Doctor Web’s July 2017 virus activity review
July 31, 2017
Overview
Usually, in the middle of summer, major information security events are rare. However, July 2017 is an exception. At the beginning of the month, Doctor Web’s specialists detected a backdoor in the electronic document management application called M.E.Doc. Later, security researchers have determined the distribution source of BackDoor.Dande that stole medication procurement information from pharmaceutical companies. In the end of the month, the Government Services Portal of the Russian Federation (gosuslugi.ru) was found to be compromised. Also, in July, several dangerous malicious programs for Android have been detected.
Principal trends in July
- Detection of a backdoor in a program called M.E.Doc
- Detection of a source of the Dande backdoor
- Compromise of the Government Services Portal
Threat of the month
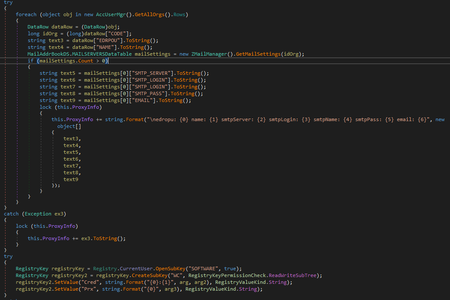
M.E.Doc is the electronic document management application popular in Ukraine. It was developed by Intellect Service. Doctor Web security researchers found that one of the M.E.Doc components, ZvitPublishedObjects.Server.MeCom, contained a record corresponding to a specific Windows system registry key: HKCU\SOFTWARE\WC.
Trojan.Encoder.12703 uses the same registry key for its operation. Security researchers examined the Dr.Web Anti-virus log obtained from one of our customer’s computers and found out that the encoder was launched on the infected machine by the application ProgramData\Medoc\Medoc\ezvit.exe, which is a component of M.E.Doc:
Further research of the program showed that one of its libraries—ZvitPublishedObjects.dll—contains a backdoor that can execute the following functions:
- Collect data for accessing mail servers;
- Execute arbitrary commands in the infected system;
- Load arbitrary files to the infected computer;
- Load, save and start any executable files;
- Upload arbitrary files to a remote server.
Besides, the M.E.Doc update module allows the payload to be launched using the tool rundll32.exe with the parameter #1—it is the way Trojan.Encoder.12544 was launched on infected computers. For more information, refer to this article published on our website.
Statistics
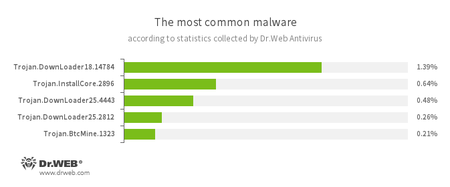
According to Dr.Web Anti-virus statistics
- Trojan.DownLoader
A family of malicious programs designed to download other malware to a compromised computer. - Trojan.InstallCore
A family of installers of unwanted and malicious applications - Trojan.BtcMine
A family of malicious programs that stealthily uses the computing resources of an infected computer to mine a variety of electronic currencies, e.g., Bitcoin.
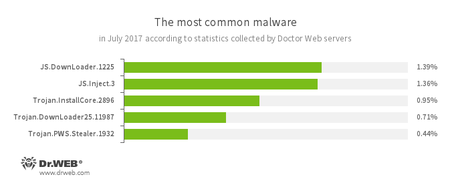
According to Doctor Web’s statistics servers
- JS.DownLoader
A family of malicious JavaScripts. Download and install malicious software. - JS.Inject.3
A family of malicious JavaScripts. They inject a malicious script into the HTML code of web pages. - Trojan.InstallCore
A family of installers of unwanted and malicious applications - Trojan.DownLoader
A family of malicious programs designed to download other malware to a compromised computer. - Trojan.PWS.Stealer
A family of Trojans designed to steal passwords and other confidential information stored on an infected computer.
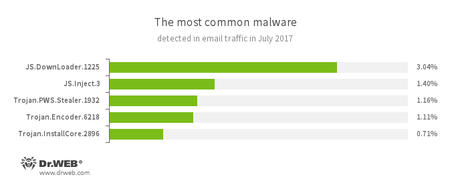
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in email traffic
- JS.DownLoader
A family of malicious JavaScripts. Download and install malicious software. - JS.Inject.3
A family of malicious JavaScripts. They inject a malicious script into the HTML code of web pages. - Trojan.PWS.Stealer
A family of Trojans designed to steal passwords and other confidential information stored on an infected computer. - Trojan.Encoder.6218
A malicious program belonging to the family of encryption ransomware Trojans that encrypt files and demand a ransom for decryption of compromised data. - Trojan.InstallCore
A family of installers of unwanted and malicious applications
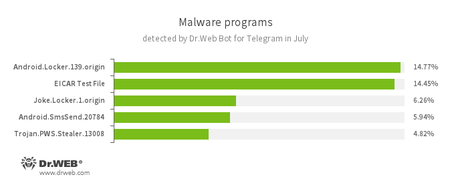
According to Dr.Web Bot for Telegram data
- Android.Locker.139.origin
A ransomware Trojan for Android. They can lock a device after alleging via an on-screen warning that the device owner has done something illegal. To unlock the device, the owner has to pay a ransom. - EICAR Test File
A special text file designed to test an anti-virus’s efficiency. Upon detecting this file, anti-virus scanners should react in exactly the same way as if the file were a virus. - Joke.Locker.1.origin
A joke program for Android that blocks a mobile device’s screen and displays the Windows BSOD (“Blue Screen of Death”). - Android.SmsSend.20784
A Trojan belonging to the family of malicious programs that are designed to send SMS messages to premium numbers and subscribe users to chargeable services and services providing paid content. - Trojan.PWS.Stealer
A family of Trojans designed to steal passwords and other confidential information stored on an infected computer.
Encryption ransomware
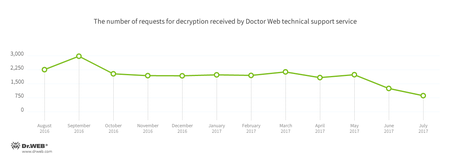
In July, cases involving the following ransomware modifications were registered by Doctor Web’s technical support service:
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 34.80% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 8.21% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.761 — 3.19% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.5342 — 3.04% of requests
- Trojan.Encoder.11423 — 2.13% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.11432 — 1.98% requests;
Dr.Web Security Space for Windows protects against encryption ransomware
Dangerous websites
During July 2017, 327,295 URLs of non-recommended websites were added to Dr.Web database.
| June 2017 | July 2017 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 229,381 | + 327,295 | + 42.6% |
In the middle of July, Doctor Web specialists have detected potentially malicious, injected code in the Government Services Portal of the Russian Federation (gosuslugi.ru). There were at least 15 domain addresses registered by an unknown individual, at least 5 of them belong to Dutch companies. The malicious code forced the browser of any visitor to the website to covertly connect to one of them. While a website page requested by a user is being generated dynamically, the container <iframe> is added to the website code. It allows any external data to be downloaded or requested from the user’s browser. All vulnerabilities of the gosuslugi.ru website were eliminated by its administration a few hours after our news article on that matter was published.
Other information security events
In 2011, Doctor Web reported on detection of BackDoor.Dande which spied on pharmaceutical companies and drugstores. Security researchers have examined the hard drive provided by one of the affected companies and determined that an ePrica component was downloading and launching the Trojan onto targeted systems. Drugstore managers use this software component to analyze drug prices and choose the best suppliers. This module downloaded the BackDoor.Dande installer from a server belonging to “Spargo Tekhnologii”, and this installer then launched the backdoor on attacked computers. In addition, the indicated module had the digital signature “Spargo”.
Analysis performed by Doctor Web showed that the BackDoor.Dande components were embedded directly into one of the earlier versions of the ePrica installer. Among the Trojan’s modules there are the backdoor installer and modules used to collect medication procurement information. These modules obtain the needed data from the databases of drugstore programs. One of the modules was used to copy pharmaceutical product procurement information from 1C databases. It is important to note that even after ePrica is removed, the backdoor stays in the system and continues to spy on users. Details of the research conducted by Doctor Web on the ePrica software are published on our website.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
At the beginning of the month, Doctor Web specialists detected Android.DownLoader.558.origin in a popular game called BlazBlue which is available on Google Play. This malicious program could covertly download and launch unchecked application components. Later security researchers examined a dangerous Trojan dubbed Android.BankBot.211.origin. It could control infected mobile devices, steal confidential banking information and other secret data, including passwords. In the end of July, Doctor Web security researchers detected Android.Triada.231. Cybercriminals injected it into an Android system library and inserted it into a firmware of several mobile device models. This malicious program infiltrated processes of all executed programs and covertly launched Trojan modules.
Among the most notable July events related to mobile malware:
- The detection of an Android Trojan in the firmware of several mobile device models;
- The detection of a loader Trojan on Google Play;
- Emergence of a banking Trojan that controlled infected devices and stole confidential information.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.