New version of Gozi banking Trojan can create P2P botnet
Real-time threat news | Hot news | All the news | Virus alerts
April 8, 2016
This malware, which runs on 32- and 64-bit Windows, is able to carry out a wide range of malicious activities. Thus, it can steal information entered by the user into web data forms and perform web injections and keylogging functions. In addition, the Trojan is also designed to get remote access to the user’s machine by means of Virtual Network Computing (VNC). Moreover, upon a command, the Trojan can run the SOCKS proxy server and download and install various plug-ins.
Like many other today’s malware programs, Trojan.Gozi uses domain generation algorithm (DGA) to determine its C&C server addresses. It downloads a text file from the NASA server, used as a glossary, from the server and modifies it regarding the current date, so that the malware can then generate domain names of its control servers. Every 15 days, the Trojan connects to a new C&C server. All information sent and received by the malware is encrypted.
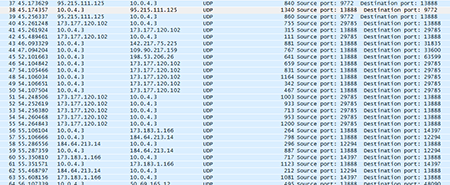
However, Trojan.Gozi has a new feature: it can generate P2P botnets, which allows the Trojan to transmit encrypted information directly to the infected machines.
All the mentioned-above functions, especially the Trojan’s ability to perform web injections, are used to steal various confidential data from the user’s computer, including login credentials to access online banking systems. Dr.Web successfully detects and removes Trojan.Gozi, and, therefore, this malicious program poses no threat to our users.