Doctor Web’s December 2017 virus activity review
December 29, 2017
The last month of this year is marked by an emergence of a new backdoor for computers and devices running Microsoft Windows. In December, Doctor Web analysts also determined that cybercriminals started hacking websites using a Linux Trojan Linux.ProxyM. Over the course of the month Dr.Web virus databases were updated with the signatures of new malicious programs for Android.
Principal trends of December
- A new Trojan for Linux
- Website hacking using a Linux Trojan
- Distribution of new malicious programs for Android
Threat of the month
In December, virus analysts examined another representative of the Anunak Trojan family capable of executing the commands of cybercriminals on an infected computer. A new backdoor has been developed to work on 64-bit Windows versions and was dubbed BackDoor.Anunak.142. The Trojan can perform the following actions on an infected computer:
- Download files from a specific remote server;
- Upload files to a remote server;
- Launch a file on an infected device;
- Execute commands in the cmd.exe console;
- Redirect traffic between ports;
- Download and install its own modules.
More information about this malicious program can be found in the news article published on our website.
According to Dr.Web Anti-virus statistics
- Trojan.Starter.7394
- A Trojan whose main purpose is to launch in an infected system with an executable file possessing a specific set of malicious functions.
- Trojan.Encoder.11432
- An encryption worm known as WannaCry.
- Trojan.Zadved
- This Trojan displays fake search results in the browser window and imitates pop-up messages from social networking sites. In addition to this, the malware can replace advertisements displayed on different Internet resources.
- JS.BtcMine.2
- A JavaScript designed to stealthily mine cryptocurrencies (mining).
- Trojan.BPlug
- These plug-ins for popular browsers display annoying advertisements to users browsing webpages.
According to Doctor Web’s statistics servers
- JS.BtcMine.2
- A JavaScript designed to stealthily mine cryptocurrencies (mining).
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts. They inject malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- Trojan.Inject
- A family of malicious programs that inject malicious code into the processes of other programs.
- Trojan.Starter.7394
- A Trojan whose main purpose is to launch in an infected system with an executable file possessing a specific set of malicious functions.
- Trojan.PWS.Stealer
- A family of Trojans designed to steal passwords and other confidential information stored on an infected computer.
- Trojan.DownLoader
- A family of malicious programs designed to download other malware to the compromised computer.
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in email traffic
- Trojan.DownLoader
- A family of malicious programs designed to download other malware to the compromised computer.
- JS.Inject
- A family of malicious JavaScripts. They inject malicious script into the HTML code of webpages.
- JS.DownLoader
- A family of malicious JavaScripts. They download and install malicious software on a computer.
- VBS.DownLoader
- A family of malicious files written in VBScript scripts. They download and install malicious software on a computer.
- JS.BtcMine.2
- A JavaScript designed to stealthily mine cryptocurrencies (mining).
Encryption ransomware
In December, cases involving the following ransomware modifications were registered by Doctor Web’s technical support service:
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 27.29% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.11539 — 12.55% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 4.09% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.11464 — 3.41% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.2667 — 2.59% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 2.05% of requests.
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
During December 2017, 241,274 URLs of non-recommended websites were added to Dr.Web database.
| November 2017 | December 2017 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| +331,895 | +241,274 | -27.3% |
Linux malware
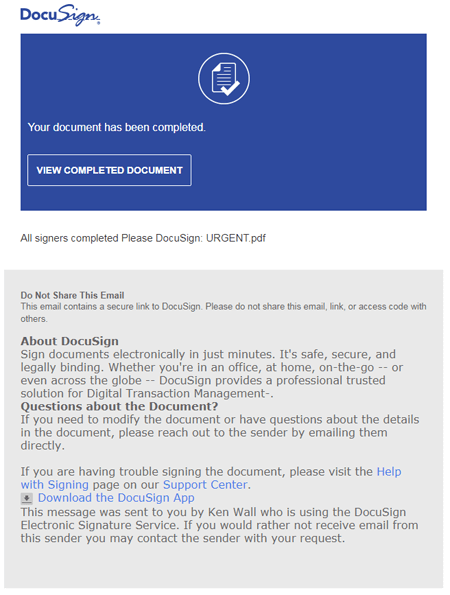
Linux.ProxyM has been known to virus analysts since May 2017. This is a quite simple malicious program that launches a SOCKS proxy server on an infected device. Cybercriminals use it to send up to 400 spam messages from each infected host, and quickly started distributing phishing email messages, in particular on behalf of DocuSign, which allowed them to work with electronic documents. Thus, cybercriminals collected the account data of its users.
In December, using a proxy server implemented in a Trojan, cybercriminals made numerous attempts at hacking websites. They used SQL injections (an injection of a malicious SQL code into a request to a website database), XSS (Cross-Site Scripting)—an attack method that involves adding a malicious script to a webpage, which is then executed on a computer when this page is opened, and Local File Inclusion (LFI)—an attack method that allows cybercriminals to remotely read files on an attacked server using specially generated commands. More information about this incident can be found in a review published by Doctor Web.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In December, Android.BankBot.243.origin and Android.BankBot.255.origin were detected on Google Play. They stole the login credentials of client accounts in credit organizations. A similar Trojan was also distributed outside the official Android software catalog. It was dubbed Android.Packed.15893. Also in December, the Dr.Web virus database was updated with Android.Spy.410.origin, which spied on Italian users.
Among the most noticeable December events related to mobile malware are the following:
- The distribution of new banking Trojans;
- Detection of a spyware that stole confidential information.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.