Doctor Web’s December 2018 virus activity review
December 28, 2018
The last month of 2018 did not see any noticeable events related to information security. Among the malware detected on computers and in emails, malicious JavaScript scenarios remain prevalent. Most of them are designed to download other malware to an infected device and mine cryptocurrencies using the infected computer’s hardware. Like in November, the multicomponent banking malware Trojan.SpyBot.699 was often detected on hard disks. Cybercriminals can use it to remotely execute various commands on a computer and launch other malicious applications.
Principal trends of December
- Distribution of malicious scripts
- The emergence of new malware for Android
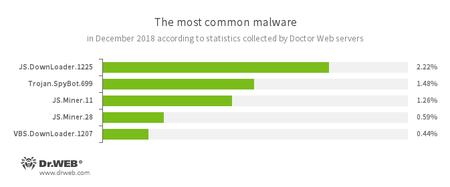
According to Doctor Web statistics servers
- JS.DownLoader
- A family of malicious scripts written in JavaScript and designed to download and install other malware programs on a computer.
- Trojan.SpyBot.699
- A multi-module banking Trojan. It allows cybercriminals to download and launch various applications on an infected device and makes it possible for their commands to be executed. The Trojan is intended to steal money from bank accounts.
- JS.Miner
- A family of JavaScript scenarios designed to covertly mine cryptocurrencies.
- VBS.DownLoader
- A family of malicious VBS scripts designed to download and install other malware on a computer.
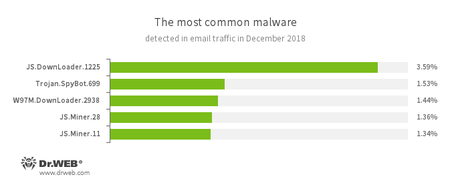
Statistics for malware discovered in email traffic
- JS.DownLoader
- A family of malicious scripts written in JavaScript and designed to download and install other malware programs on a computer.
- Trojan.SpyBot.699
- A multi-module banking Trojan. It allows cybercriminals to download and launch various applications on an infected device and their commands to be executed. The Trojan is intended to steal money from bank accounts.
- W97M.DownLoader
- A family of downloader Trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in office applications and can download other malicious programs to a compromised computer.
- JS.Miner
- A family of JavaScript scenarios designed to covertly mine cryptocurrencies.
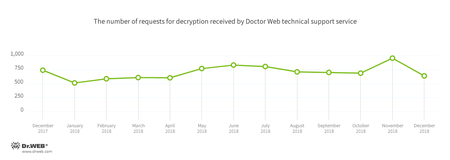
Encryption ransomware
In December, cases involving the following ransomware modifications were registered by Doctor Web’s technical support service:
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 22.34% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.11464 — 11.71% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.11539 — 10.17% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.25574 — 5.08% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 4.93% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.5342— 1.54% of requests.
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
A total of 257,197 URLs from non-recommended websites were added to the Dr.Web database in December 2018.
| November 2018 | December 2018 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 231,074 | + 257,197 | +11.3% |
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In December, Doctor Web experts found the malicious application Android.BankBot.495.origin that targeted Brazilian users on Google Play. It stole confidential banking details and could covertly manage other programs using the accessibility features of Android. Other than that, Google Play turned out to contain adware Trojans from the Adware.HiddenAds and Adware.Patacore families and other malicious and unwanted applications. Virus analysts have also discovered a new version of the commercial spyware Program.Spyzie.1.origin that allowed attackers to spy on mobile device owners.
The following December events related to mobile malware were most noteworthy:
- a banking Trojan targeted Brazilian users;
- a new version of dangerous spyware was detected;
- many malicious and unwanted applications were found on Google Play.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.