Doctor Web’s March 2022 virus activity review
April 18, 2022
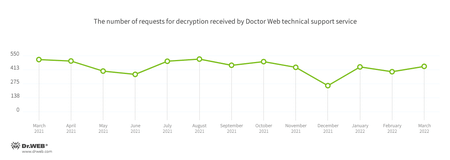
In March, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders increased by 13.2% compared to February. Trojan.Encoder.26996 was the most active, accounting for almost a quarter of all incidents.
Principal trends in March
- An increase in the number of unique threats
- Adware remains the top threat
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
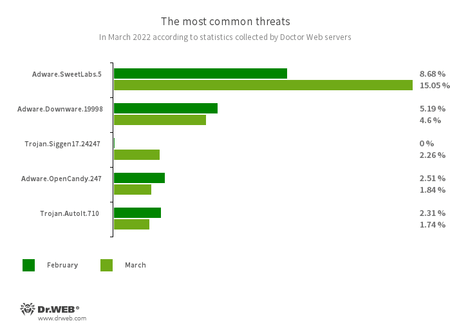
The most common threats in March:
- Adware.SweetLabs.5
- An alternative App Store and Add-On for Windows GUI (graphical user interface) by the creators of the “OpenCandy" Adware.
- Adware.Downware.19998
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirate software.
- Trojan.Siggen17.24247
- Trojan from the Siggen family.
- Adware.OpenCandy.247
- A family of applications that install other software on the system.
- Trojan.AutoIt.710
- A malicious utility program written in AutoIt language and distributed as part of a miner or RAT trojan.
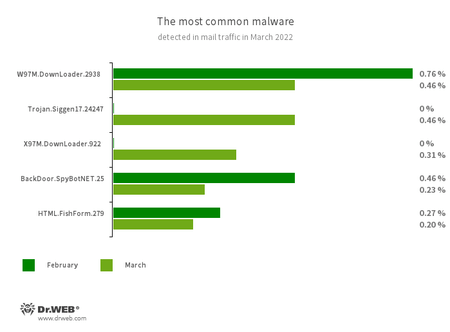
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- X97M.DownLoader.922
- A family of downloader trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents. It can also download other malicious programs to a compromised computer.
- Trojan.Siggen17.24247
- Trojan from the Siggen family.
- BackDoor.SpyBotNET.25
- A backdoor written in VB.NET. It can operate with a file system (copy, create, delete catalogs, etc.), terminate processes, and take screenshots.
- HTML.FishForm.279
- A web page spread via phishing emails. It is a bogus authorization page that mimics well-known websites. The credentials that user sends on the page are sent to the attacker.
Encryption ransomware
User requests to decrypt files affected by encoders increased by almost 13.26% compared to February.
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 26.23%
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 13.99%
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 8.04%
- Trojan.Encoder.30356 — 1.40%
- Trojan.Encoder.11539 — 1.05%
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
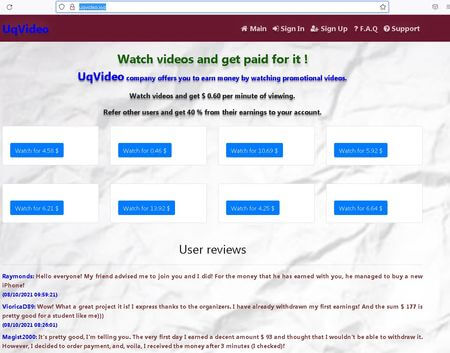
In March 2022, Doctor Web’s analysts’ attention was drawn to increased sites, that supposed to pay money for watching videos. It is assumed that the potential victim will end up on a site where the obligatory part of registration will be the input of bank card number. In fact, the cybercriminals will receive valuable data, and the victim will not be paid anything.
The snapshot shows an example of a website like this. Here are the prices for watching the video and the excited reviews from those who have already allegedly made money on it.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In March, Doctor Web warned users about CoinSteal trojans designed to steal cryptocurrencies from owners of Android and iOS devices. Attackers have embedded malicious applications into some versions of popular crypto wallets such as imToken, MetaMask, Bitpie and TokenPocket to distribute them as original ones. Trojans stole secret seed-phrases needed to access crypto wallets.
Besides that, our virus laboratory found another threats on Google Play. Among them were Android.FakeApp and a trojan called Android.PWS.Facebook.134. The former is used in various scam schemes. The latter is made for stealing confidential information required to access user Facebook accounts.
According to the detection statistics of Dr.Web anti-virus products for Android, in March, the Android.Spy.4498 trojan became the most common threat again. This trojan steals information from notifications from other applications. At the same time, its activity slightly decreased compared to the previous month. Withal, advertising trojans again showed high activity.
The following March events related to mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- A decline in the Android.Spy.4498 activity
- High activity of adware trojans
- The discovery of malicious applications designed to steal cryptocurrencies from Android and iOS device users.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.