity, on the contrary, increased slightly compared to April.
During May, Doctor Web analysts discovered new malicious programs in the Google Play catalog. Among them are fraudulent apps from the Android.FakeApp family and Android.Subscription trojans that subscribe users to paid services. Above that, new variants of trojans from Android.PWS.Facebook family were revealed. They steal credentials and other data that is needed to hack Facebook accounts. Fraudsters also spread Android.HiddenAds advertisement trojans in the Google Play catalog.
The following May events related to mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- Decreased activity of Android.Spy.4498 spyware;
- Increased activity of advertising trojans;
- New malicious applications emerging on Google Play.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.