Doctor Web’s January 2021 virus activity review
February 24, 2021
Our January analysis of Dr.Web’s statistics revealed a 4.92% increase in the total number of threats compared to the previous month. The number of unique threats also increased by 13.11%. Adware and malware browser extensions still occupy the top spot for detected threats. Various modifications of the AgentTesla stealers, a backdoor written in VB.NET and malicious programs exploiting vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office utilities were the most frequently detected malicious software in email traffic.
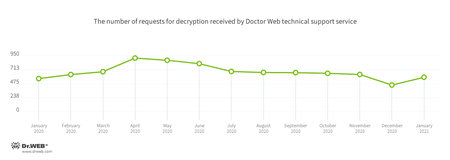
In January, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders increased by 29.27% compared with December. Trojan.Encoder.26996 was the most active, accounting for 24.11% of all incidents.
Principal trends in January
- Growth in malware spreading activity
- Adware remain among the most active threats
- An increase in the number of requests to decrypt files affected by encoders
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
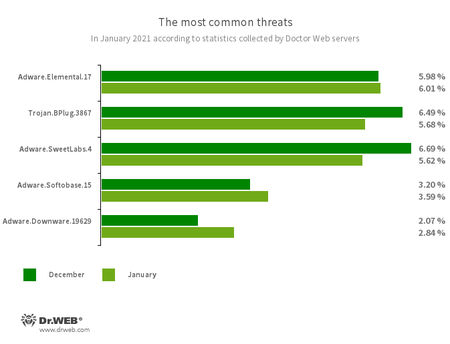
The most common threats in January:
- Adware.Elemental.17
- Adware that spreads through file sharing services as a result of link spoofing. Instead of normal files, victims receive applications that display advertisements and install unwanted software.
- Trojan.BPlug.3867
- A malicious browser extension designed to perform web injections into viewed webpages and block third-party advertisements.
- Adware.SweetLabs.4
- An alternative app store and add-on for Windows GUI from the creators of Adware.Opencandy.
- Adware.Softobase.15
- Installation adware that spreads outdated software and changes the browser settings.
- Adware.Downware.19629
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirate software.
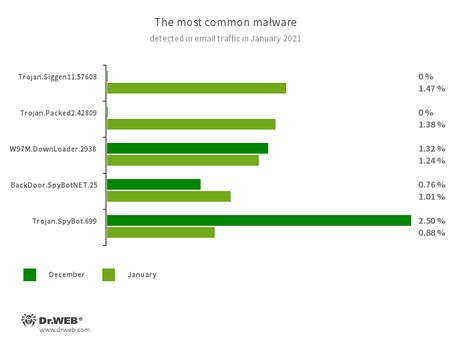
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- Trojan.Siggen11.57608
- A modification of the stealer malware, known as AgentTesla. It can be used as a keylogger and is designed to steal confidential data.
- Trojan.Packed2.42809
- One of the many modifications of the AgentTesla stealer, obfuscated by a packer tool.
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploits vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents and can download other malicious programs onto a compromised computer.
- BackDoor.SpyBotNET.25
- A backdoor written in VB.NET and designed to operate with a file system (to copy, create, delete catalogs, etc.), terminate processes, and take screenshots.
- Trojan.SpyBot.699
- A multi-module banking trojan that allows cybercriminals to download and launch various applications on an infected device and run arbitrary code.
Encryption ransomware
In January, Doctor Web’s virus laboratory registered 29.27% more requests to decode files encoded by trojan ransomware than in December.
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 24.11%
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 13.10%
- Trojan.Encoder.29750 — 7.44%
- Trojan.Encoder.11549 — 2.08%
- Trojan.Encoder.30356 — 1.49%
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
During January 2021, Doctor Web Internet analysts uncovered many fraudulent and phishing websites used by the cybercriminals to steal users’ money and personal data. The victims were most often propositioned to receive some nonexistent payment from the state or a remittance from a private individual. In all cases, a commission was required to receive the payments.
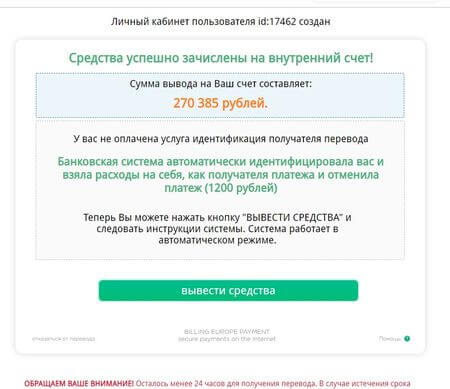
This is a snapshot of the fraudulent webpage. It invites a victim to receive a fake payment and claims that the amount has been transferred to an “internal” account. The trick is that the user has to pay a fee first in order to complete the transfer.
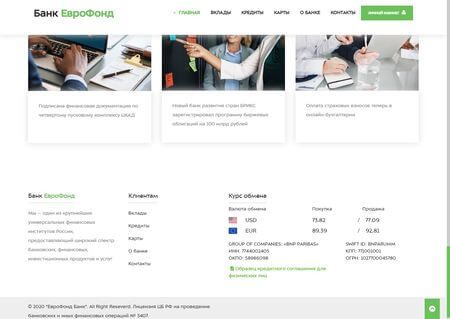
Also in January, analysts discovered several fake banking websites. The fraudsters registered the websites in the “.рф” domain and used the same template to create the same type of webpages that differ only in the fictitious names of the banks. These bogus resources were used to steal funds from the accounts of gullible users.
This is a snapshot of nonexistent bank’s website. A user can browse the clickable sections and read the contents.
In January, Doctor Web specialists also detected numerous fake online payment services that were used in conjunction with fraudulent marketplaces and allowed cybercrooks to steal not only money, but also users ' bank card data.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
The total number of January threats on Android devices decreased by 11.32% compared to the previous month. With that, the malicious applications that can download other software and execute arbitrary code, as well as trojans that showed ads were among the most common mobile threats.
During the month, Doctor Web’s virus analysts identified many malicious apps of the Android.FakeApp family, designed to load fraudulent websites in the Google Play catalog. In addition, other modifications of the Android.Joker multi-functional trojan family were uncovered. One of their features is to subscribe users to expensive mobile services. The malware creators also distributed applications with built-in unwanted advertising modules called Adware.NewDich.
These modules loaded various websites in the browser, which could include both harmless and malicious resources, as well as webpages with ads.
The banking trojans were also active. One of them was discovered in Google Play and the others were distributed via malicious websites.
The following January events related to mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- A decline in malware activity on protected devices
- The emergence of many new malicious and unwanted programs in the Google Play catalog.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.