Doctor Web’s July 2016 virus activity review
July 29, 2016
July is traditionally considered a quiet month in terms of information security. Thus, in most cases, our specialists detected modifications of already-known threats. For example, at the beginning of July, we added to our virus database yet another signature for Linux.Encoder.4, which works in Linux operating systems. Judging by information posted on one foreign blog, this Trojan was the result of a student research project, and it was not being spread in the wild.
In the end of July, our security researchers registered the emergence of Trojan.MulDrop6.48664—a dropper Trojan that installs the infamous BackDoor.TeamViewer.49 on computers. (For more details about BackDoor.TeamViewer.49, refer to this news article.) However, this time, hackers disguised the dropper as a questionnaire application that was allegedly being distributed by a popular Russian airline.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN JULY
- Dangerous encryption ransomware for Linux
- Distribution of a dropper Trojan for Windows
- New malicious programs for Android
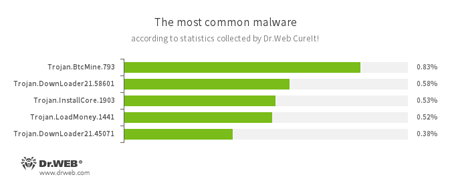
According to statistics collected by Dr.Web CureIt!
- Trojan.BtcMine.793
A Trojan designed to covertly use the infected computer’s resources in order to generate cryptocurrency—for example, Bitcoin. - Trojan.DownLoader
A family of malicious programs designed to download other malware to the compromised computer. - Trojan.InstallCore.1903
A Trojan that can install unwanted and malicious applications. - Trojan.LoadMoney
A family of downloader programs generated by servers belonging to the LoadMoney affiliate program. These applications download and install unwanted software on the victim's computer.
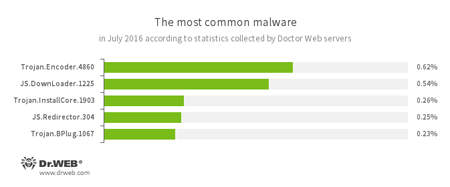
According to Doctor Web statistics servers
- Trojan.Encoder.4860
A ransomware Trojan also known as JS.Crypt. Written completely in JScript, this Trojan is distributed under the name “RAA virus”, and all locked files are appended with the extension *.locked. - JS.Downloader
A family of malicious scripts that are written in JavaScript and designed to download and install other malware programs on the computer. - Trojan.InstallCore.1903
A Trojan that can install unwanted and malicious applications. - JS.Redirector
A family of malicious scripts written in JavaScript and designed to automatically redirect users to other webpages. - Trojan.BPlug
These plug-ins for popular browsers display annoying advertisements to users browsing webpages.
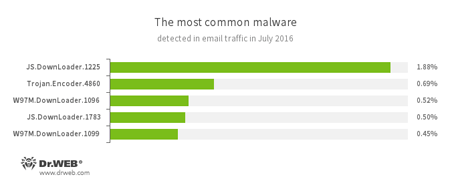
Statistics concerning malicious programs discovered in email traffic
- JS.Downloader
A family of malicious scripts written in JavaScript and designed to download and install other malware programs on the computer. - Trojan.Encoder.4860
A ransomware Trojan also known as JS.Crypt. Remarkable in the fact that it is written entirely in JScript, this Trojan is distributed under the name “RAA virus”, and all locked files are appended with the extension *.locked. - W97M.DownLoader
A family of downloader Trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in office applications and can download other malicious programs to the compromised computer.
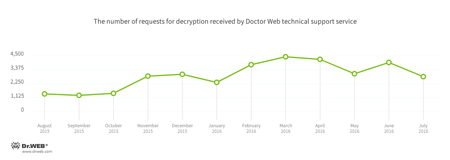
Encryption ransomware
Dr.Web Security Space 11.0 for Windows
protects against encryption ransomware
This feature is not available in Dr.Web Anti-virus for Windows.
| Data Loss Prevention | |
|---|---|
 |  |
Dangerous websites
During July 2016, 139,803 URLs were added to the Dr.Web database of non-recommended websites.
| June 2016 | July 2016 | Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| +1,716,920 | +139,803 | -91.8% |
Currently, Doctor Web is revising the databases of Dr.Web SpIDer Gate and Parental Control to remove links to non-operational or non-existent websites, which will reduce the number of files downloaded to user computers. That is why the number of URLs for non-recommended websites decreased considerably in July.
Non-recommended websitesMalicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices
In July, Doctor Web specialists discovered over 150 applications on Google Play that contain an adware Trojan named Android.Spy.305.origin. The Trojan can display ads on top of running applications and on the status bar, and steal private information. In addition, the past month was marked by the emergence of Android.Spy.178.origin, the Trojan incorporated into a modification of the popular game—Pokémon Go. Criminals used this Trojan to gain access to confidential user data.
Among the most notable July events related to mobile malware:
- A new adware Trojan distributed via Google Play;
- A new spyware Trojan incorporated into a modified version of Pokémon Go.
Find out more about malicious and unwanted programs for mobile devices in our special overview.