Doctor Web’s February 2020 virus activity review
March 19, 2020
In February, an analysis of Dr.Web’s statistics revealed an increase in the total number of threats by 4.86% compared with the previous month. The number of unique threats dropped by 8.38%. Adware still made up the majority of detected threats. Email traffic was dominated by malware that exploits vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office programs. With that, detections of the Trojan.SpyBot.699 banking trojan continued to increase.
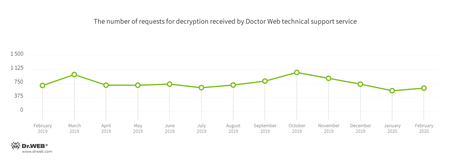
In February, the number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encoders increased by 12.32% compared with January. Trojan.Encoder.26996 was the most active encoder, accounting for 29.06% of all incidents.
Principal trends in February
- Adware remains amongst the most common threats
- A growth in ransomware activity
Threat of the month
In February, Doctor Web virus analysts reported that the VSDC video editor’s download link had been compromised on the popular software platform CNET. Instead of the genuine program, visitors received a modified installer bundled with TeamViewer valid files and a downloader trojan that further retrieved malicious auxiliary modules from the repository. Thus, the computer was infected with a trojan from the BackDoor.TeamViewer family, which allowed attackers to establish an unauthorised connection to an infected computer, as well as with a script for bypassing Microsoft Windows’s built-in anti-virus protection. Utilising BackDoor.TeamViewer, the attackers were able to deliver payload modules with malware such as stealers, keyloggers and RAT to infected devices.
According to Doctor Web’s statistics service
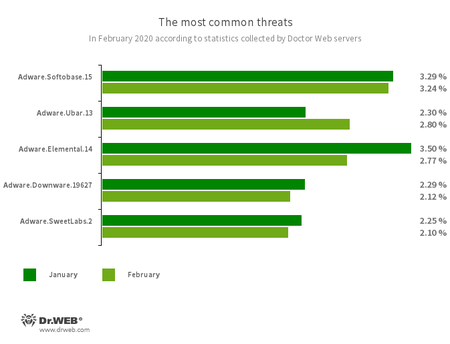
The most common threats in February:
- Adware.Softobase.15
- Installation adware that spreads outdated software and changes browser settings.
- Adware.Ubar.13
- A torrent client designed to install unwanted programs on a user’s device.
- Adware.Elemental.14
- Adware that spreads through file sharing services as a result of link spoofing. Instead of normal files, victims receive applications that display advertisements and install unwanted software.
- Adware.Downware.19627
- Adware that often serves as an intermediary installer of pirate software.
- Adware.SweetLabs.2
- An alternative app store and add-on for Windows GUI from the creators of Adware.Opencandy.
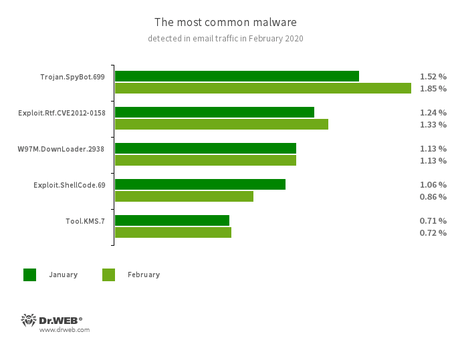
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- Trojan.SpyBot.699
- A multi-module banking trojan. It allows cybercriminals to download and launch various applications on an infected device and run arbitrary code.
- Exploit.CVE-2012-0158
- A modified Microsoft Office document that exploits the CVE-2012-0158 vulnerability in order to run malicious code.
- W97M.DownLoader.2938
- A family of downloader trojans that exploits vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents and can download other malicious programs to a compromised computer.
- Exploit.ShellCode.69
- A malicious Microsoft Office Word document that exploits the CVE-2017-11882 vulnerability.
- Tool.KMS.7
- Hacking tools that are used to activate illegal copies of Microsoft software.
Encryption ransomware
In February, Doctor Web’s virus laboratory registered 12.32% more requests to decode files encoded by trojan ransomware than in January.
- Trojan.Encoder.26996 — 18.48%
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 10.38%
- Trojan.Encoder.29750 — 4.81%
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 3.54%
- Trojan.Encoder.11464 — 2.78%
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
In February 2020, Doctor Web added 90,385 URLs to the Dr.Web database of non-recommended websites.
| January 2020 | February 2020 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 97 166 | + 90 385 | - 6.98% |
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In February, Dr.Web’s statistics for Android devices confirmed an almost 12% decrease in the total number of threats on protected devices compared with January. Malware, adware and riskware showed less activity, while the number of detected potentially unwanted programs increased.
Doctor Web virus analysts uncovered new threats on Google Play such as adware trojans, fraudulent applications, and other malicious software.
The following February events related to mobile malware are the most noteworthy:
- Detection of new threats on Google Play
- Decline in malware activity on protected devices
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.