Doctor Web’s November 2021 virus activity review
December 9, 2021
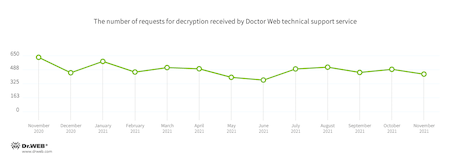
In November, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders decreased by 11.4% compared with October. Trojan.Encoder.26996 was the most active encoder, accounting for 32.93% of all incidents.
Principal trends in November
- Malware activity massively drops.
- Adware remains among the top threats.
- User requests to decrypt files affected by encoders witness a decline.
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
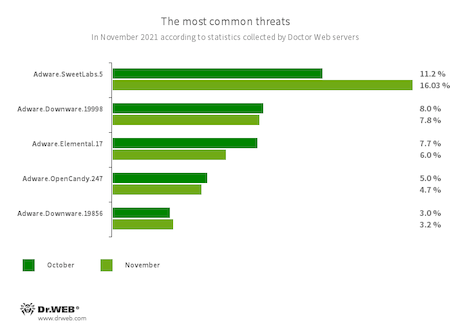
The most common threats in November:
- Adware.SweetLabs.5
- An alternative App Store and Add-On for Windows GUI (graphical user interface) by the creators of Adware, such as “OpenCandy".
- Adware.Downware.19998
- Adware.Downware.19856
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirate software.
- Adware.Elemental.17
- Adware that spreads through file-sharing services as a result of link spoofing. These links aren’t normal files. They’re applications that display advertisements and install unwanted software.
- Adware.OpenCandy.247
- A family of applications that install other software on the system.
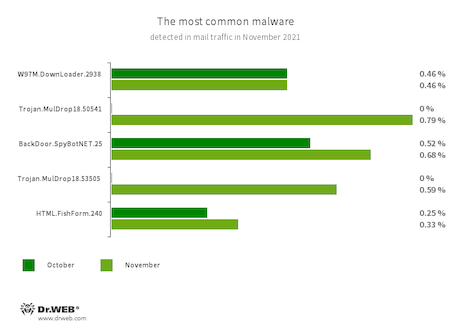
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploits vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents and can download other malicious programs to a compromised computer. It is designed to download other malware onto a compromised computer.
- Trojan.MulDrop18.50541
- Trojan.MulDrop18.53505
- A malicious program that downloads unwanted applications to a victim's computer.
- BackDoor.SpyBotNET.25
- A backdoor written in VB.NET and designed to operate with a file system (to copy, create, delete catalogs, etc.), terminate processes, and take screenshots.
- HTML.FishForm.240
- This is a web page that spreads via phishing emails. It is a fake authorization page that mimics well-known websites.
Encryption ransomware
User requests to decrypt files affected by encoders decreased by almost 7.66% compared to October.
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 32.93%
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 10.77%
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 4.31%
- Trojan.Encoder.11539 — 3.38%
- Trojan.Encoder.30356 — 2.77%
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
In November 2021, Doctor Web’s analysts’ attention was drawn to increased fraud investment sites disguised as one of the biggest oil companies. Through these fake websites, fraudsters offer more than 300 euros per day to every person who wants to invest in oil products.
This snapshot shows the Shell phishing page that contains cybercriminals’ call for investing in the popular company. If the user isn’t careful, they can fall victim to this attack.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In November, Doctor Web published research that showcased vulnerabilities in children’s smart watches. The results of the research show that these watches’ safety levels are unsatisfactory. In particular, some of them may contain trojans.
Moreover, Doctor Web malware analysts detected new threats on the Google Play and AppGallery catalogs. They discovered trojans that enroll victims in paid services. Dr.Web anti-virus products for Android detected adware trojans and other malicious programs that download applications capable of executing arbitrary code.
The following November events regarding mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- High activity of adware trojans
- Emergence of new malicious applications on Google Play
- Emergence of new Trojan in the AppGallery catalog
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.