Doctor Web’s December 2016 virus activity review
December 26, 2016
In the last month of 2016, Doctor Web’s specialists detected an Android Trojan that could infect the system libraries of devices. They also found a Trojan for Windows that is designed to install unwanted applications. And, later in the month, they discovered several Android Trojans in the firmware of many popular mobile devices.
Principal trends of December
- The distribution of a Trojan that installs unwanted applications
- The detection of numerous Trojans in the firmware of Android devices
- The emergence of an Android Trojan capable of infecting system libraries
Threat of the month
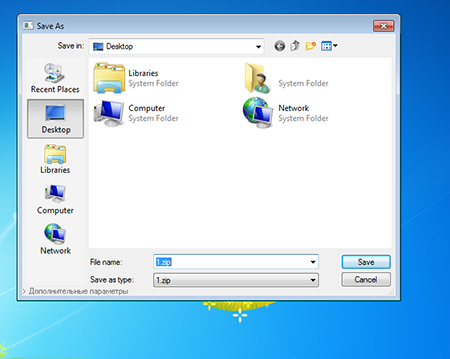
Many modern Trojans download and install various applications on a computer without the user’s knowledge: virus makers use the services of affiliate programs to get paid for every download. These Trojans are usually very simple, unlike Trojan.Ticno.1537. Once launched, it tries to detect the presence of the virtual environment and debugging tools and starts operating only if it has not found anything suspicious. The Trojan saves a file named 1.zip on the disk and opens a dialog similar to the Microsoft Windows “Save” window:
The link “Additional parameters” is in the bottom-left corner. Once it is clicked, Trojan.Ticno.1537 shows the list of programs it is going to install. Among them are the Amigo browser, the application HomeSearch@Mail.ru, and the Trojans Trojan.ChromePatch.1, Trojan.Ticno.1548, Trojan.BPlug.1590, Trojan.Triosir.718, Trojan.Clickmein.1 and Adware.Plugin.1400. For more information about Trojan.Ticno.1537, refer to this news article.
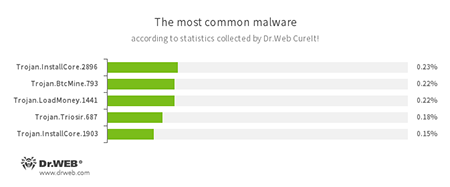
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web CureIt!
- Trojan.InstallCore
A Trojan family that can install unwanted and malicious applications. - Trojan.BtcMine.793
A Trojan designed to covertly use an infected computer’s resources in order to generate cryptocurrency—for example, Bitcoin. - Trojan.LoadMoney
A family of downloader programs generated by servers belonging to the LoadMoney affiliate program. These applications download and install unwanted software on a victim’s computer. - Trojan.Triosir.687
A plug-in for web browsers that is designed to display annoying advertisements to users as they browse webpages.
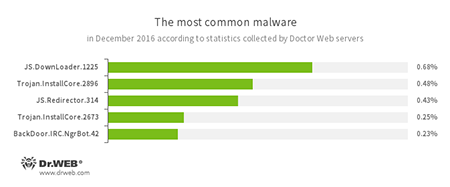
According to Doctor Web’s statistics servers
- JS.DownLoader
A family of malicious scripts written in JavaScript and designed to download and install other malware programs on a computer. - Trojan.InstallCore
A Trojan family that can install unwanted and malicious applications. - JS.Redirector
A family of malicious scripts written in JavaScript and designed to automatically redirect users to other webpages. - BackDoor.IRC.NgrBot.42
A fairly common Trojan, which is known to information security researchers since 2011. Malicious programs of this family are able to execute intruder-issued commands on infected machine controlled by cybercriminals via the IRC (Internet Relay Chat) text-messaging protocol.
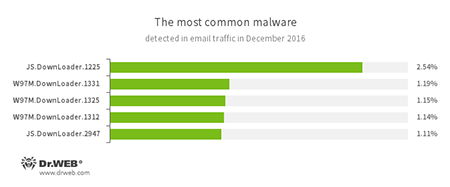
Statistics on malicious programs discovered in email traffic
- JS.Downloader
A family of malicious scripts written in JavaScript and designed to download and install other malware programs on a computer. - W97M.DownLoader
A family of downloader Trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in office applications and can download other malicious programs to a compromised computer.
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web Bot for Telegram
- Android.Locker.139.origin
A ransomware Trojan for Android. Its different modifications can lock a device after displaying a warning to the device’s owner that they have done something illegal. To unlock the device, the owner has to pay a ransom. - Joke.Locker.1.origin
A joke program for Android that locks the home screen of a device and displays a Microsoft Windows BSOD (Blue Screen of Death) error. - BackDoor.Bifrost.29284
A backdoor Trojan that executes commands received from cybercriminals. - Trojan.PWS.Spy.11887
A Trojan for Windows that steals private information including user passwords. - Android.HiddenAds.24
A Trojan that delivers annoying advertisements.
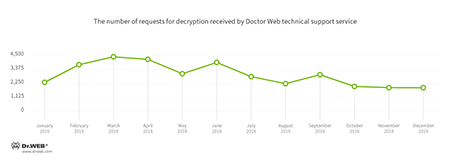
Encryption ransomware
In December, cases involving the following ransomware modifications were registered by Doctor Web’s technical support service:
- Trojan.Encoder.858 — 37.99% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.761 — 12.27% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 4.11% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.3976 — 3.89% of requests;
- Trojan.Encoder.567 — 1.70% of requests.
Dr.Web Security Space 11.0 for Windows
protects against encryption ransomware
This feature is not available in Dr.Web Anti-virus for Windows
| Data Loss Prevention | |
|---|---|
 |  |
Dangerous websites
During December 2016, 226,744 URLs of non-recommended websites were added to Dr.Web database.
| November 2016 | December 2016 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| +254,736 | +226,744 | -10.98% |
Malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In December, Doctor Web’s security researchers found Android.Loki.16.origin which was infecting Android system libraries, injecting itself into application processes, and covertly installing other programs. In addition, December was marked by the emergence of Android.DownLoader.473.origin and Android.Sprovider.7 which were preinstalled on dozens of models of Android devices. These Trojans also downloaded and installed unwanted applications.
Among the most noticeable December events related to mobile malware we can mention:
- The emergence of an Android application infecting system libraries and performing injections into application processes;
- The detection of malware programs that had been preinstalled on numerous Android devices.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.