Doctor Web’s April 2020 virus activity review
May 22, 2020
In April, an analysis of Dr. Web’s statistics revealed a 34.5% decrease in the total number of threats compared to the previous month. The number of unique threats dropped by 11.42%. Adware and malware browser extensions still made up the majority of detected threats. The Trojan.SpyBot.699 banking trojan along with malware that exploits vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office programs were the most frequently detected malicious software in email traffic. In addition, the most common threats included malicious HTML documents distributed as email attachments and redirecting users to phishing websites.
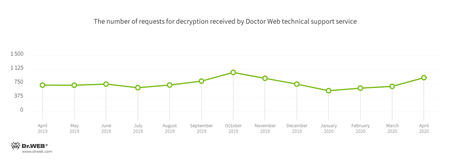
In April, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders increased by 34.27% compared with March. Trojan.Encoder.26996 was the most active encoder, accounting for 32.71% of all incidents.
Principal trends in April
- A decline in malware spreading activity
- Adware remain amongst the most active threats
- A notable rise in encoder activity
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
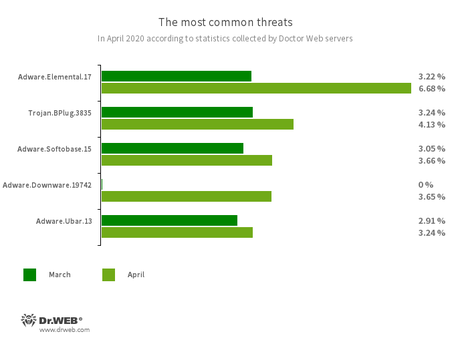
The most common threats in April:
- Adware.Elemental.17
- Adware that spreads through file sharing services as a result of link spoofing. Instead of normal files, victims receive applications that display advertisements and install unwanted software.
- Trojan.BPlug.3835
- A malicious browser extension designed to perform web injections into viewed webpages and block third-party advertisements.
- Adware.Softobase.15
- Installation adware that spreads outdated software and changes the browser’s settings.
- Adware.Downware.19742
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirate software.
- Adware.Ubar.13
- A torrent client designed to install unwanted programs on a user’s device.
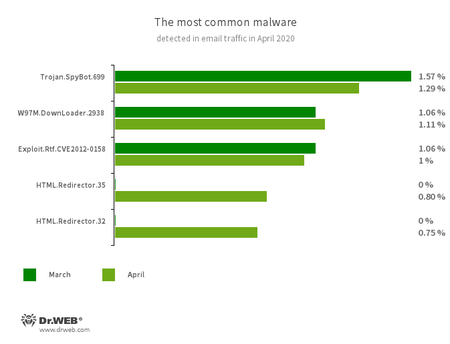
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- Trojan.SpyBot.699
- A multi-module banking trojan that allows cybercriminals to download and launch various applications on an infected device and run arbitrary code.
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploits vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents and can download other malicious programs to a compromised computer.
- Exploit.CVE-2012-0158
- A modified Microsoft Office document that exploits the CVE-2012-0158 vulnerability in order to run malicious code.
- HTML.Redirector.35
- HTML.Redirector.32
- Malicious HTML documents that are often disguised as harmless email attachments. Upon opening, the code redirects users to phishing websites or downloads payload with malware to the computers.
Encryption ransomware
In April, Doctor Web’s virus laboratory registered 34.27% more requests to decode files encoded by trojan ransomware than in March.
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 32.71%
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 7.84%
- Trojan.Encoder.29750 — 2.73%
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 2.39%
- Trojan.Encoder.31430 — 1.87%
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
In April 2020, Doctor Web added 140,188 URLs to the Dr.Web database of non-recommended websites.
| March 2020 | April 2020 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 186,881 | + 140,188 | - 24.99% |
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In April, the total number of threats on Android devices increased by 16.46%, as compared to March. The Doctor Web laboratory uncovered new threats on the Google Play catalog. These include other modifications of the Android.Circle family, which spread under the guise of harmless applications and were executing criminal commands. In addition, Doctor Web virus analysts added new signatures for the Android.HiddenAds.2124 advertising trojan and the Android.Joker.164 malware program, which subscribed victims to paid services and ran arbitrary code.
The following April events related to mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- Detection of new threats on Google Play
- Growth in malware activity on protected devices
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.