January 2017 virus activity review from Doctor Web
January 31, 2017
In the first month of 2017, Doctor Web security researchers detected a worm that infects archives and deletes other malicious applications. They also detected several thousand Linux devices infected with a new Trojan. Also in January, a significant number of new malicious programs for Android were added to the Dr.Web virus databases. One such Trojan infiltrated Play Store with a module that downloaded various applications from Google Play. Another belongs to the banking Trojan family: cybercriminals made its source code public so Doctor Web security researchers are anticipating a major, imminent distribution of bankers created on the basis of this threat.
Principal trends in January
- The distribution of a worm capable of infecting archives and deleting other malicious software
- The detection of several thousand infected Linux devices
- The emergence of an Android Trojan that embeds its module in Play Store
- The distribution of a new, dangerous banking Android Trojan that has been made openly accessible
Threat of the month
Typically Trojans are called worms when they can distribute themselves on their own without user intervention but are not capable of infecting executable files. In January, Doctor Web security researchers detected a new worm – BackDoor.Ragebot.45. It receives commands via the IRC (Internet Relay Chat) text-messaging protocol, and once it has infected a computer, it runs an FTP server. The Trojan uses this server to download its copy onto the attacked computer.
The worm connects to other network computers via the remote access system to the Virtual Network Computing (VNC) by searching for passwords in the dictionary. If the hack is successful, the Trojan establishes a VNC connection with the remote computer. Then it sends keystroke signals, which allow it to start the CMD and execute the code needed to download its copy via the FTP protocol. Thus the worm is automatically distributed.
In addition, BackDoor.Ragebot.45 can search for and infect RAR archives on removable devices and copy itself to the folders of numerous programs. However, its main feature is its capability to search for other Trojans in the system when commanded by cybercriminals, shut down their processes, and delete their executable files. More information on this Trojan and how it works can be found in a review published by Doctor Web.
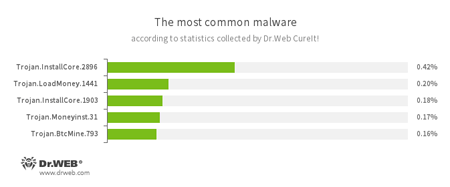
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web CureIt!
- Trojan.InstallCore
A family of installers of unwanted and malicious applications. - Trojan.LoadMoney
A family of downloader programs generated by servers belonging to the LoadMoney affiliate program. These applications download and install unwanted software on the victim's computer. - Trojan.Moneyinst.31
A malicious program that installs various software, including other Trojans, on a victim's computer. - Trojan.BtcMine.793
A Trojan that stealthily uses the computing resources of an infected computer to mine a variety of electronic currencies, e.g., Bitcoin.
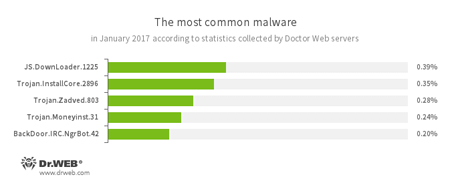
According to Doctor Web statistics servers
- JS.DownLoader
A family of malicious JavaScripts. Download and install malicious software. - Trojan.InstallCore
A family of installers of unwanted and malicious applications. - Trojan.Zadved
This Trojan displays fake search results in the browser window and imitates pop-up messages from social networking sites. In addition to this, the malware can replace advertisements displayed on different Internet resources. - Trojan.Moneyinst.31
A malicious program that installs various software, including other Trojans, on a victim's computer. - BackDoor.IRC.NgrBot.42
A fairly common Trojan which is known to the information security researchers since 2011. Malicious programs of this family are able to execute intruder-issued commands on infected machines, and cybercriminals use the IRC (Internet Relay Chat) text-messaging protocol to control those PCs.
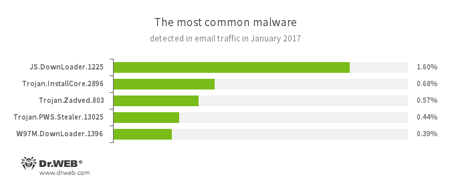
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in email traffic
- JS.DownLoader
A family of malicious JavaScripts. Download and install malicious software. - Trojan.InstallCore
A family of installers of unwanted and malicious applications. - Trojan.Zadved
This Trojan displays fake search results in the browser window and imitates pop-up messages from social networking sites. In addition to this, the malware can replace advertisements displayed on different Internet resources. - Trojan.PWS.Stealer
A family of Trojans designed to steal passwords and other confidential information stored on an infected computer. - W97M.DownLoader
A family of downloader Trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in office applications. Designed for downloading other malware to a compromised computer.
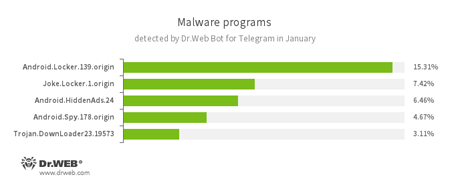
According to Dr.Web Bot for Telegram data
- Android.Locker.139.origin
A ransomware Trojan for Android. Different modifications of these malicious programs can lock a device after alleging via an on-screen warning that the device owner has done something illegal. To unlock the device, the owner has to pay a ransom. - Joke.Locker.1.origin
A joke program for Android that blocks a mobile device’s screen and displays the Windows BSOD (“Blue Screen of Death”). - Android.HiddenAds.24
A Trojan designed to display unwanted ads on mobile devices. - Android.Spy.178.origin
A Trojan for Windows, that steals confidential information, including user passwords. - Trojan.DownLoader
A family of malicious programs designed to download other malware to the compromised computer.
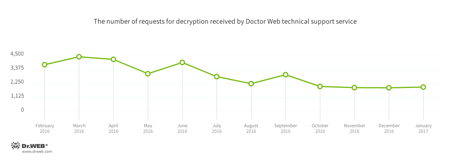
Encryption ransomware
In January, Doctor Web’s technical support was most often contacted by victims of the following modifications of encryption ransomware:
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 36.71% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.3953 — 5.00% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 3.97% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.761 — 3.33% requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.3976 — 2.88% requests.
Dr.Web Security Space 11.0 for Windows
protects against encryption ransomware
This feature is not available in Dr.Web Anti-virus for Windows.
| Data Loss Prevention | |
|---|---|
 |  |
During January 2017, 223,127 URLs of non-recommended websites were added to Dr.Web database.
| December 2016 | January 2017 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| + 226,744 | + 223,127 | -1.59% |
Linux malware
The spread of Linux malware on a large scale does not happen that often; however, it was detected by Doctor Web security researchers in January 2017. The Trojan in question was Linux.Proxy.10, whose purpose is to run a SOCKS5 proxy server on an infected device. Such infected devices are used by cybercriminals to ensure their online anonymity. According to Doctor Web security researchers, as of January 24, 2017, the number of infected Linux devices was running into the several thousands.
Linux.Proxy.10 is distributed by logging into vulnerable devices with a predetermined login and password combination: users with such account details are usually created by other Linux Trojans (or they are installed on the device by default). That means that Linux.Proxy.10 mainly attacks devices that are already infected with other malicious software. Detailed information regarding this malware can be found in a review published by Doctor Web.
Moreover, yet another Linux.Lady was detected — Linux.Lady.4. In this version of the Trojan, cybercriminals deleted the function for downloading and running the cryptocurrency mining application and added the capability to attack Redis network-attached storage. In addition, the Trojan has an additional module that can use RPC (Remote Procedure Call) to communicate with remote servers, send them information about the infected system, and execute shell commands.
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In the first month of 2017, Doctor Web security researchers detected the Trojan Android.Skyfin.1.origin which infiltrated the Play Store running process and stealthily downloaded Google Play applications, artificially increasing their popularity. Later, security researchers detected Android.BankBot.149.origin, an Android banker whose source code was published online by cybercriminals. Another Android banker detected in January was dubbed Android.BankBot.140.origin. It was distributed as the game Super Mario Run, which is not yet available for Android devices. Also in the last month, a new ransomware Trojan was detected in Google Play; dubbed Android.Locker.387.origin, it blocked smartphones and tablets.
The most notable January events related to mobile malware include:
- the detection of an Android Trojan that infiltrated the Play Store running process and covertly downloaded applications from Google Play;
- the distribution of banking Trojans;
- the emergence of a ransomware Trojan on Google Play.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.