Doctor Web’s January 2022 review of virus activity on mobile devices
March 15, 2022
During the month, our specialists discovered more threats on Google Play. Numerous fake apps from the Android.FakeApp family were among them. Malicious actors use these in various scam schemes. Moreover, a new trojan from the Android.PWS.Facebook family has been found. It is designed to steal information required to hack into Facebook accounts. In addition, Doctor Web’s malware analysts uncovered new trojans from the Android.Subscription family. These subscribe users to paid mobile services.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN JANUARY
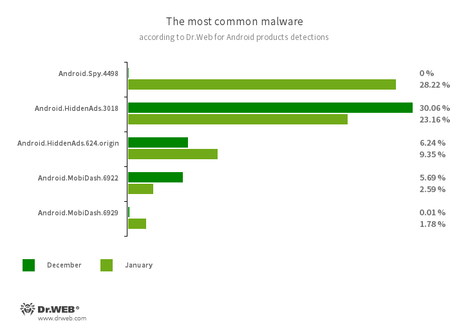
- Android.Spy.4498 trojan became the leader among the threats detected on protected Android devices
- Adware trojans remain one of the most active threats for Android users
- Activity decline in malicious applications that download and execute arbitrary code
- The discovery of new threats on Google Play
Threat of the month
In January, Doctor Web malware analysts traced the spread of a new Android trojan dubbed Android.Spy.4498. Threat actors built it into some versions of unofficial modifications (mods) of WhatsApp messenger, including GBWhatsApp, OBWhatsApp, and WhatsApp Plus. Then, they distributed them through malicious websites.
The main functionality of the Android.Spy.4498 is to hijack the contents from other apps’ notifications. Yet, it also can download apps and offer users to install them and display dialog boxes with the contents it receives from the attackers.
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web for Android
- Android.Spy.4498
- A trojan that steals the contents of other apps’ notifications. In addition, it can download apps and offer users to install them, and can also display various dialog boxes.
- Android.HiddenAds.3018
- Android.HiddenAds.624.origin
- Trojans designed to display obnoxious ads. Trojans of this family are often distributed as popular and harmless applications. In some cases, other malware can install them in the system directory. When these trojans infect Android devices, they typically conceal their presence from the user. For example, they “hide” their icons from the home screen menu.
- Android.MobiDash.6922
- Android.MobiDash.6929
- Trojans that display obnoxious ads. They represent special software modules that the developers incorporate into applications.
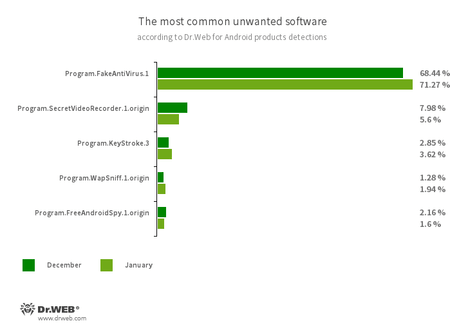
- Program.FakeAntiVirus.1
- The detection name for adware programs that imitate anti-virus software. These apps inform users of non-existing threats, mislead them, and demand they purchase the software’s full version.
- Program.SecretVideoRecorder.1.origin
- An application designed to record videos and take photos in the background using Android devices’ built-in cameras. It can operate covertly, allowing to disable notifications about ongoing recordings. It also allows replacing the app’s icon and name with fake ones. This functionality makes this software potentially dangerous.
- Program.KeyStroke.3
- An Android application capable of intercepting keystrokes. Some modifications of this software can also track incoming SMS, control call history, and record phone calls.
- Program.WapSniff.1.origin
- An Android program designed to intercept WhatsApp messages.
- Program.FreeAndroidSpy.1.origin
- An application that spies on Android users and can be used for cyber espionage. It controls the device’s location, gains access to the user’s phone book and contact list, and can also copy multimedia files, like photos and videos.
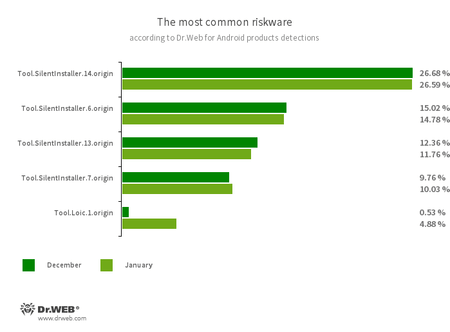
- Tool.SilentInstaller.14.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.6.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.13.origin
- Tool.SilentInstaller.7.origin
- Riskware platforms that allow applications to launch APK files without installation. They create a virtual runtime environment that does not affect the main operating system.
- Tool.Loic.1.origin
- A piece of software capable of sending various types of network packets from Android devices to targeted IP addresses. One of the scenarios for its use is servers’ diagnostics and testing. Yet, it can also be used to perform DDoS (distributed denial-of-service) attacks. That’s why Dr.Web detects it as a potentially dangerous tool.
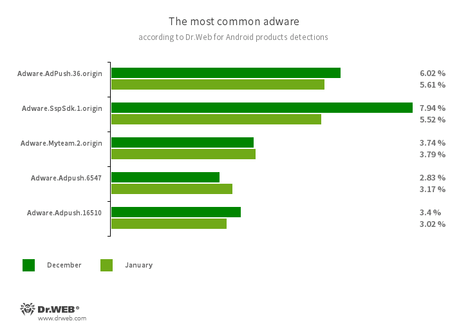
Program modules incorporated into Android applications. These are designed to display obnoxious ads on Android devices. Depending on their family and modifications, they can display full-screen ads and block other apps’ windows, show various notifications, create shortcuts, and load websites.
- Adware.AdPush.36.origin
- Adware.SspSdk.1.origin
- Adware.Myteam.2.origin
- Adware.Adpush.16510
- Adware.Adpush.6547
Threats on Google Play
In January, Doctor Web’s specialists discovered many threats on Google Play. A large number of trojan apps from the Android.FakeApp family were among them. Malicious actors used these in various scam schemes. For example, Android.FakeApp.777 and Android.FakeApp.778 trojans spread under the guise of software that claimed it helped users search and receive social benefits and monetary aids. These were targeting Russian users. In fact, these trojans only loaded fraudulent sites. There, potential victims had to provide their personal information, only to have their money stolen by deception.
Other fake software was distributed as investing apps. These apps claimed to help users allegedly become investors and receive passive income without any financial knowledge. They claimed that all the work would be done for them by a certain trading algorithm or a personal manager. For example, Android.FakeApp.771, Android.FakeApp.772, Android.FakeApp.773, Android.FakeApp.774, Android.FakeApp.775, Android.FakeApp.776, Android.FakeApp.779, and Android.FakeApp.780 trojans spread as “Газпром Инвест”, “Gaz Investor”, “Инвестиции АктивГаз”, and other apps. These allegedly related to the Gazprom company and oil and natural gas market. What’s more, some modifications of the Android.FakeApp.780 allegedly allowed making money on the stock market and cryptocurrencies. These were hiding in the apps called “ТОН” and “Chain Reaction”.
However, all these trojans were also only loading fraudulent websites where potential victims were prompted to create an account. Next, they had to wait for a call from an “operator” or a “personal broker”, and place money into their account so that the “unique algorithm” could proceed with trading and making money.
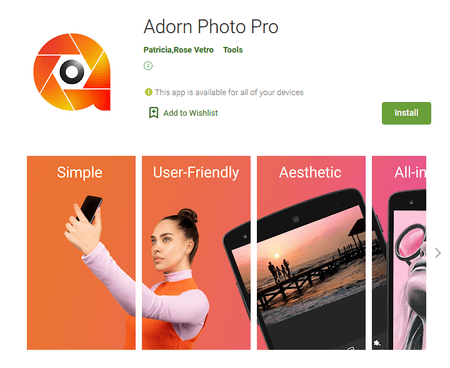
What’s more, another trojan targeting confidential data required to hack into Facebook accounts was uncovered. Dubbed Android.PWS.Facebook.123, this malicious app was distributed as “Adorn Photo Pro” image editing software.
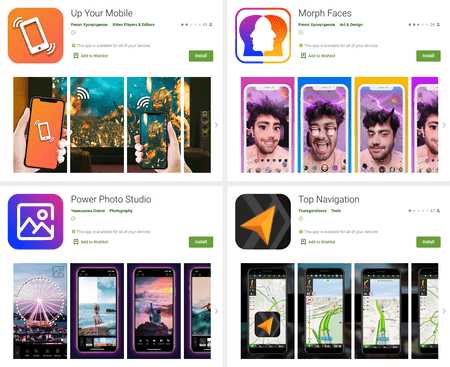
Our malware analysts also discovered new trojans from the Android.Subscription family that subscribe users to paid mobile services. One of them, dubbed Android.Subscription.5, was hiding in various apps. These apps included image editing software, navigation app, multimedia player, and others. Another one, dubbed Android.Subscription.6, spread under the guise of a launcher that followed the design of Apple’s mobile operating system.
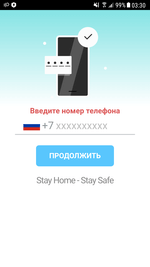
These malicious programs loaded websites of affiliate services that enabled paid subscriptions through the Wap Click technology. On these websites, potential victims are asked to enter their mobile phone number. When they do that, an attempt to automatically activate the service is made.
To protect your Android device from malware and unwanted programs, we recommend installing Dr.Web for Android.

Your Android needs protection.
Use Dr.Web
- The first Russian anti-virus for Android
- Over 140 million downloads—just from Google Play
- Available free of charge for users of Dr.Web home products